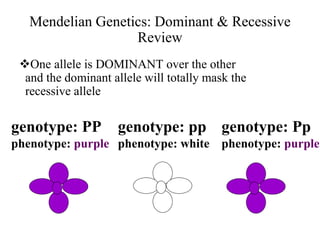
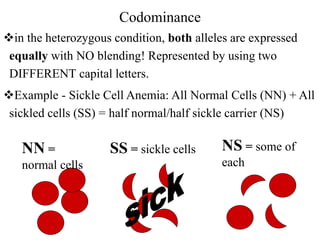
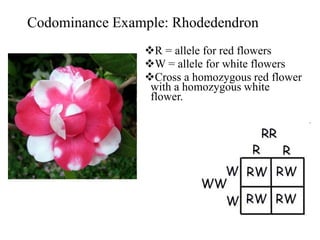
This document discusses several types of non-Mendelian inheritance patterns, including incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, and sex-linked traits. In incomplete dominance, a new phenotype appears as a blend of the dominant and recessive phenotypes in heterozygotes, such as pink flowers from crossing red and white. Codominance occurs when both alleles are fully expressed in heterozygotes, like black and white feathers on checkered chickens. Multiple alleles exist for some traits, such as the three blood type alleles in humans that result in A, B, AB, and O blood types. Problems are provided as examples for readers to work through crosses demonstrating these inheritance patterns.