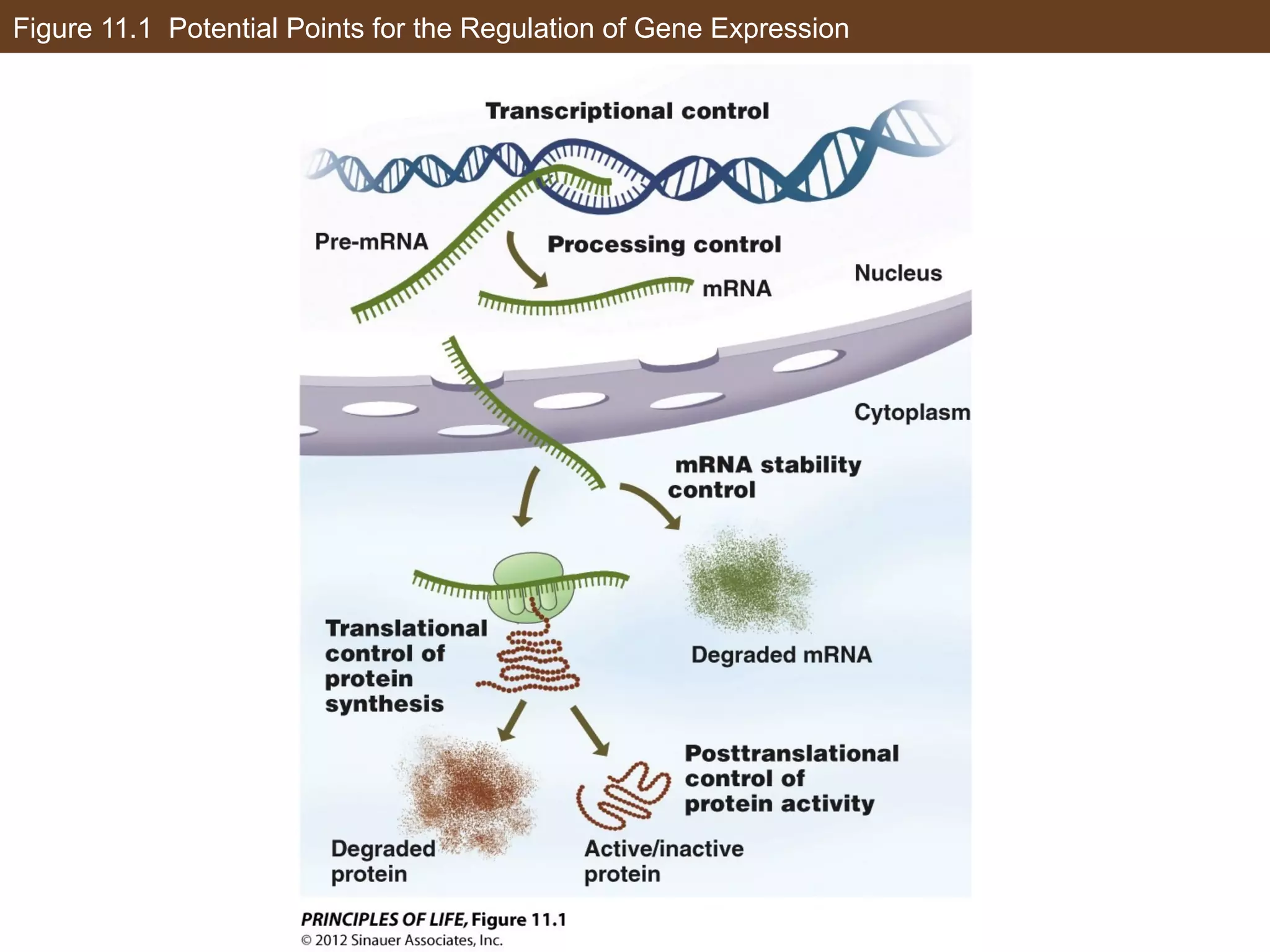
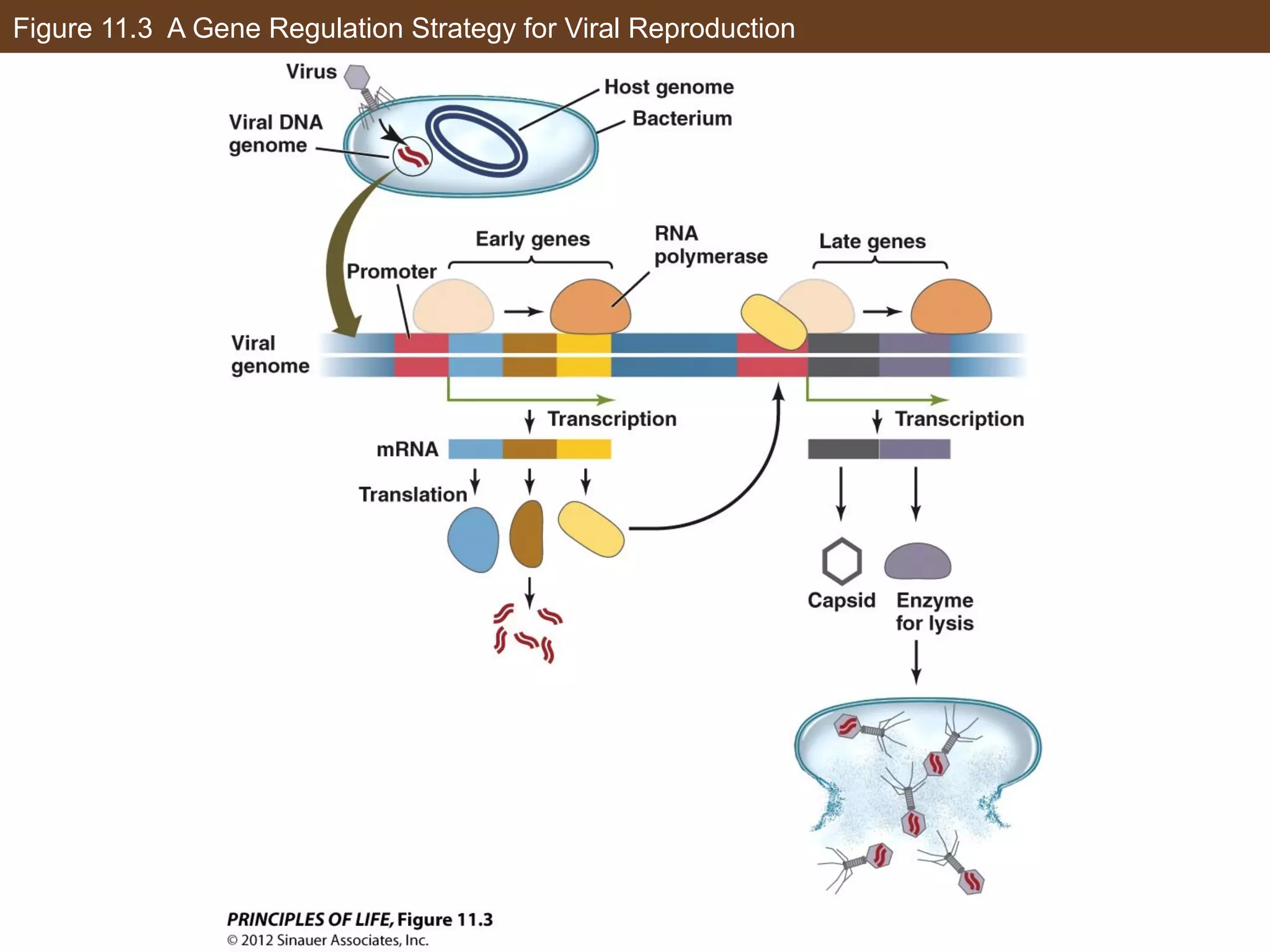
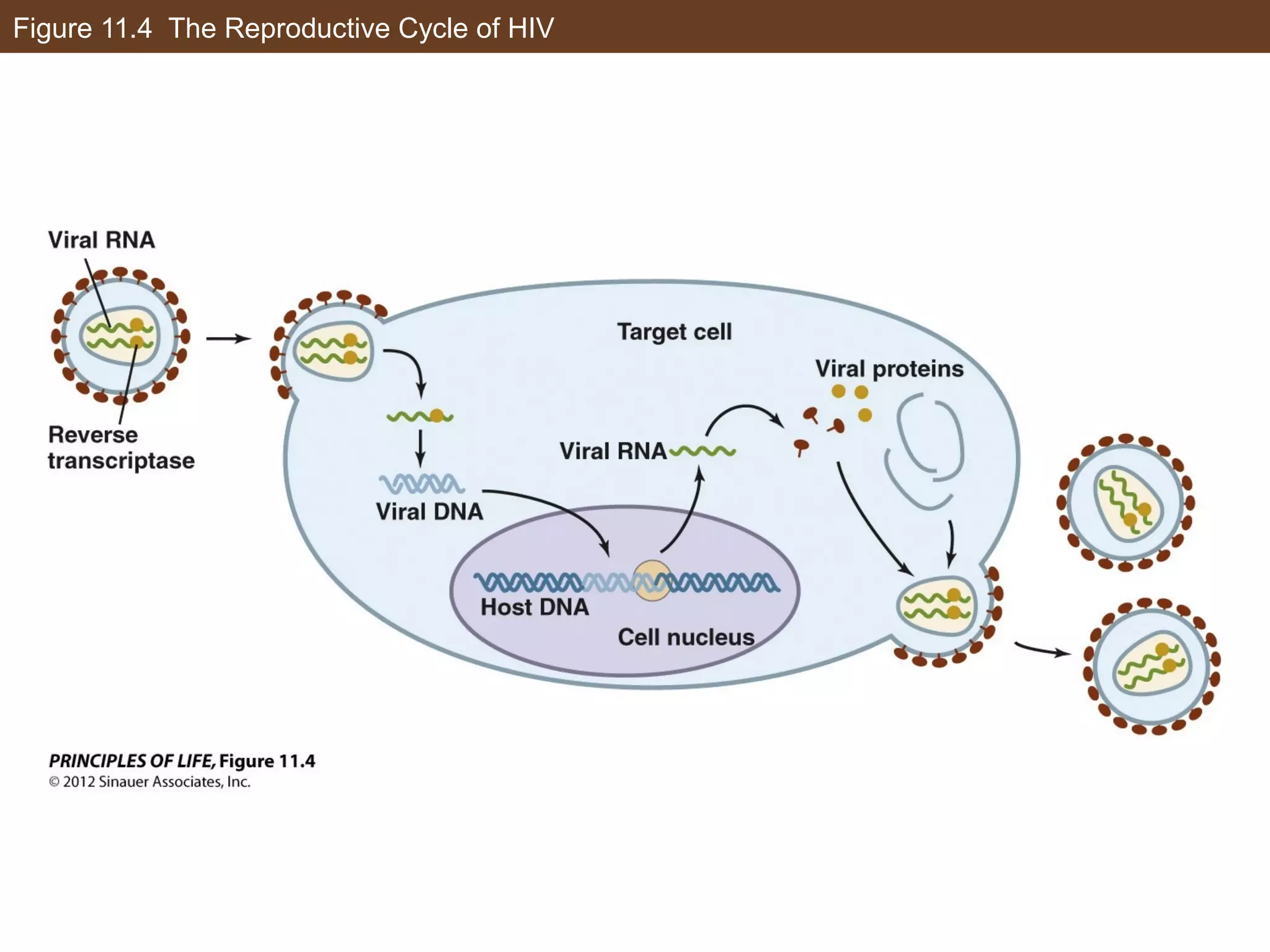
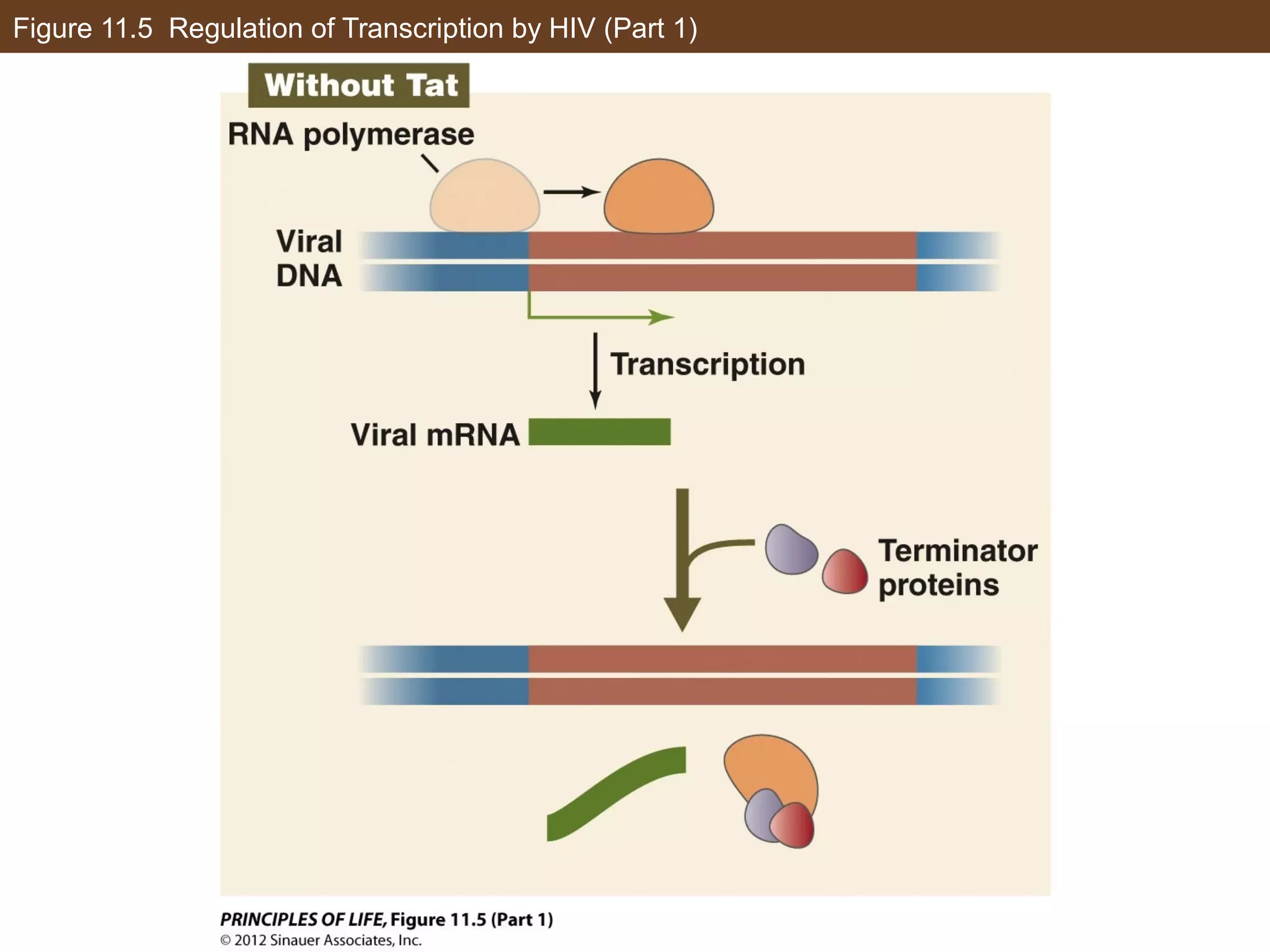
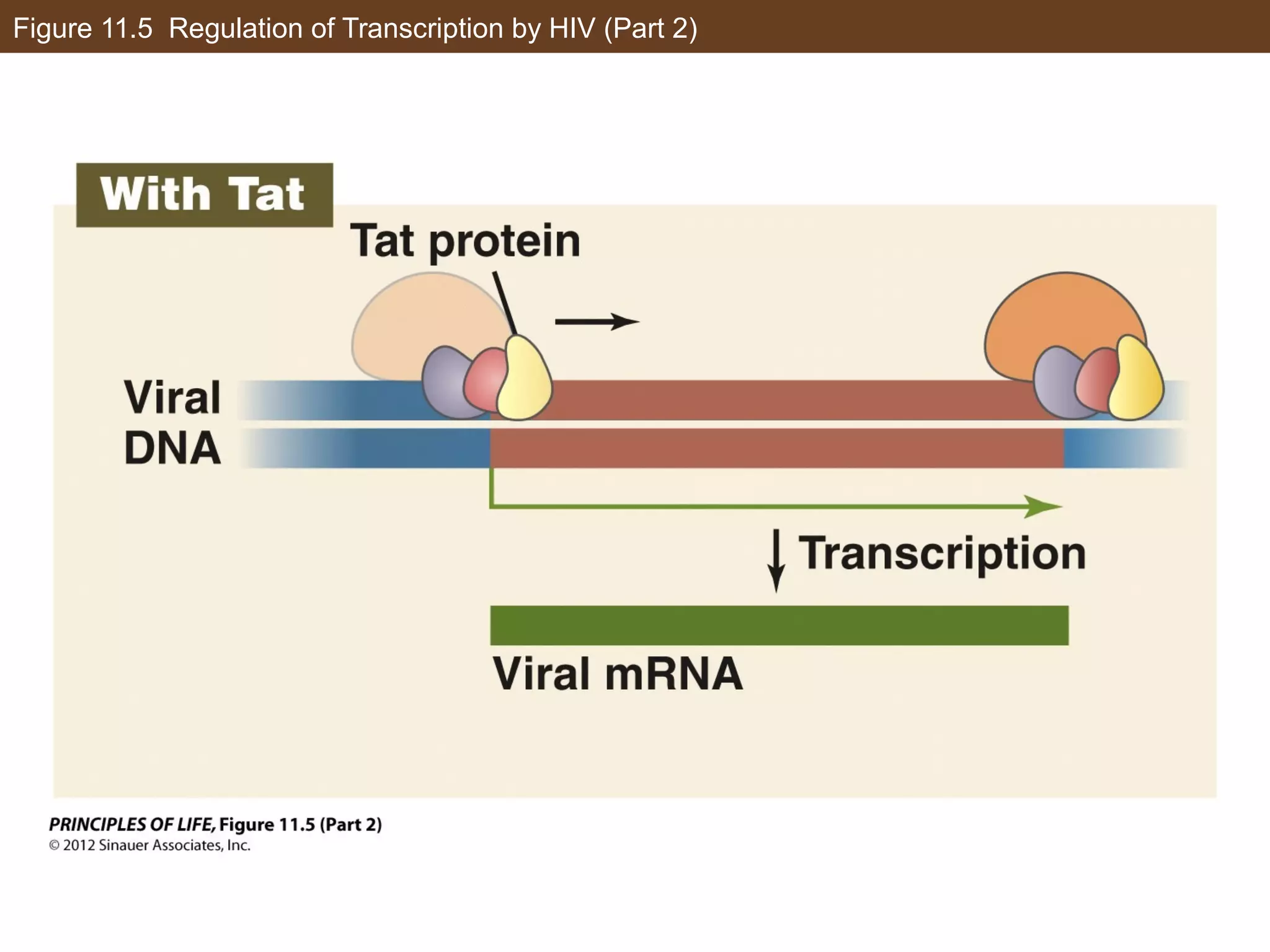
