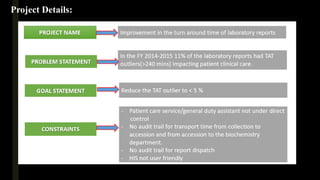
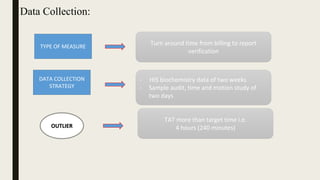
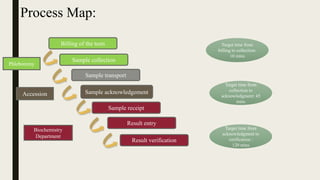
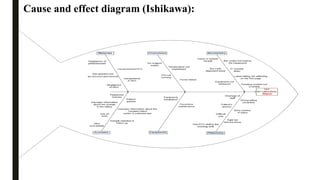
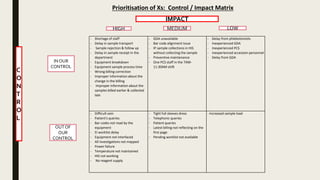
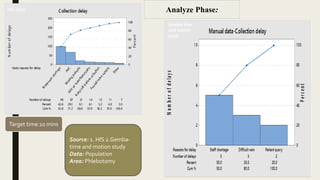
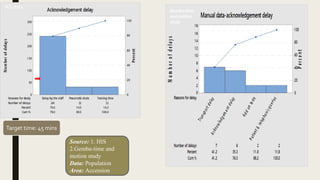
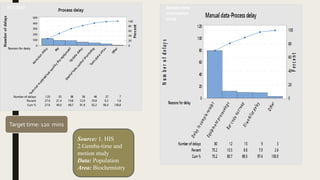
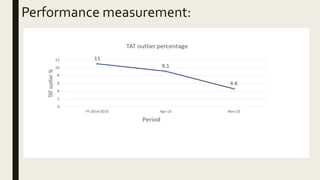
This document summarizes a project to improve turnaround time (TAT) for biochemistry reports at a hospital. The project team used Lean Six Sigma methodology to analyze current processes, identify issues causing delays, and implement strategies to address them. Their improvements reduced TAT outliers from 9.1% to 4.6%, increased the number of daily tests by 76, and increased financial benefits from Rs. 3960/day to Rs. 1,82,400/day, meeting and exceeding their targets. Monitoring systems were established to sustain the gains. The stakeholders recognized the improved TAT, and staff felt motivated by contributing suggestions to the project's success.