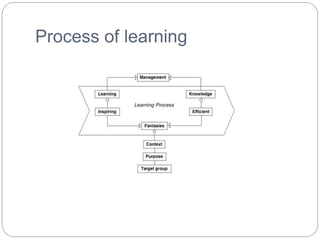
This document discusses learning and its determinants and theories. It defines learning as the process of enriching human life and affecting behavior in organizations. The determinants of learning include motives like drives that promote action, and stimuli from the environment, which can lead to generalization, discrimination, responses, reinforcement, and retention. Theories of learning discussed are classical conditioning as proposed by Ivan Pavlov, operant learning from B.F. Skinner, cognitive theory focusing on symbols and knowledge, and social learning theory involving observational and experiential learning through attention, retention, reproduction, and reinforcement of role models. The document also outlines the process of learning as involving experience, behavioral change, and observable learning.