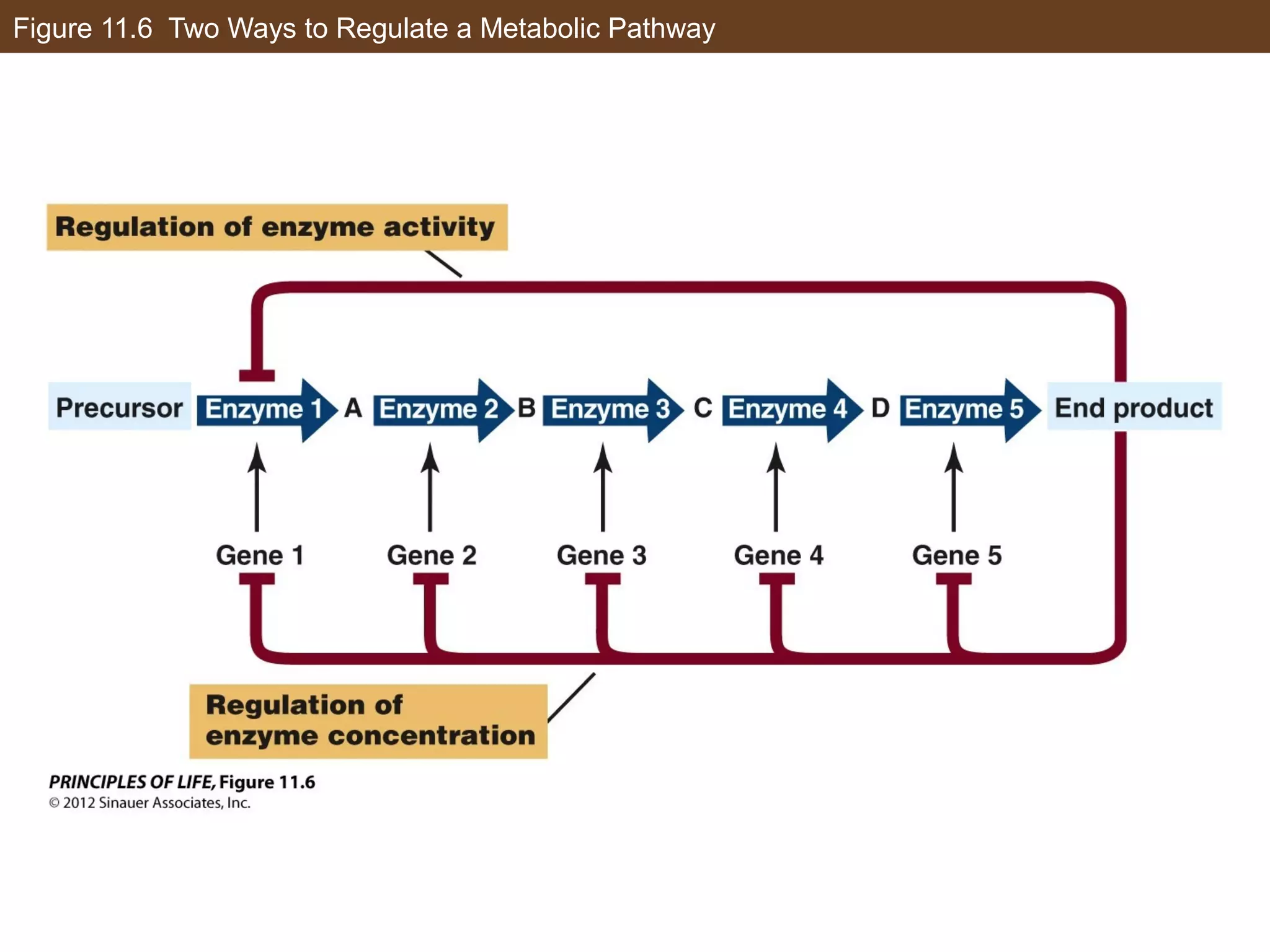
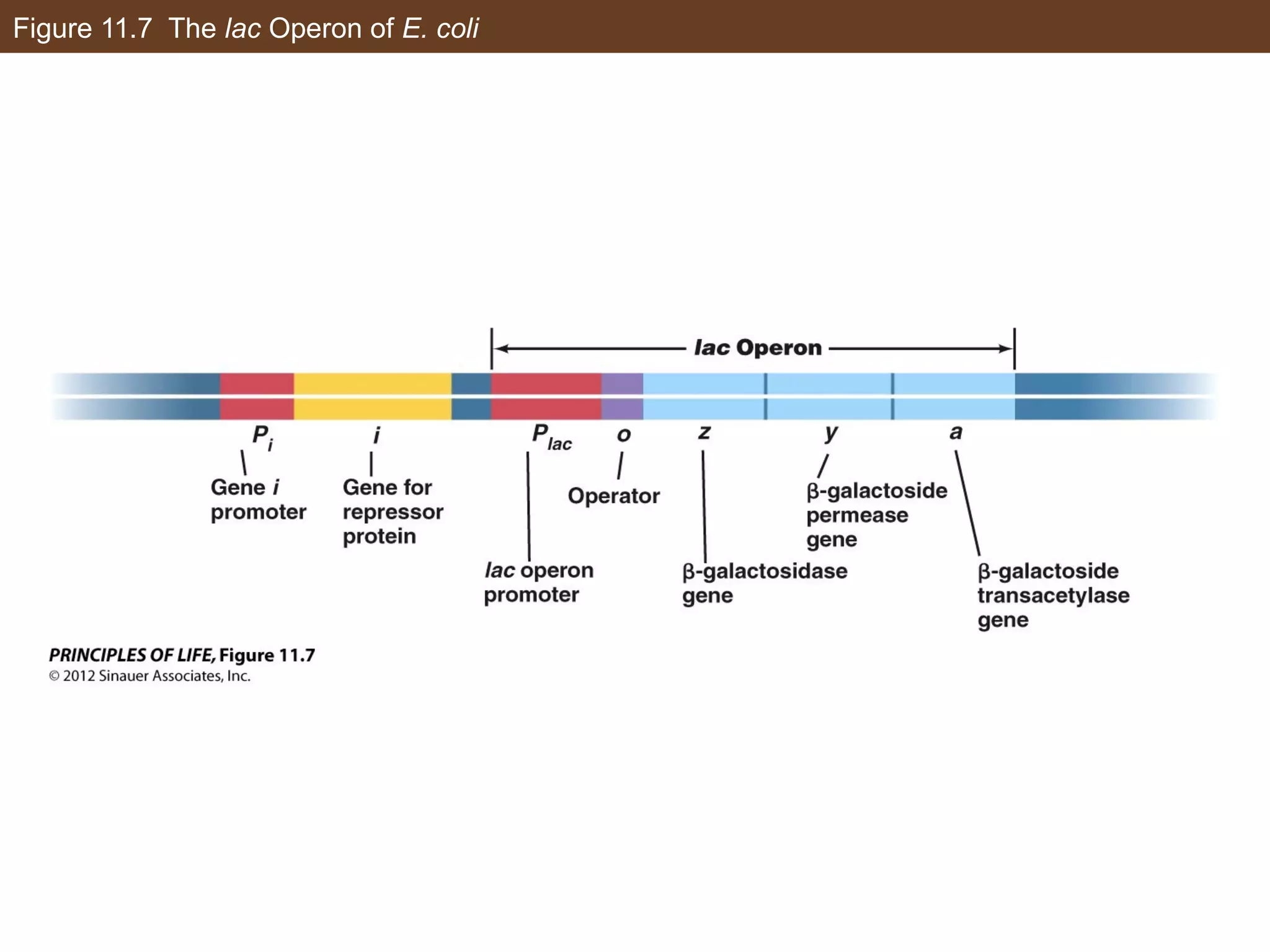
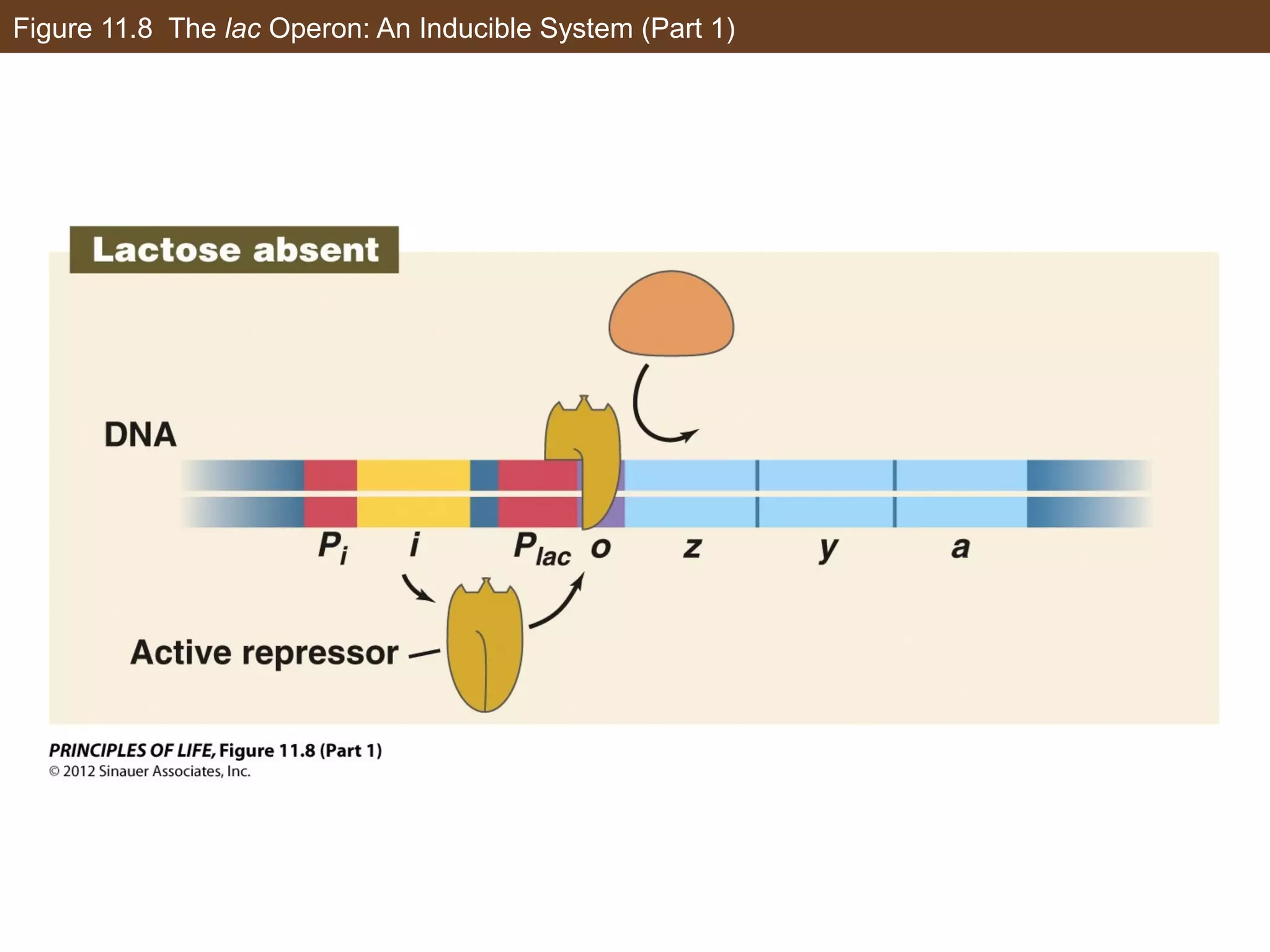
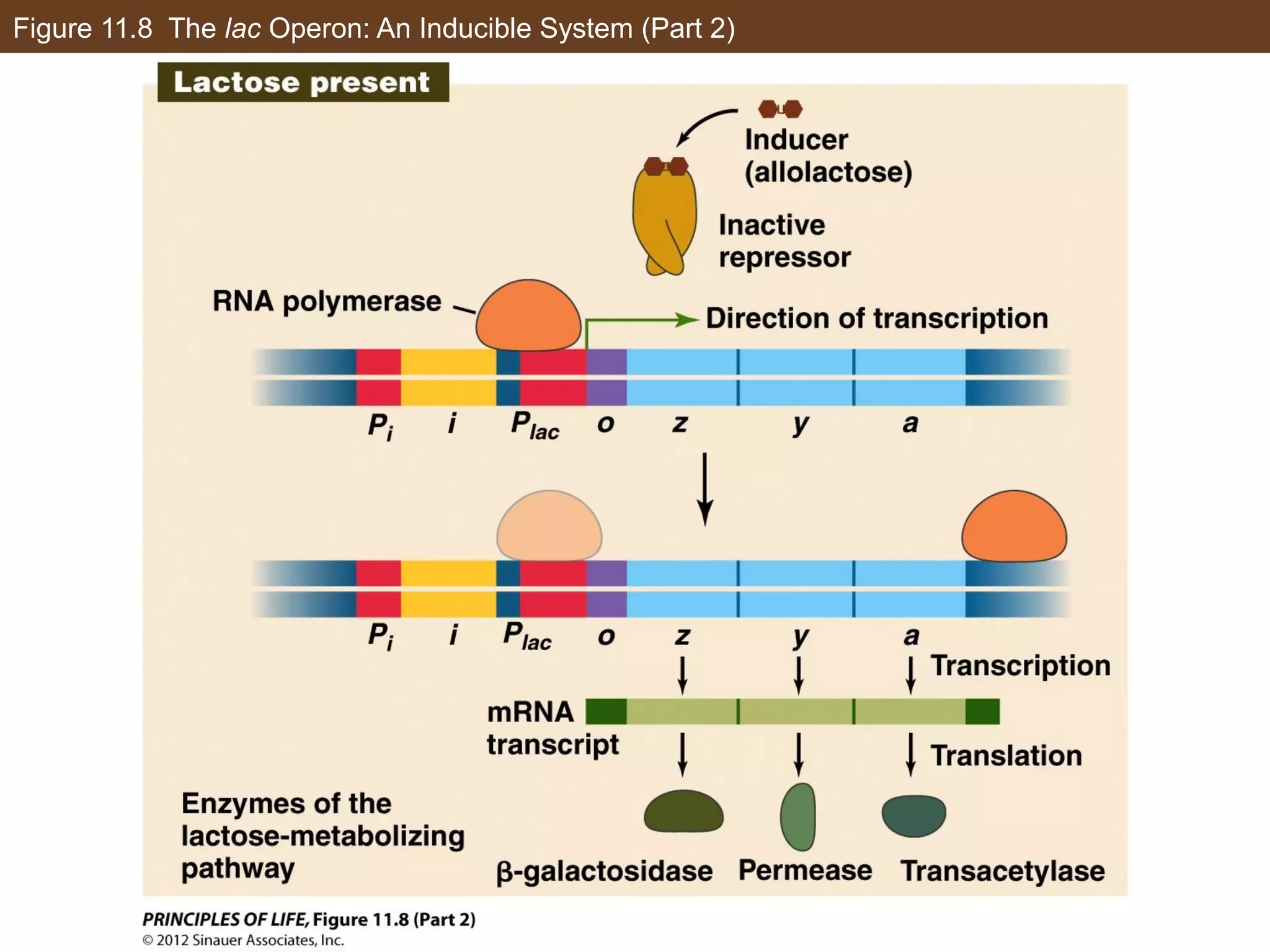
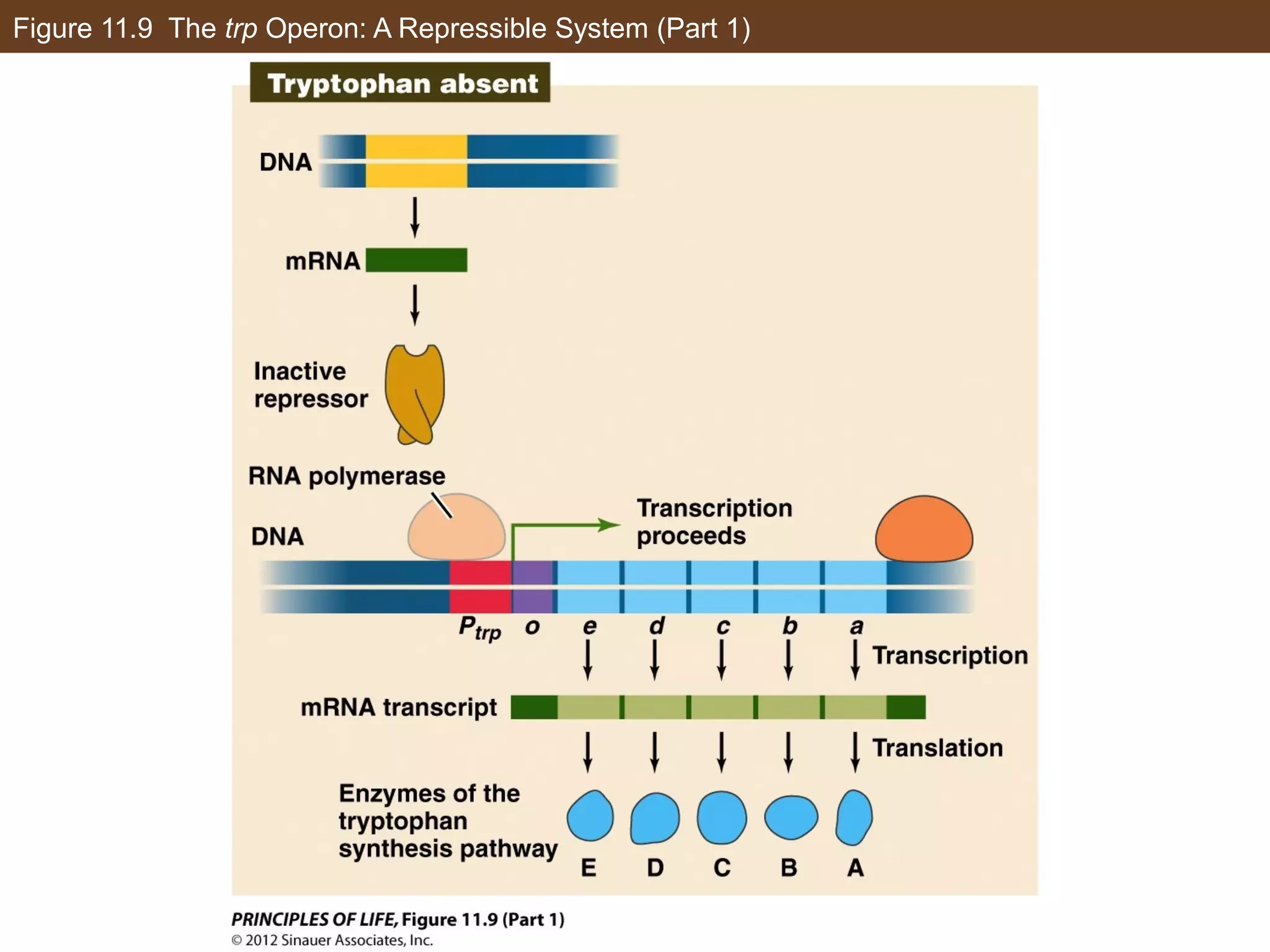
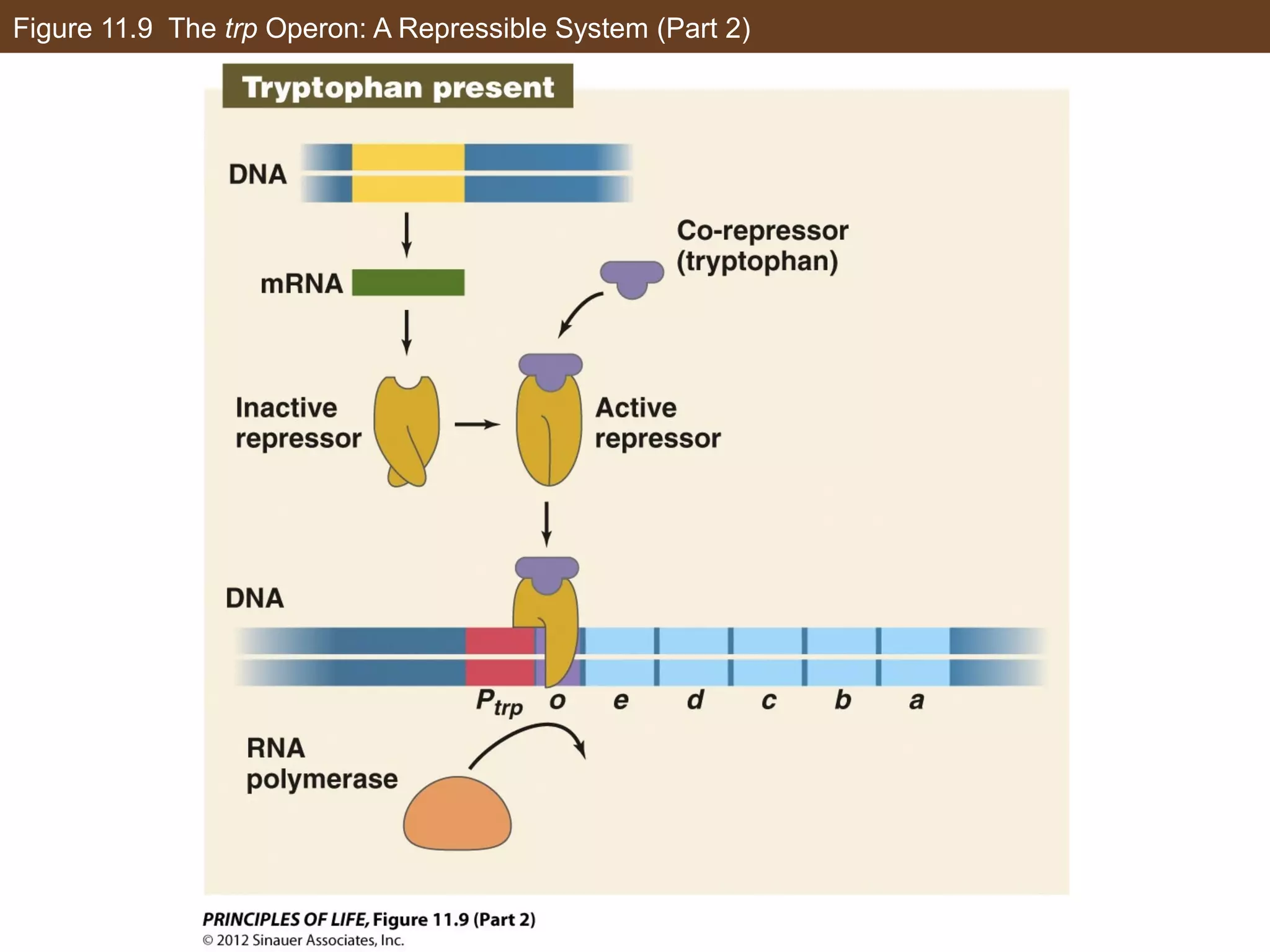
