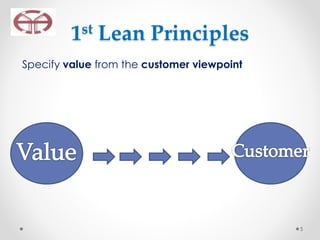
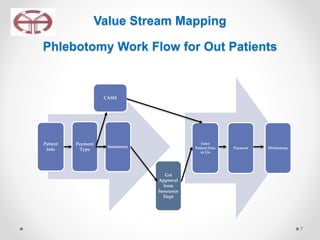
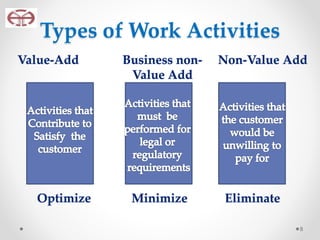
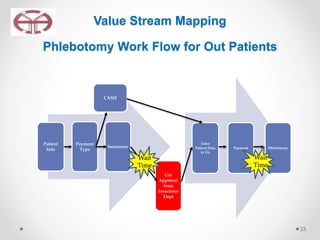
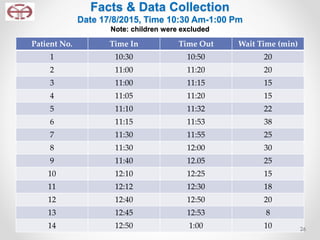
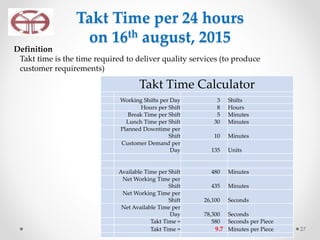
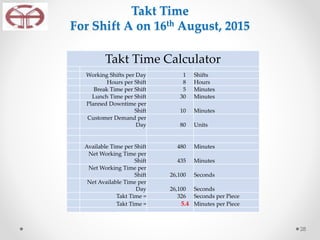
The document outlines the application of lean thinking principles at the Arab Medical Center, emphasizing value creation and waste elimination to improve healthcare services. It details the types of waste identified in the phlebotomy workflow, methods for reducing patient wait times, and the implementation of standardized work practices for better efficiency and safety. Additionally, it discusses the PDCA cycle for continuous improvement and employee involvement in the process.