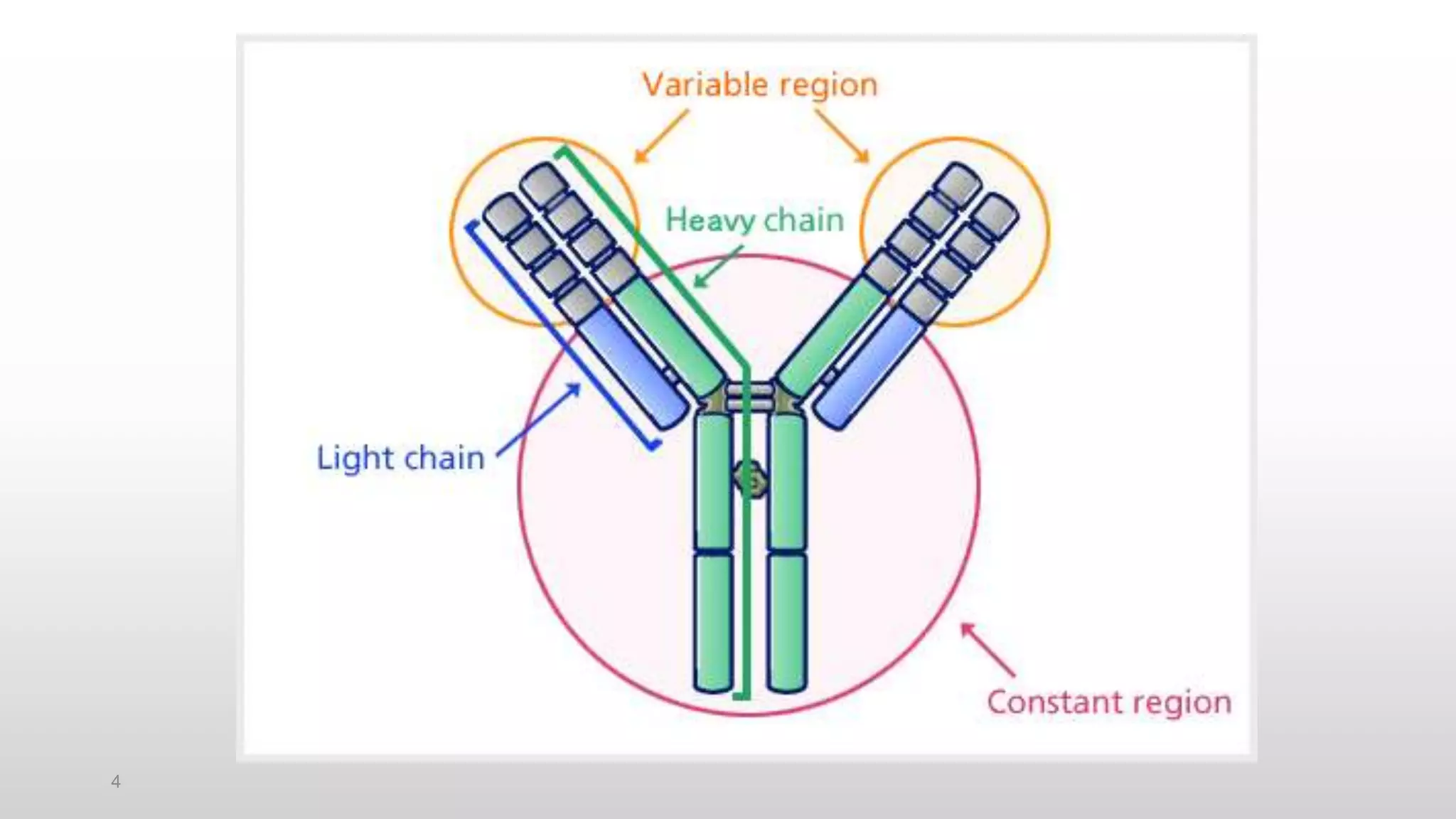