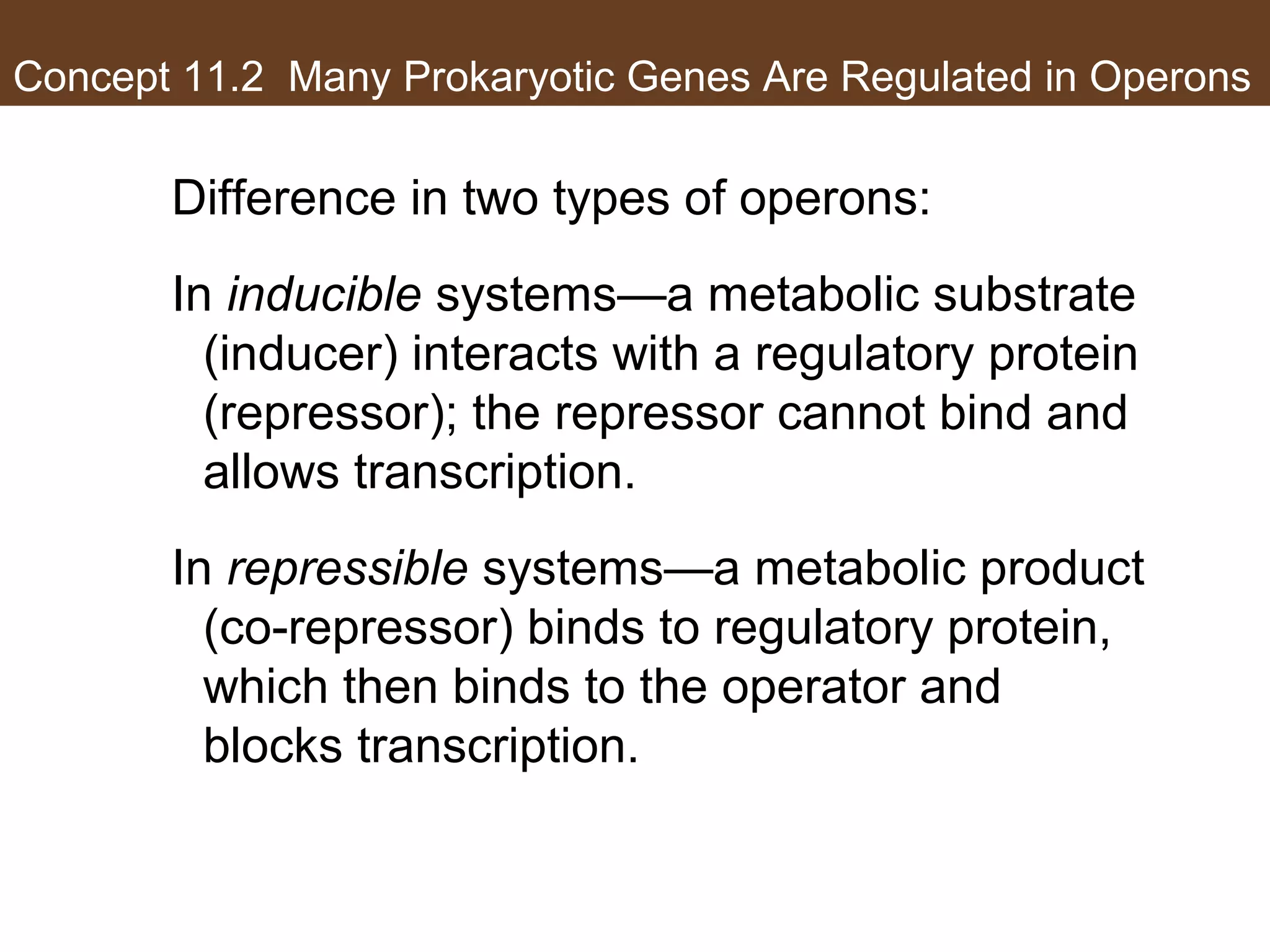
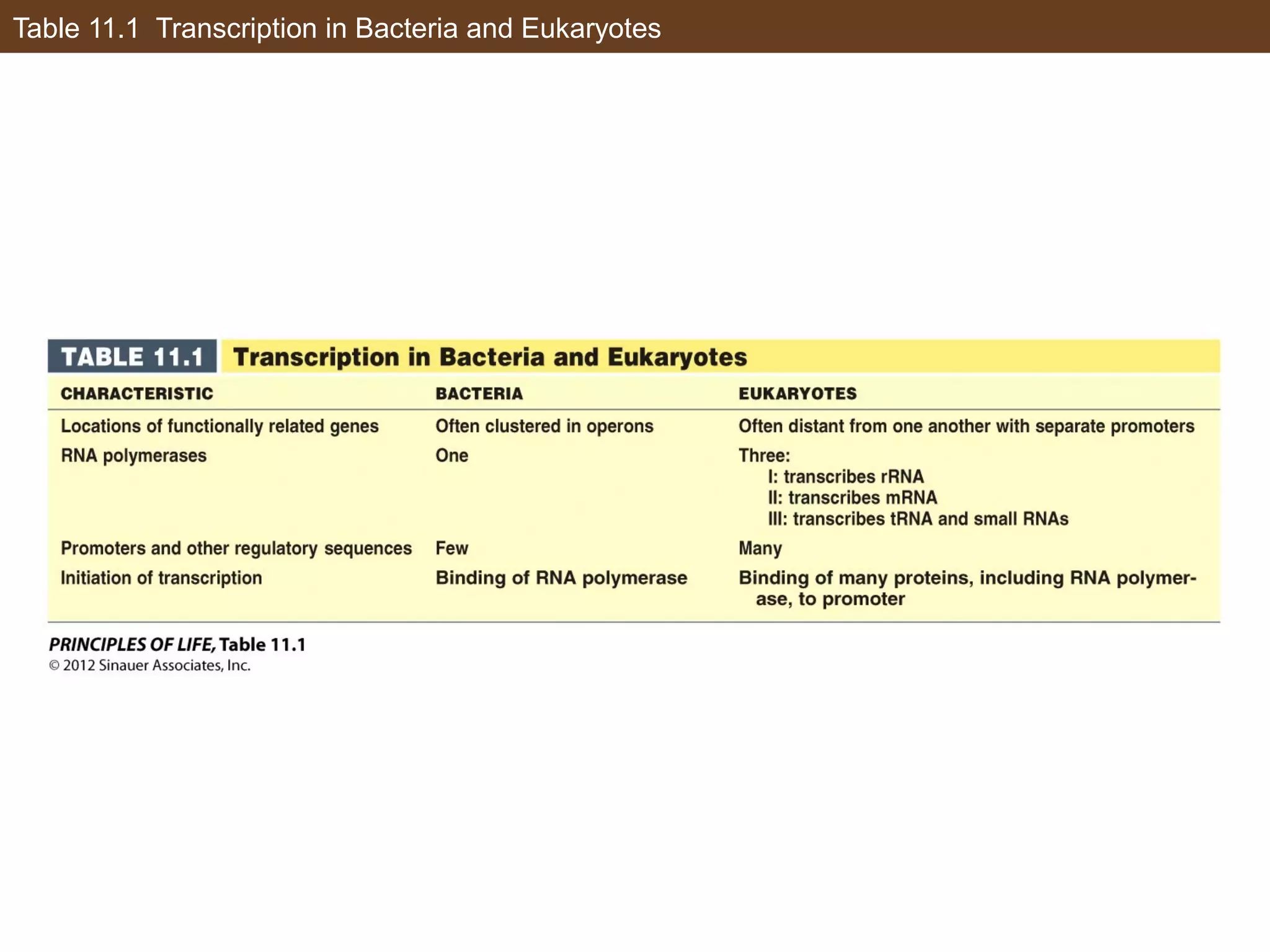
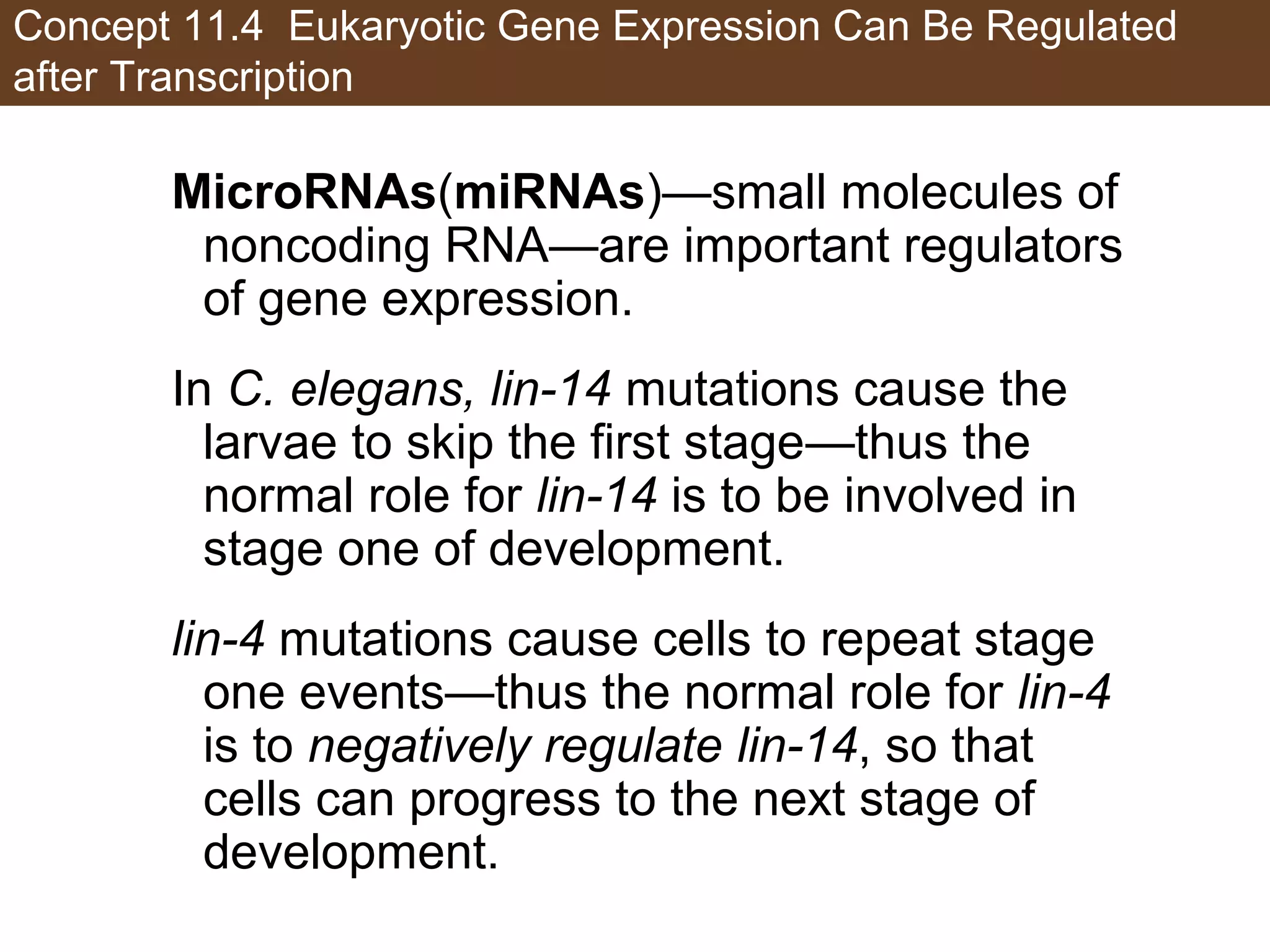
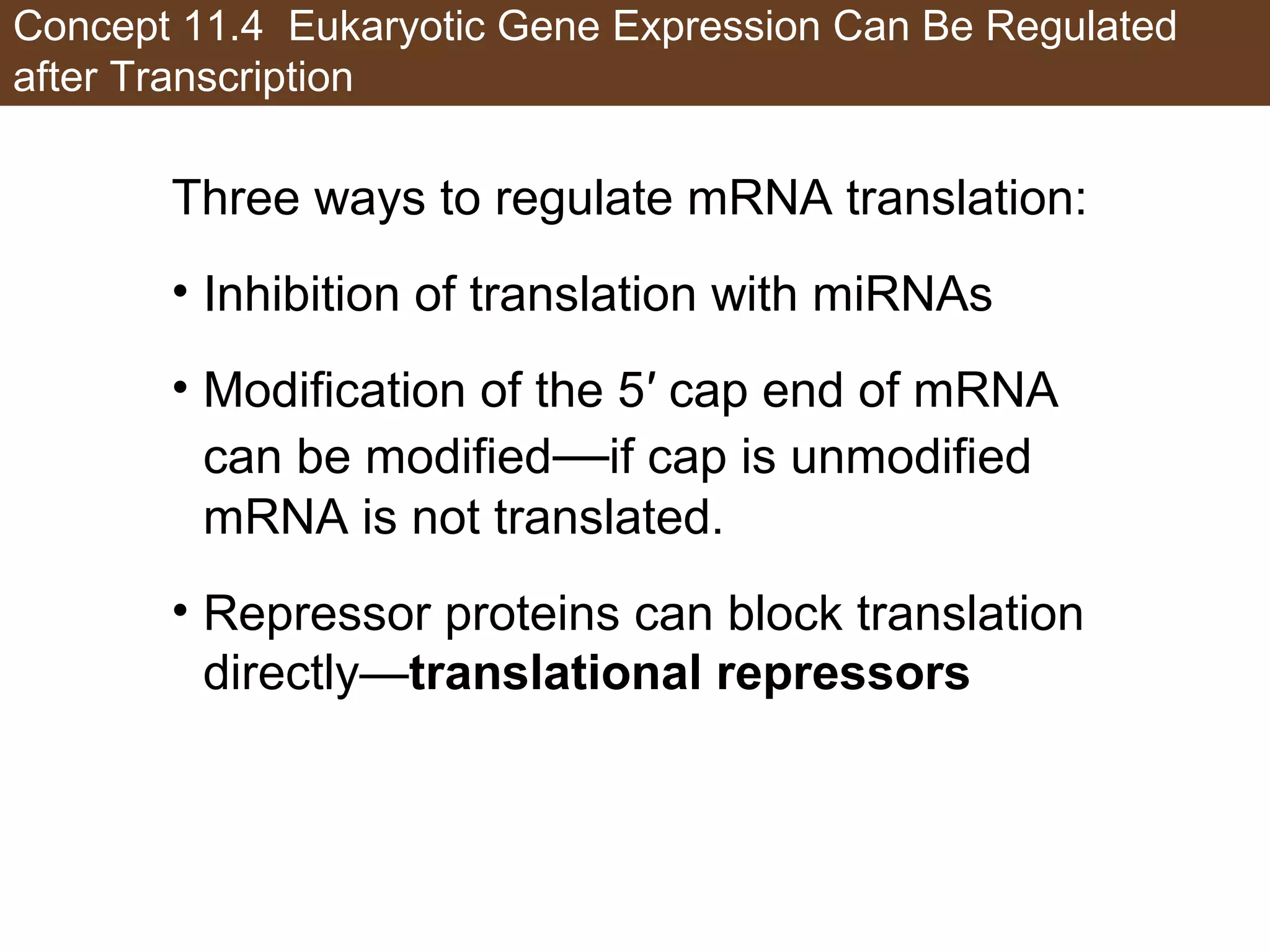
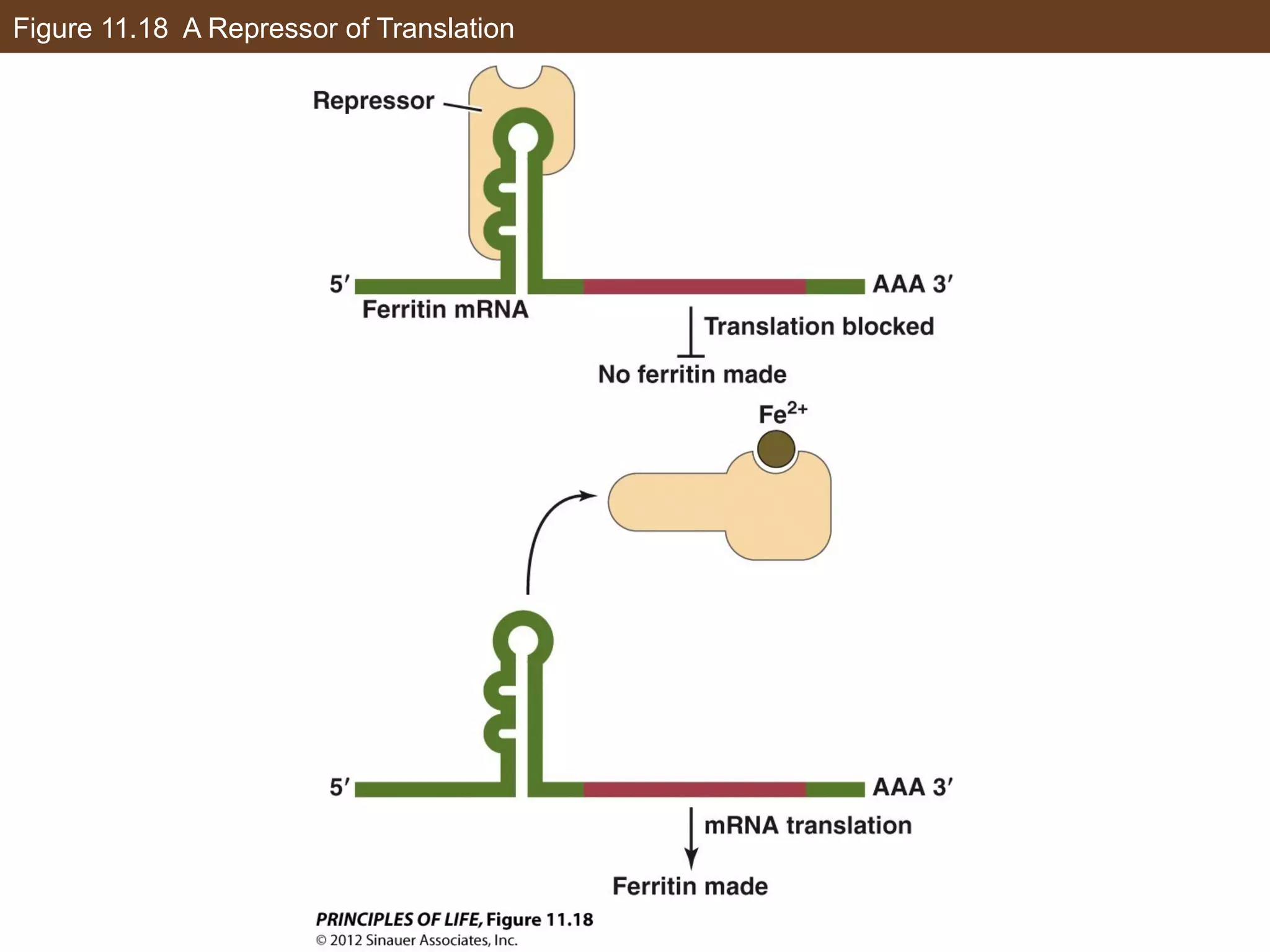
