1. Incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele of a gene is fully dominant over the other. The heterozygous phenotype is a blending of the two homozygous phenotypes. For example, a cross between red and white flowers produces pink flowers.
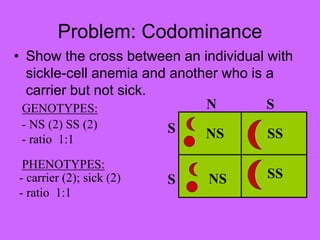
2. Codominance occurs when both alleles of a gene are fully expressed in the heterozygote. The phenotype shows a combination of both traits. For example, in humans, a person with one allele for A blood and one for B blood has type AB blood and their red blood cells have both A and B antigens.
3. Human blood types (A, B, AB, O) demonstrate both codominance and multiple alleles at a single gene locus.