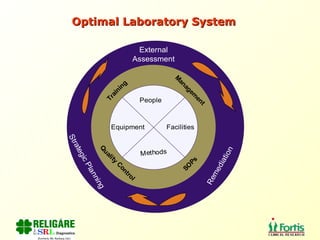
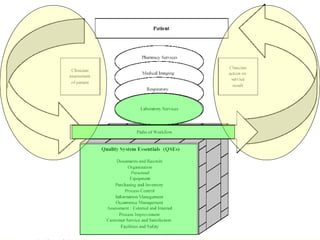
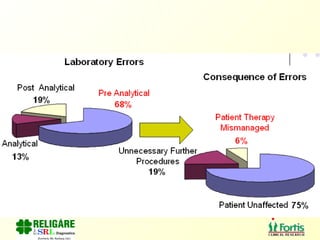
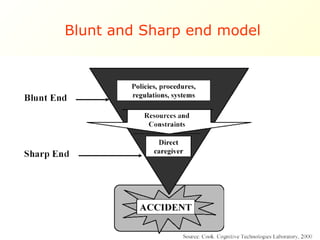
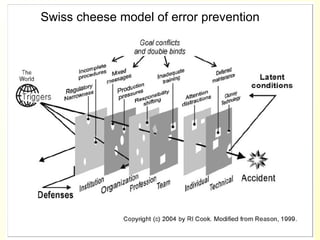
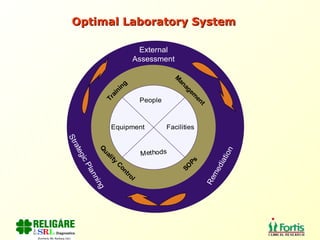
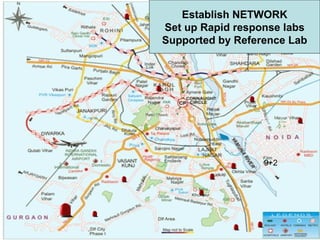
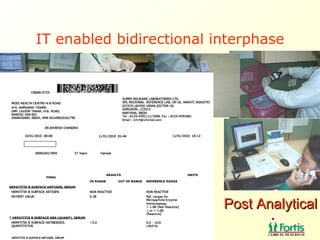
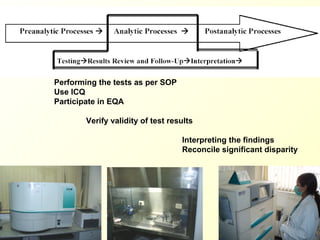
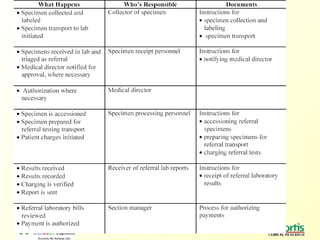
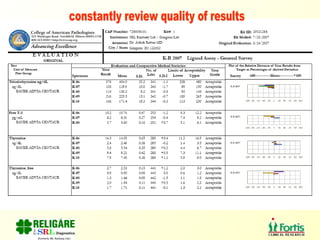
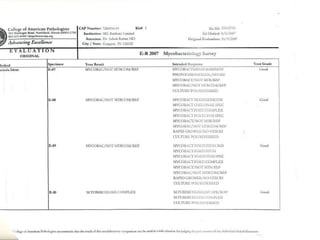
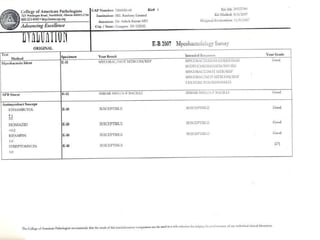
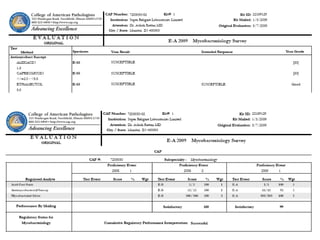
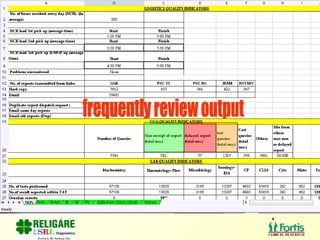
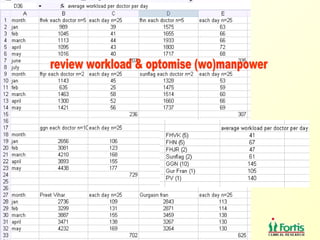
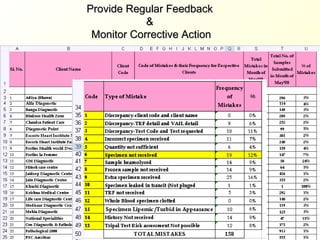
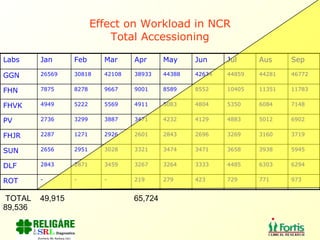
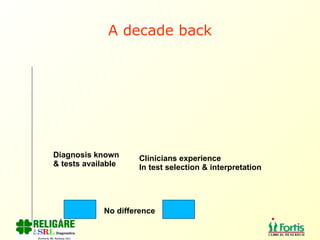
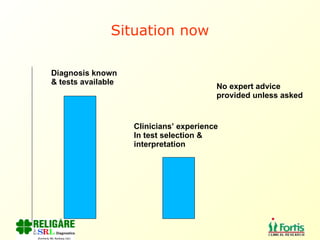
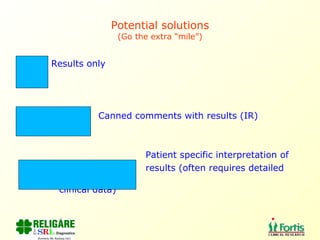
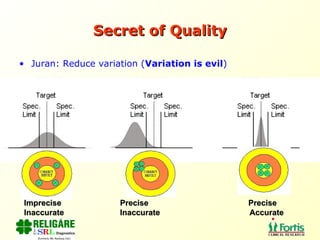
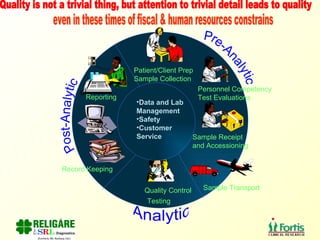
The document discusses the importance of laboratory quality management amidst fiscal and human resource constraints, highlighting the need for accreditation, quality assurance, and total quality management. It emphasizes that medical errors often stem from systemic issues rather than individual mistakes and advocates for better data management and actionable processes to enhance laboratory services. Recommendations include improved test selection, interpretative services for complex results, and continuous monitoring to optimize performance and reduce errors.