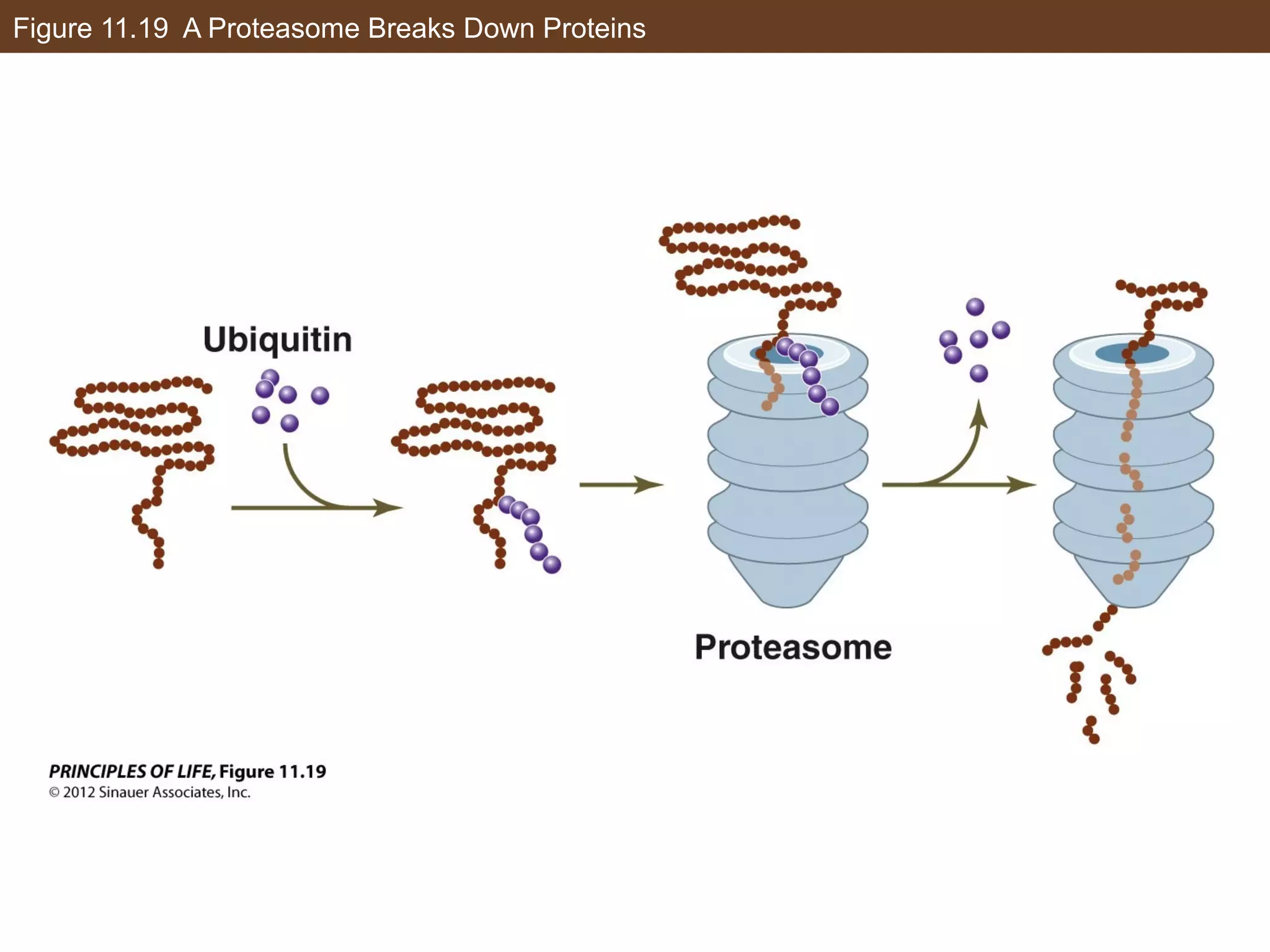
1) Gene expression in eukaryotes is regulated at multiple levels, including transcription, epigenetic modifications to DNA and histones, alternative splicing of mRNA, and microRNAs inhibiting translation.
