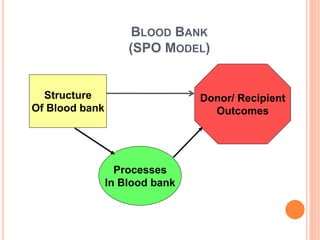
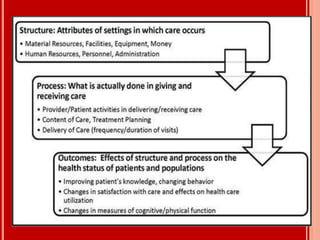
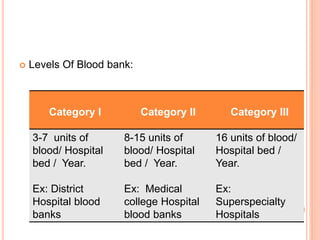
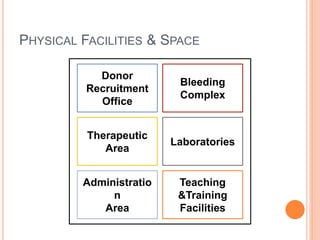
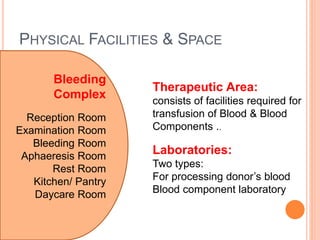
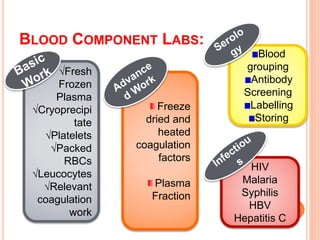
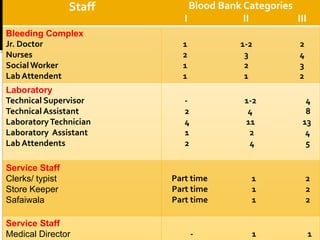
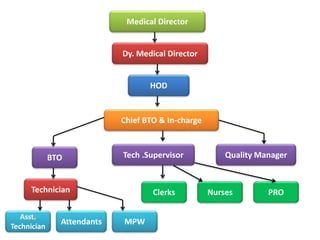
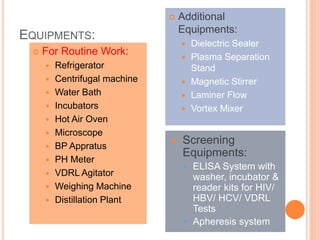
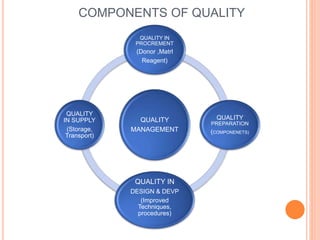
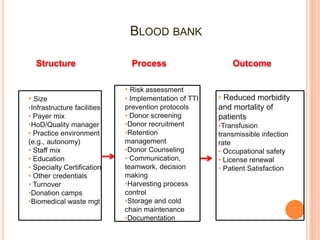
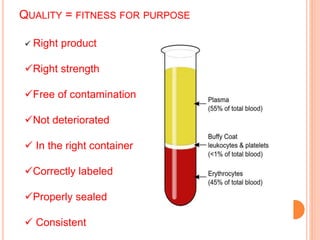
The document outlines the critical role of blood transfusion in saving lives and discusses regulations and infrastructure related to blood banks in India, including the establishment of national policies and council. It details the physical facilities, staff requirements, and necessary equipment for various categories of blood banks, as well as the importance of quality management in blood processing and transfusion. Furthermore, it emphasizes the need for effective donor recruitment, safety protocols, and quality control to ensure safe blood transfusion practices.