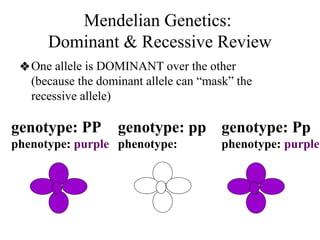
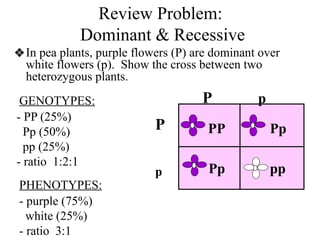
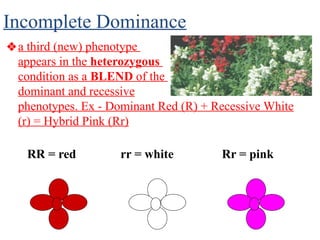
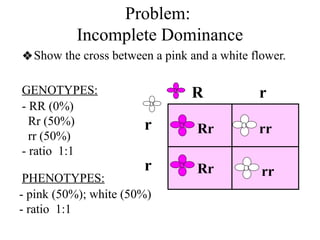
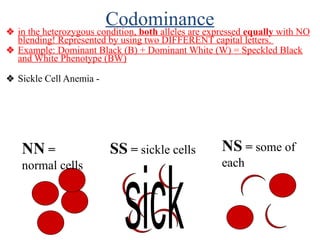
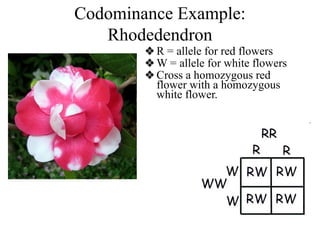
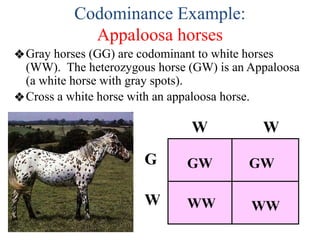
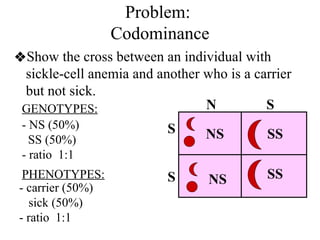
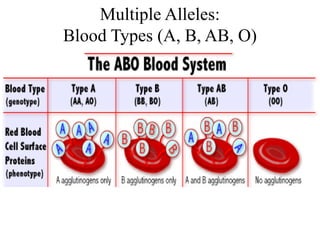
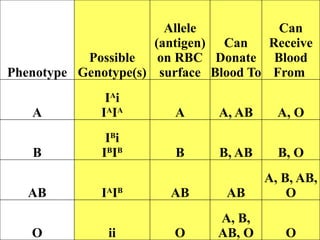
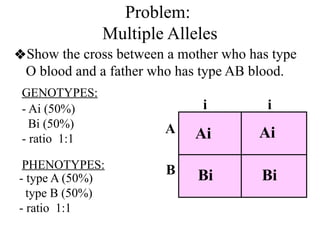
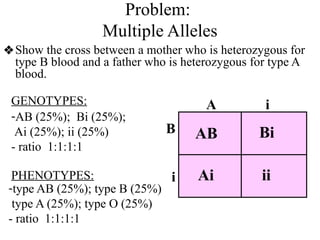
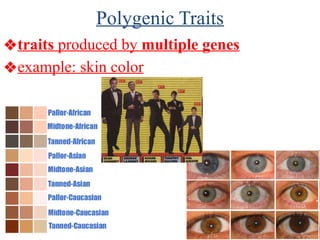
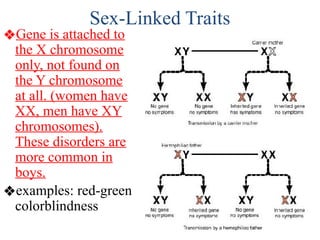
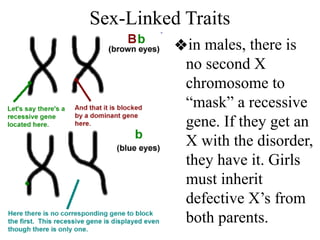
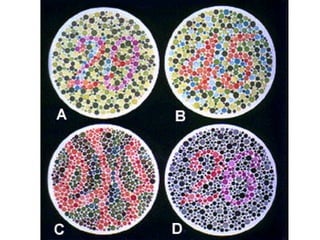
The document discusses non-Mendelian genetics, detailing concepts such as incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, and sex-linked traits. It includes examples and explanations of how these genetic principles differ from traditional Mendelian inheritance, illustrating with case studies like flower color in plants and blood types in humans. The document also provides problems and sample crosses to reinforce understanding of these genetic concepts.