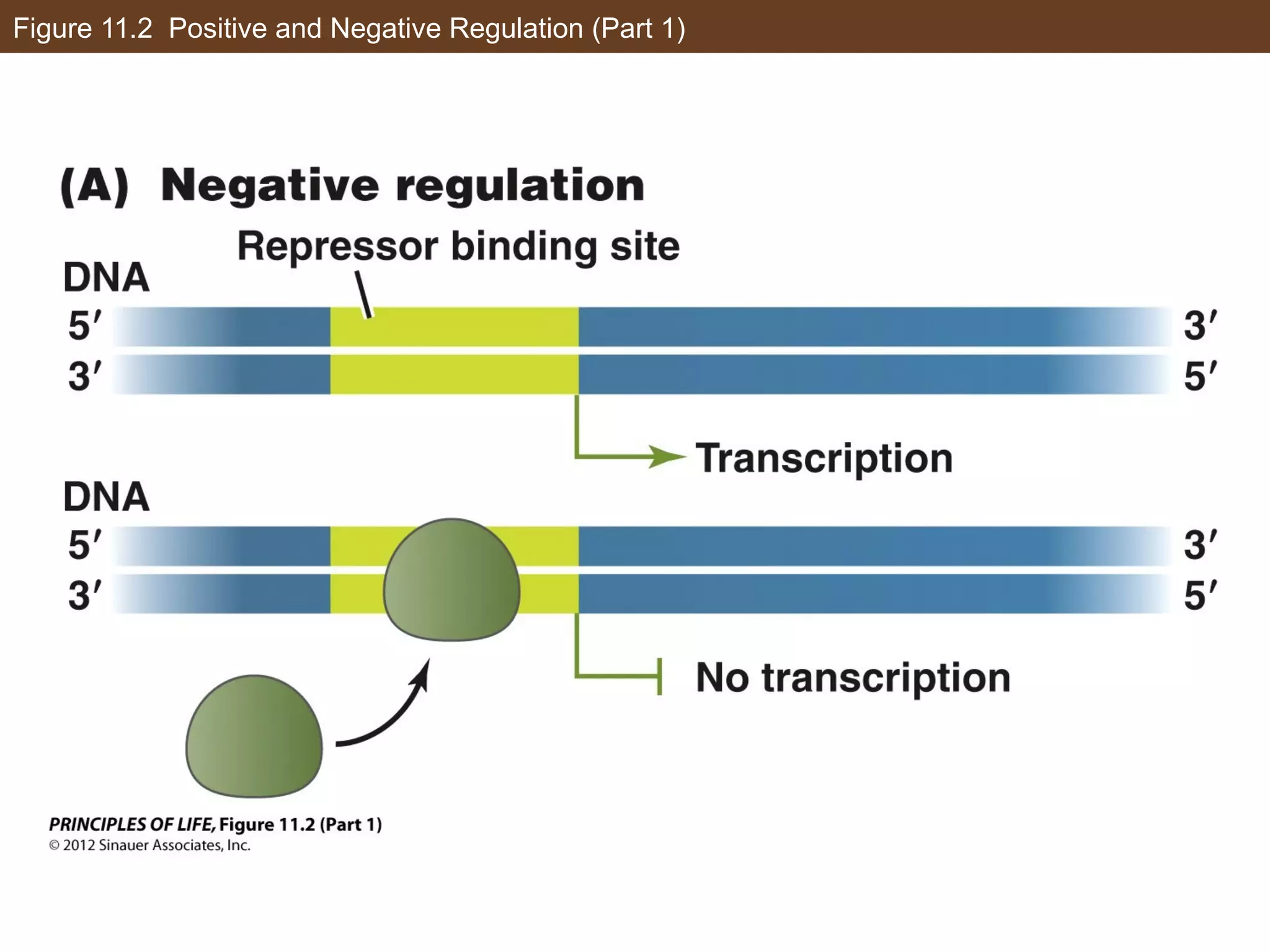
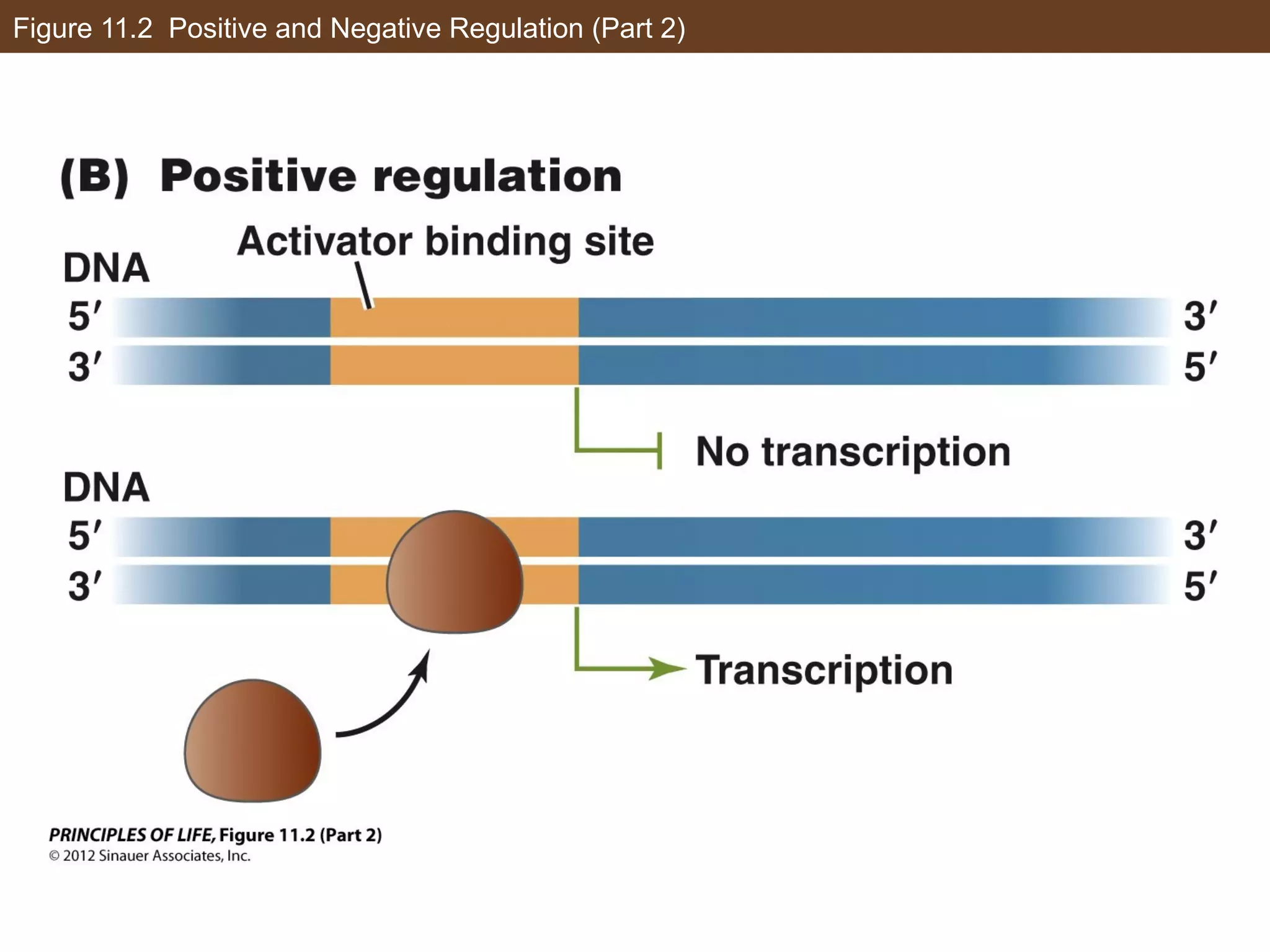
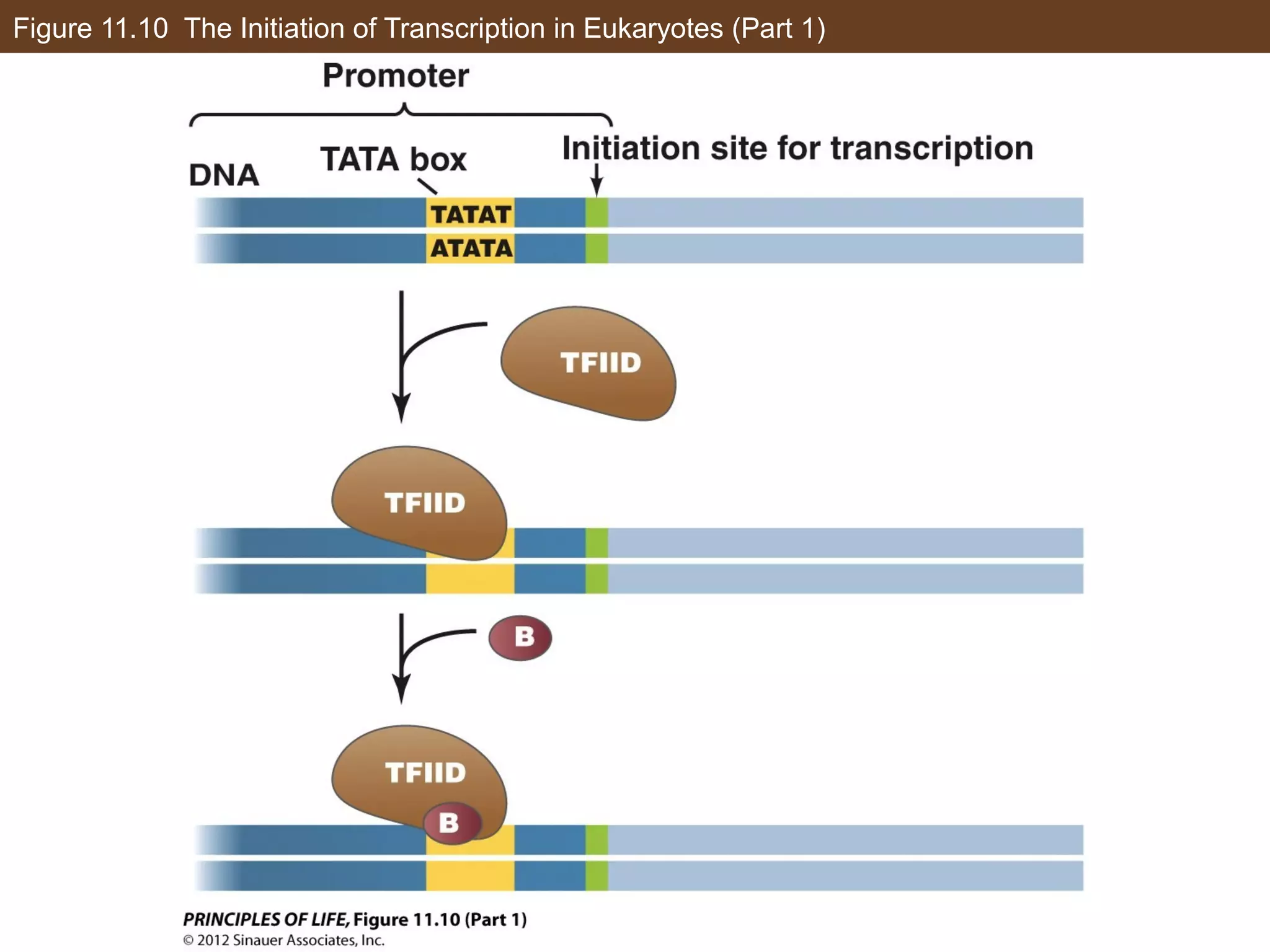
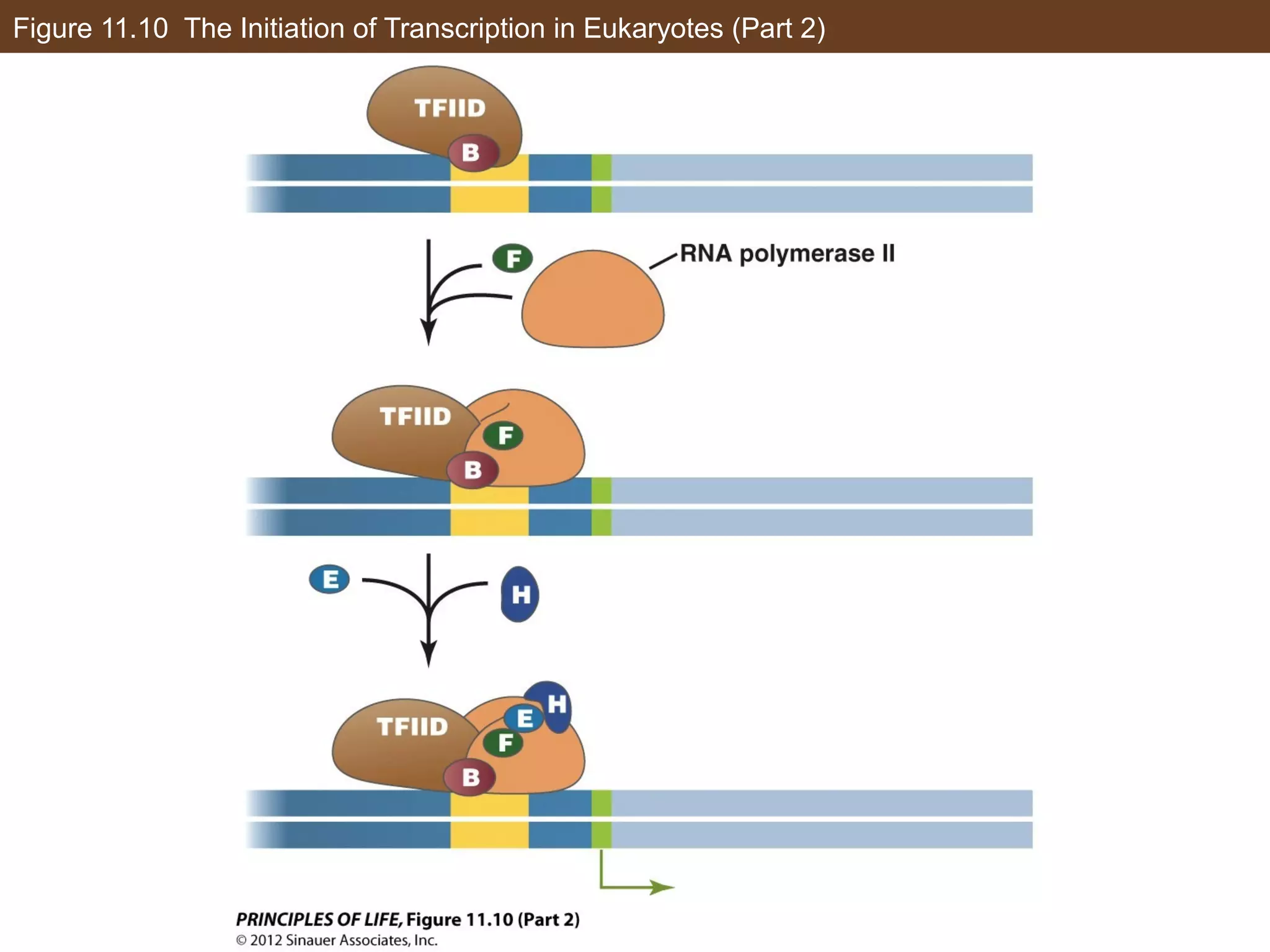
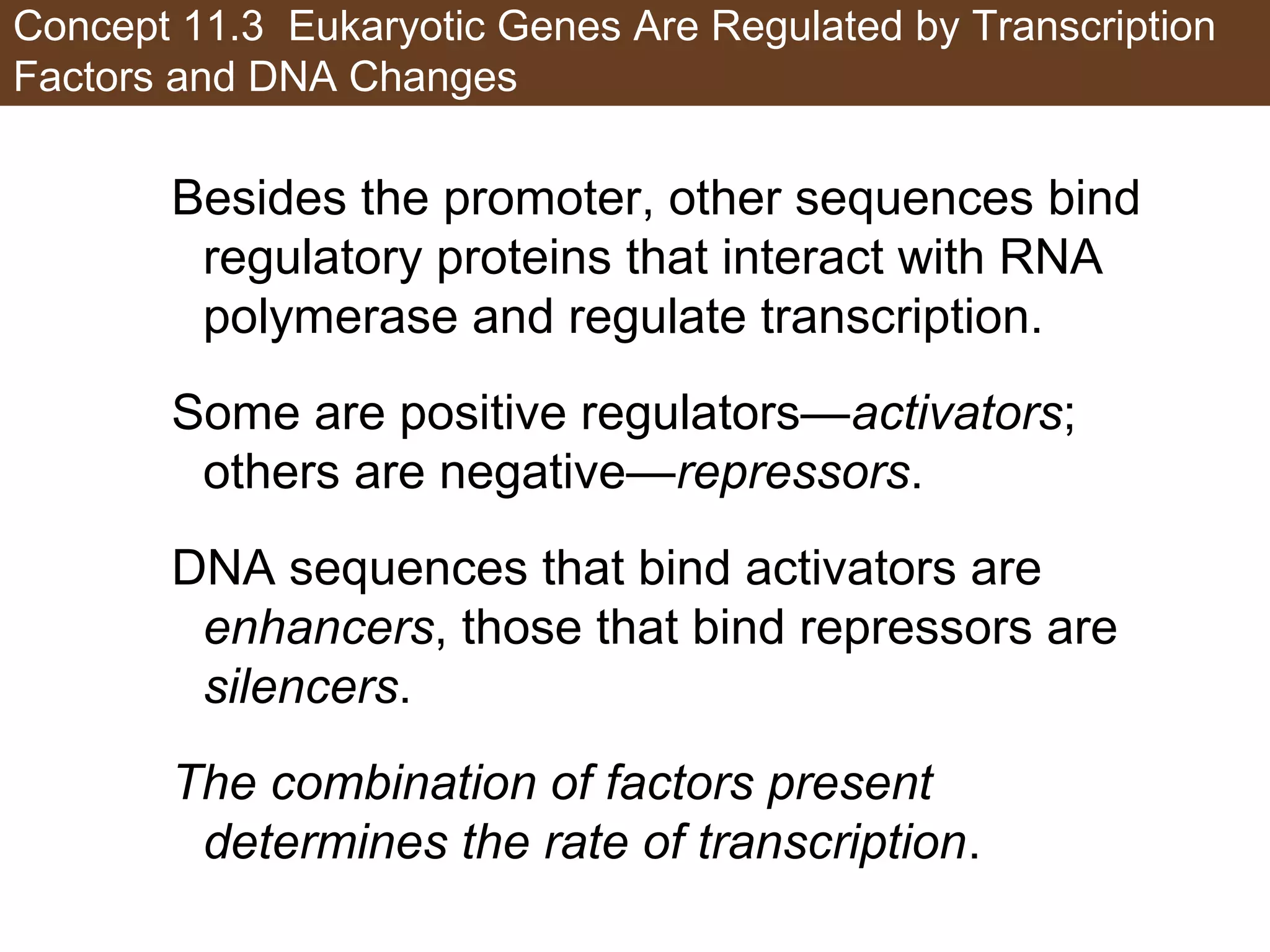
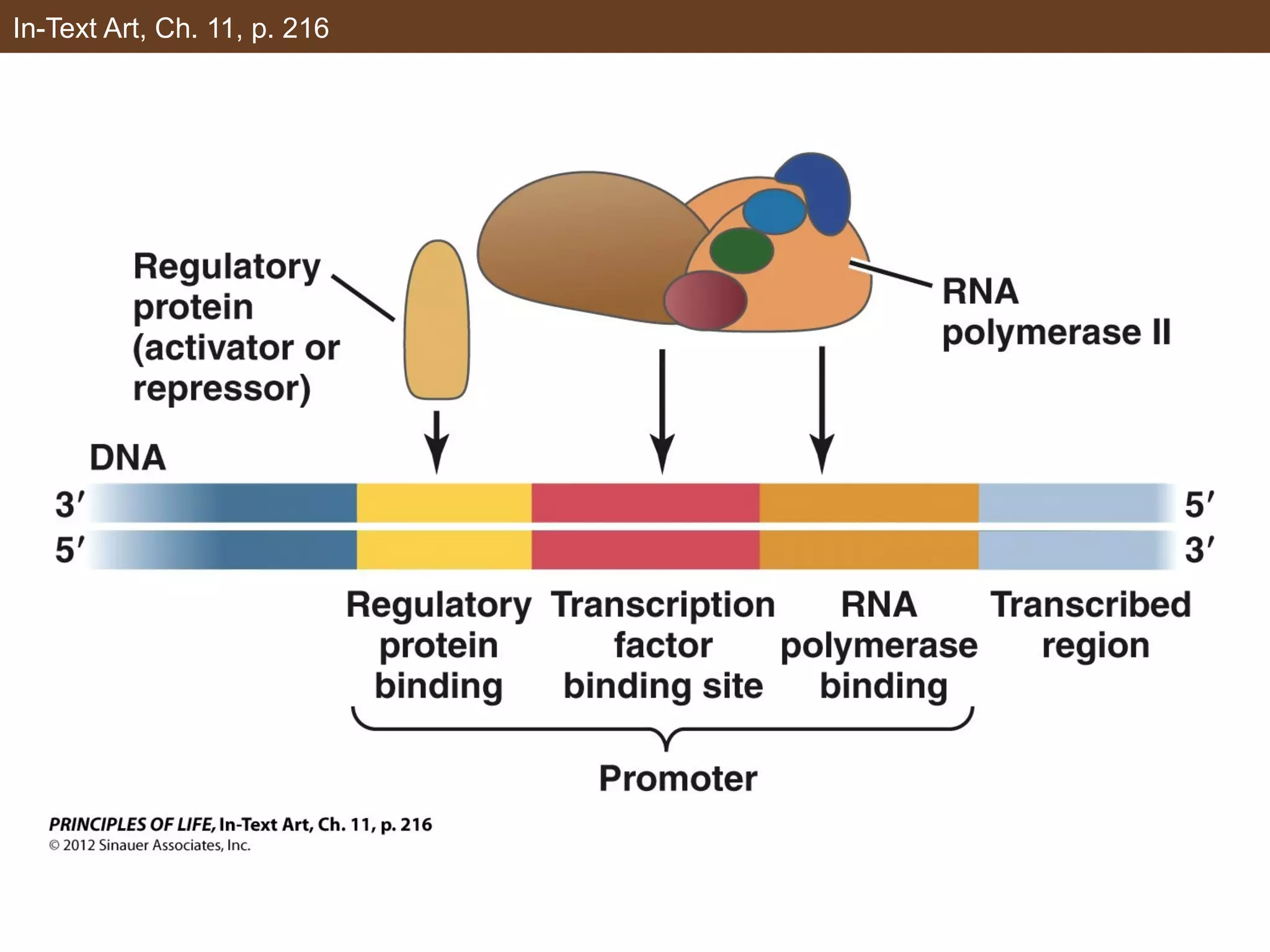
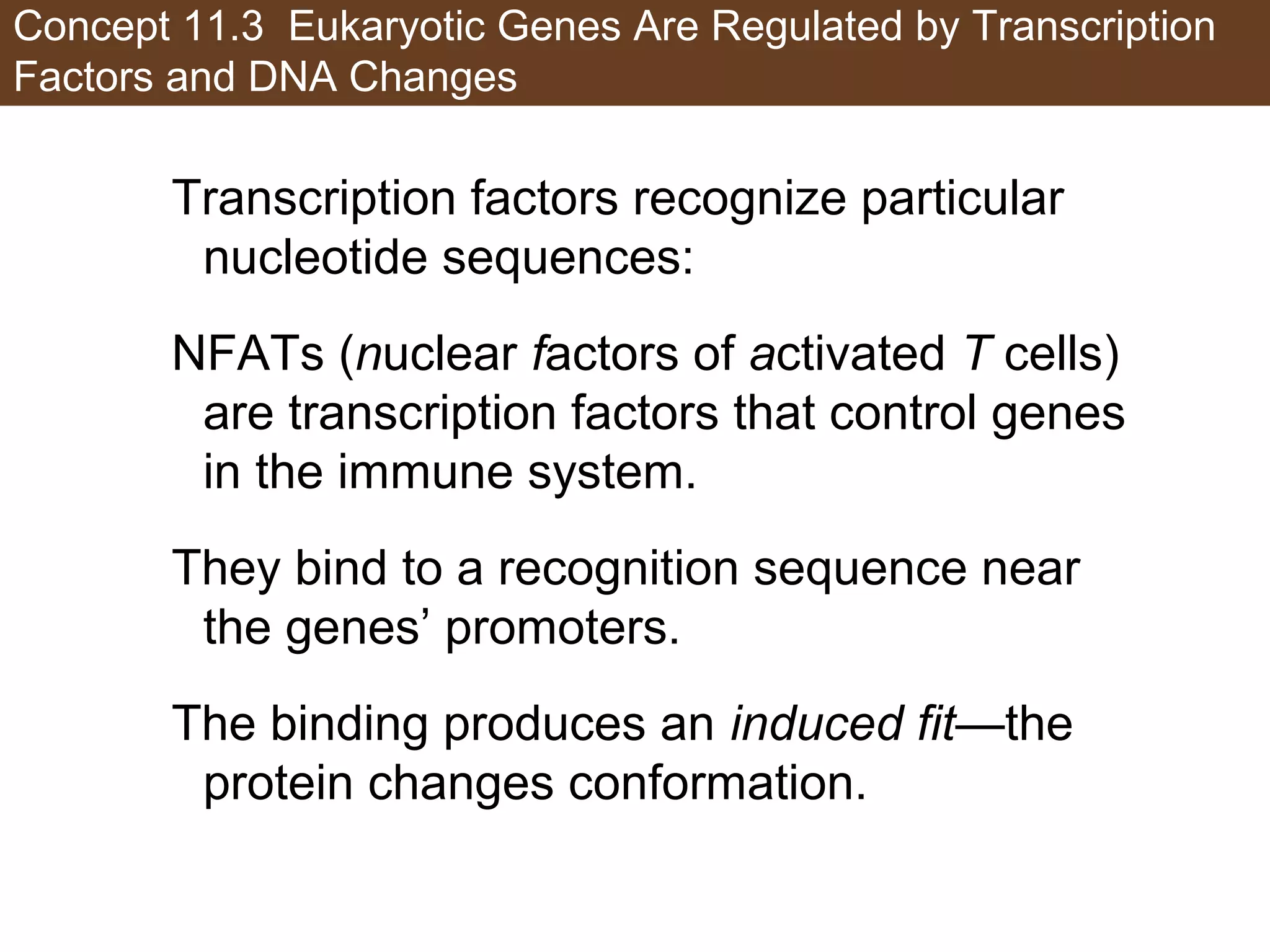
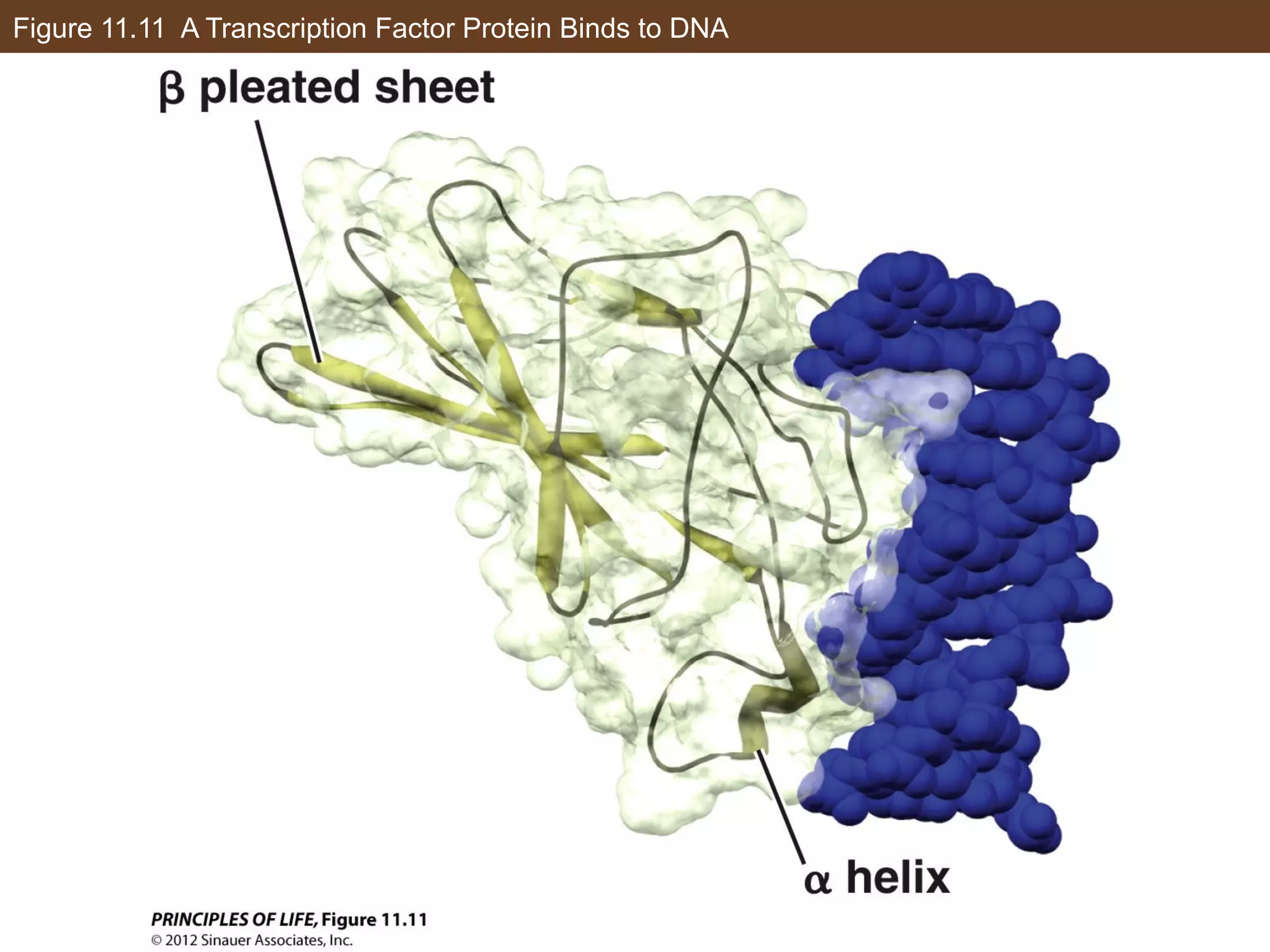
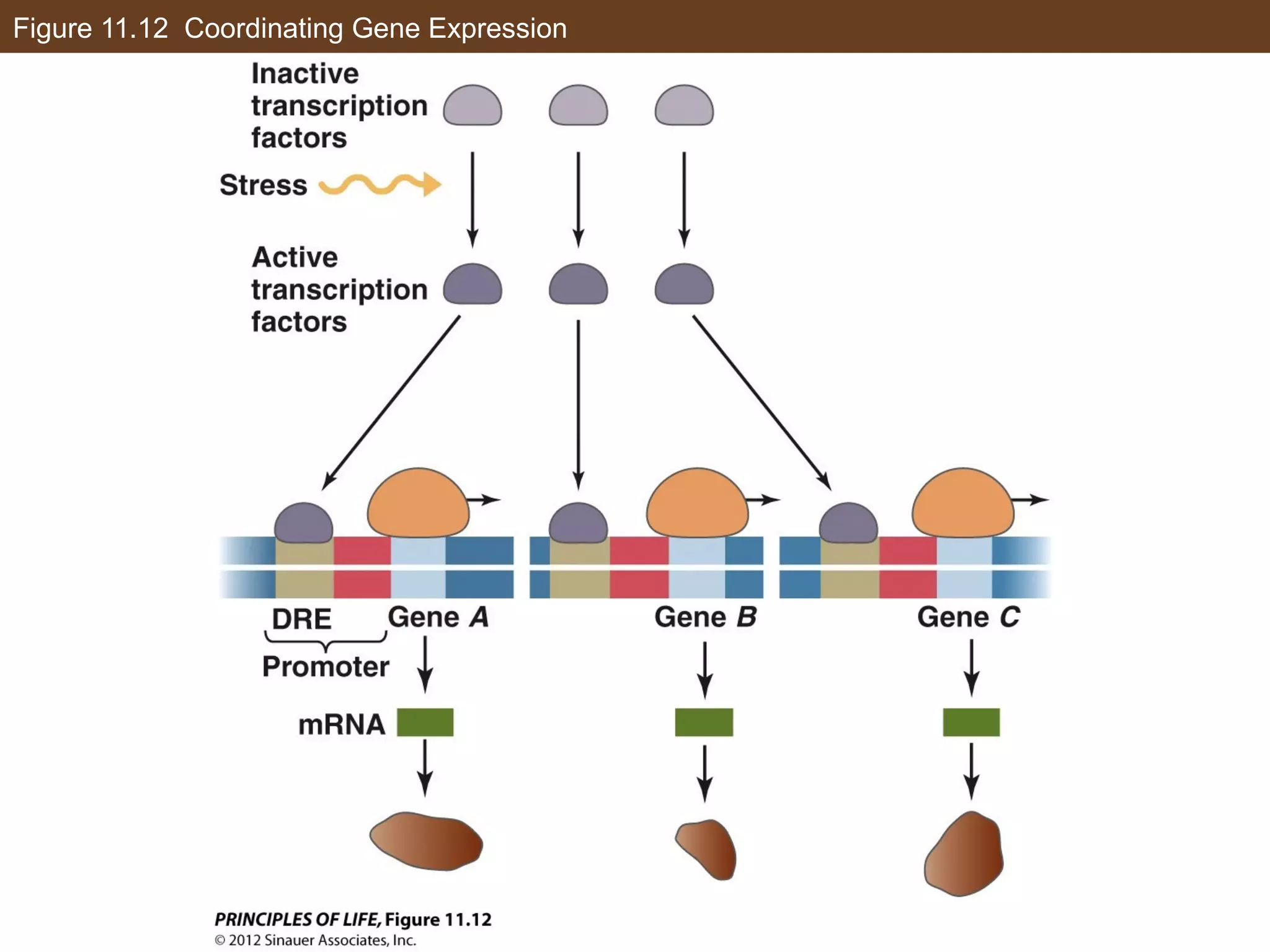
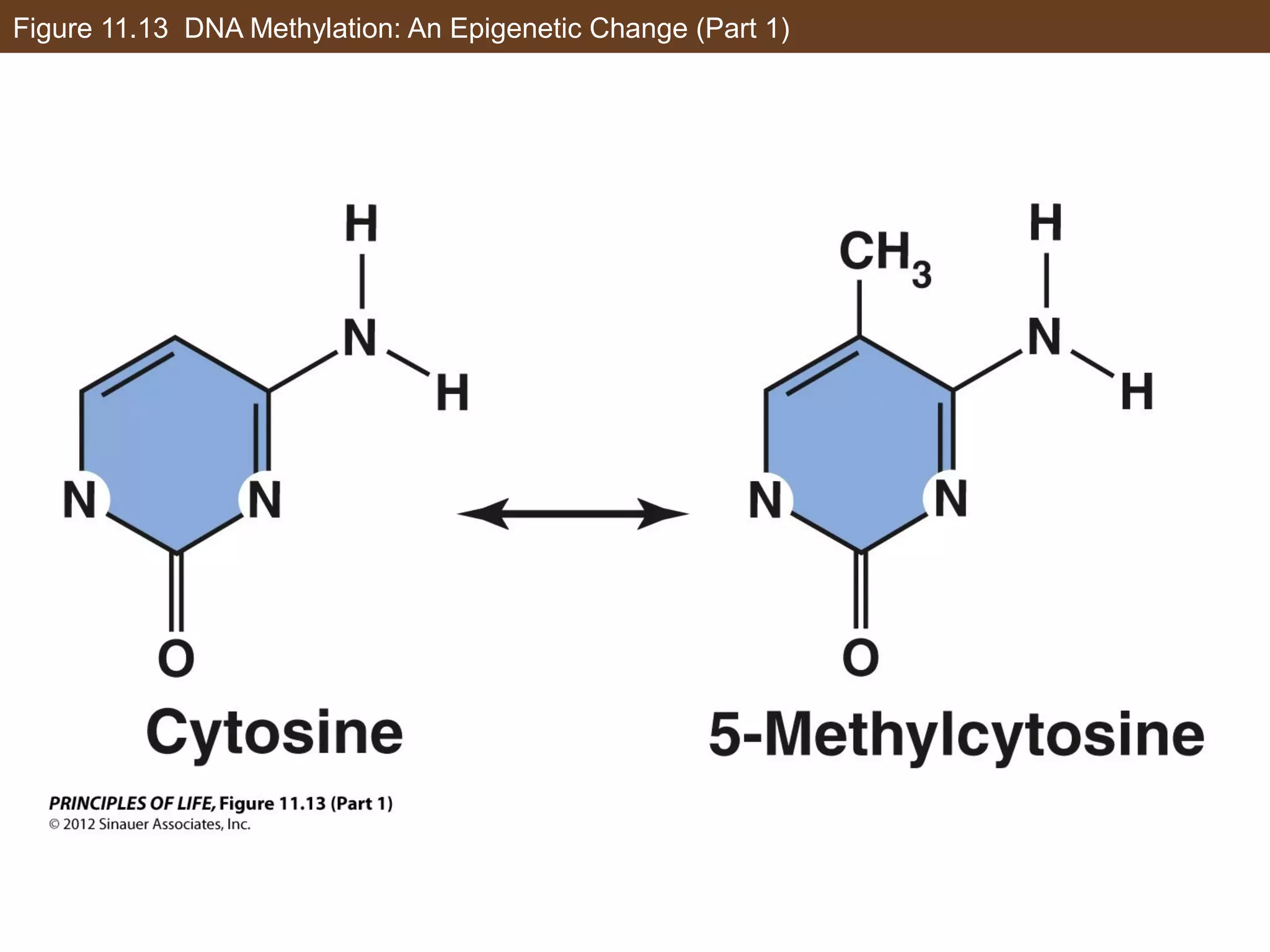
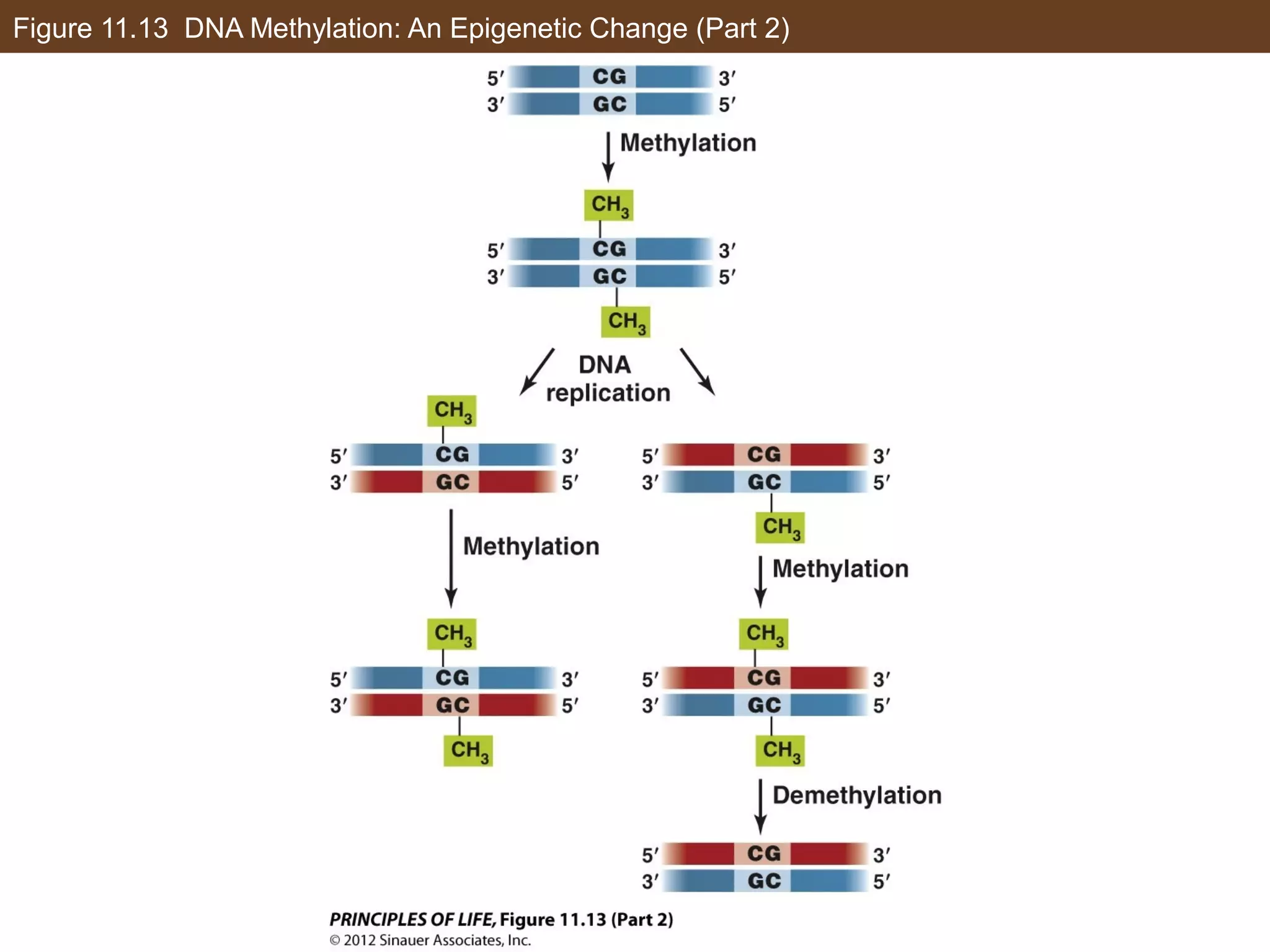
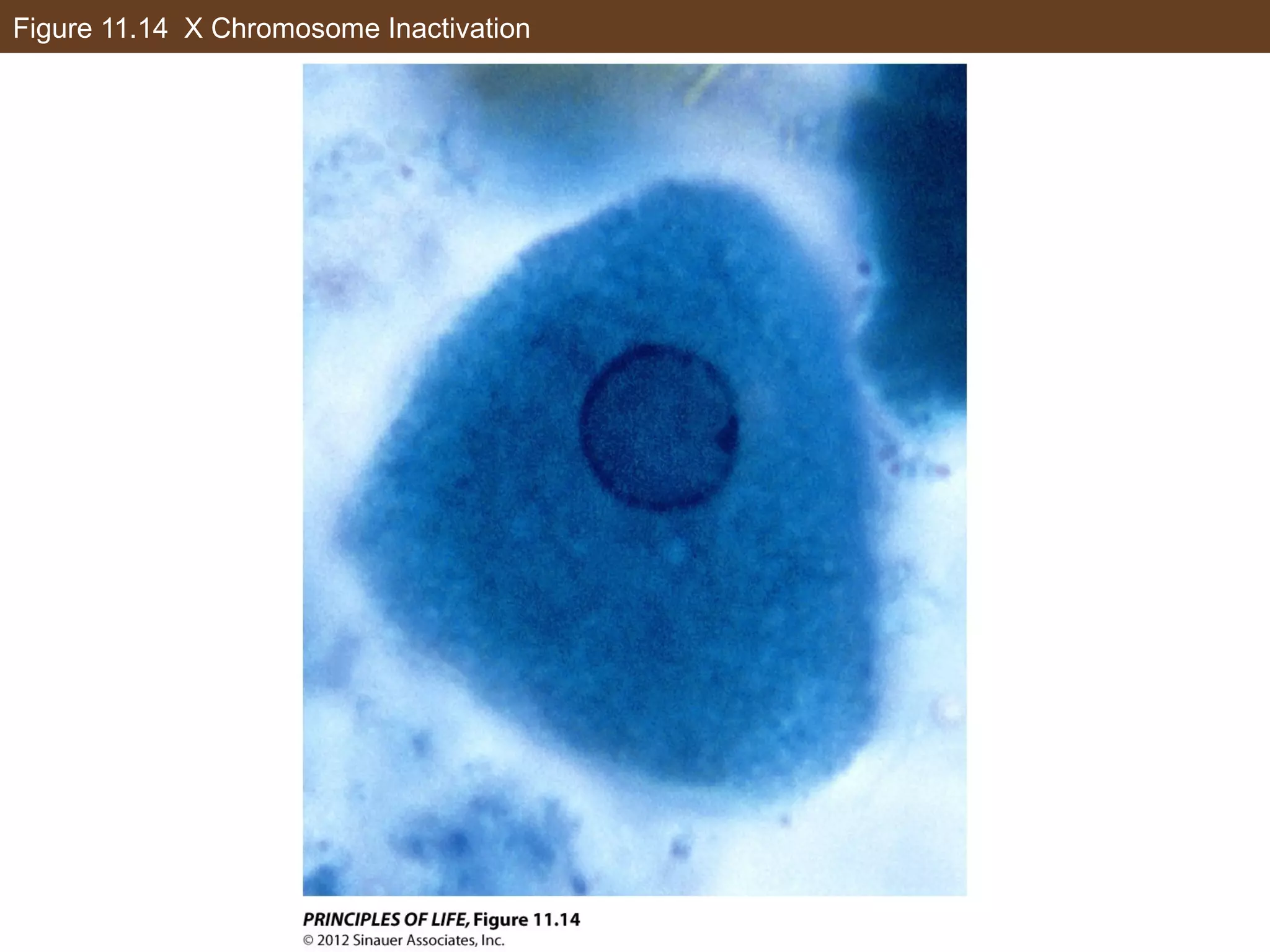
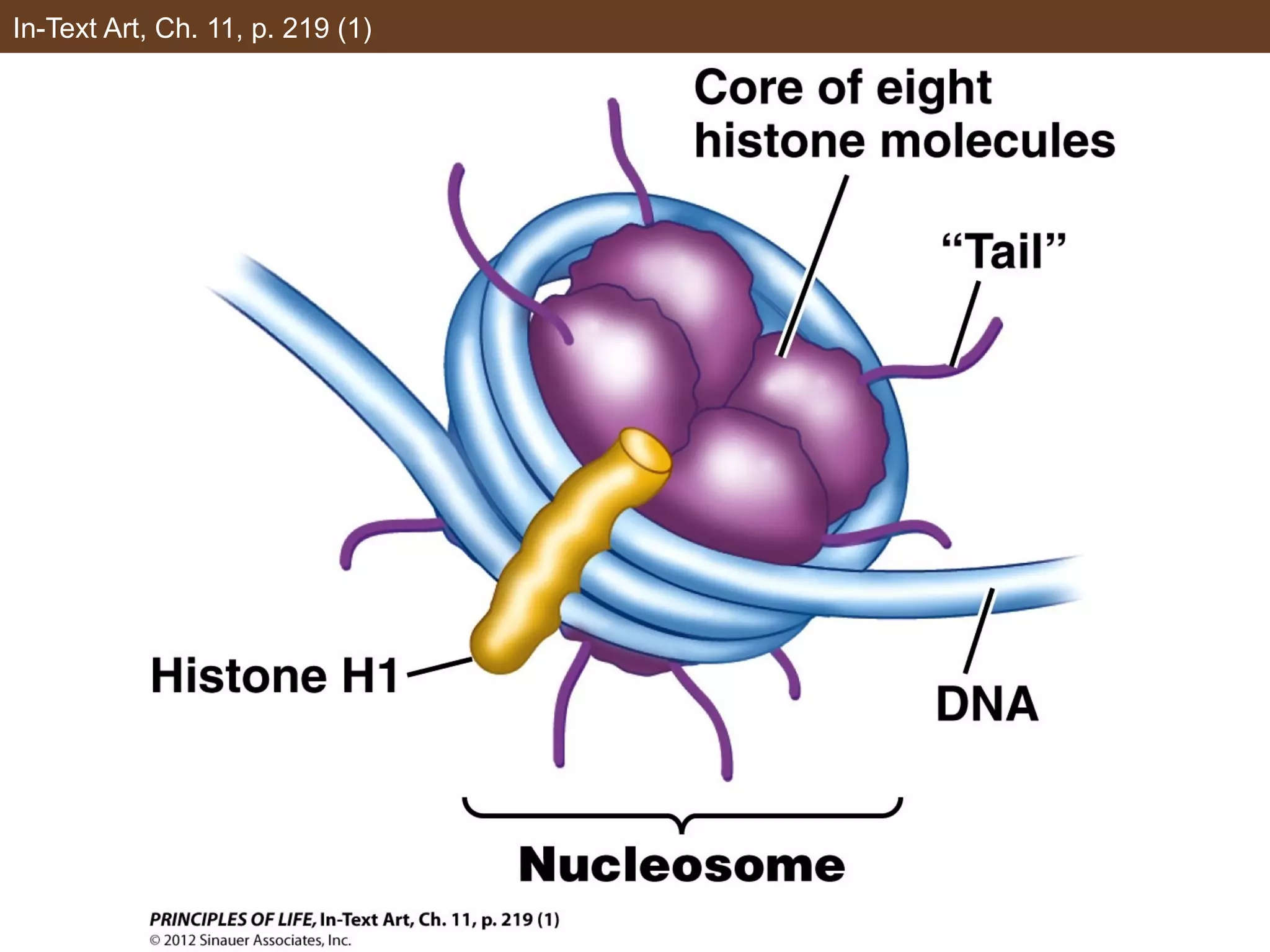
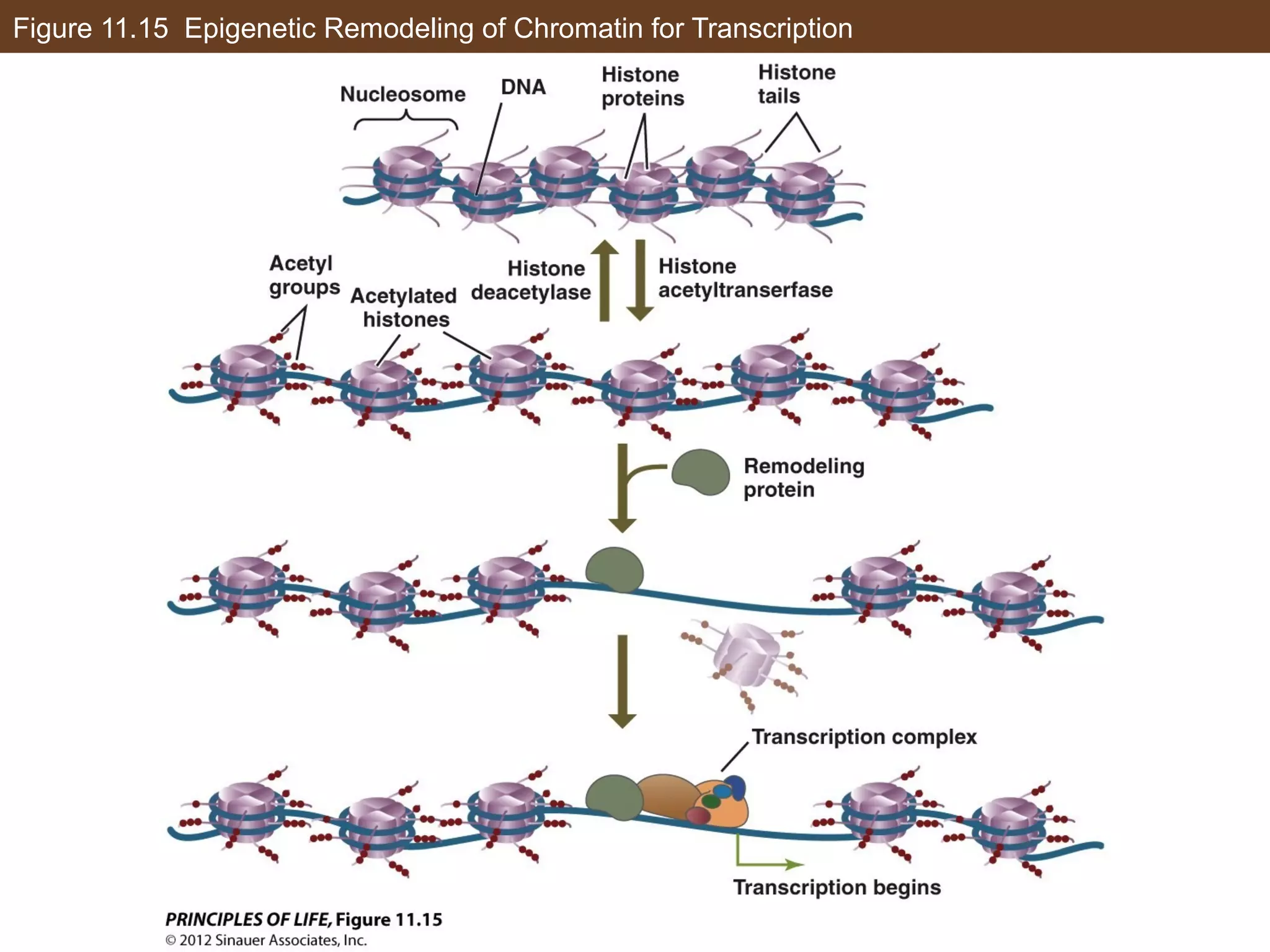
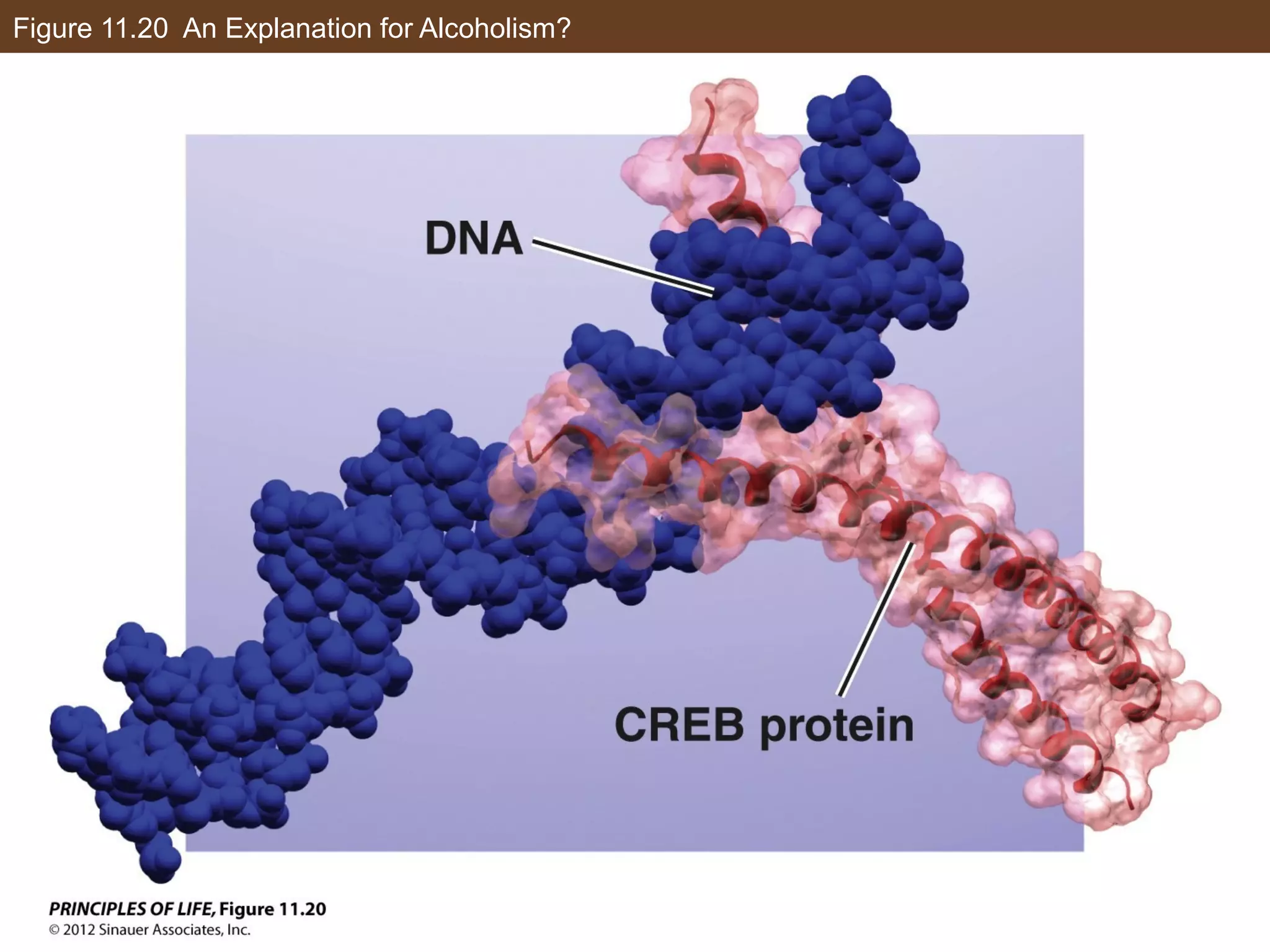
2) Transcription is regulated through the binding of transcription factors to enhancer and silencer regions near gene promoters. DNA methylation and histone modifications can alter chromatin structure and gene activity.
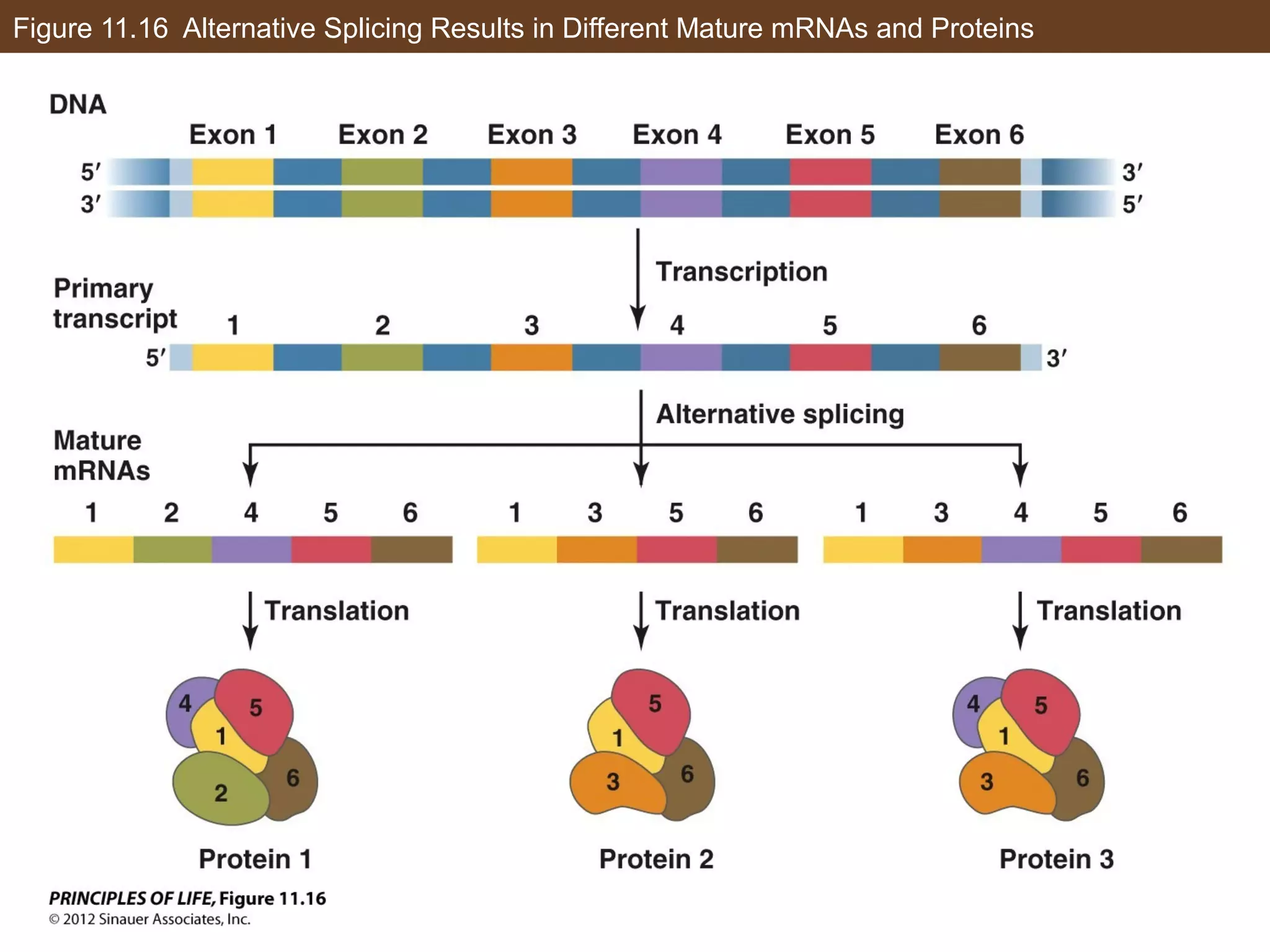
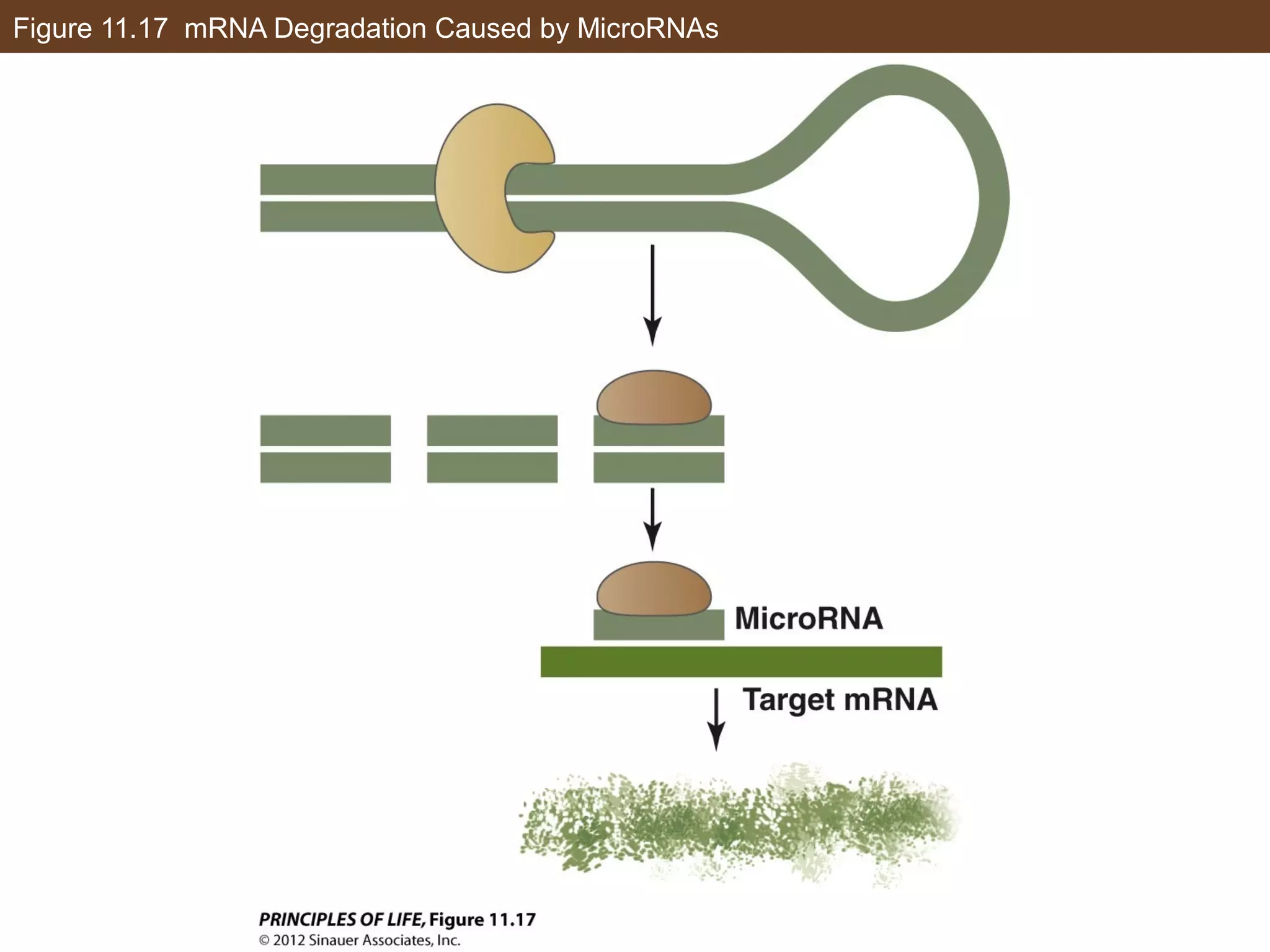
3) Alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and the actions of microRNAs introduce additional regulatory mechanisms by generating different protein isoforms from a single gene or inhibiting specific mRNAs post-transcriptionally.