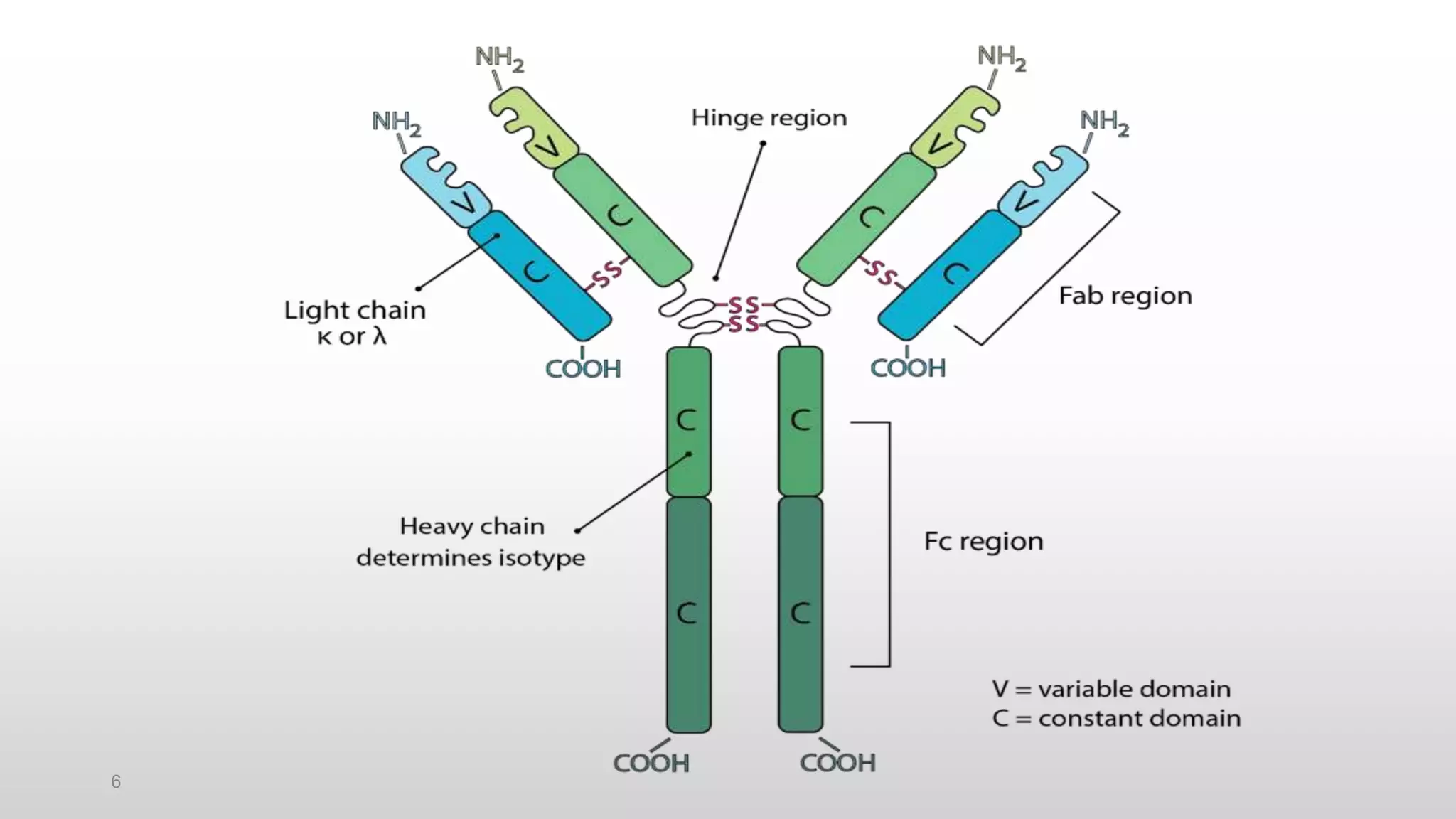
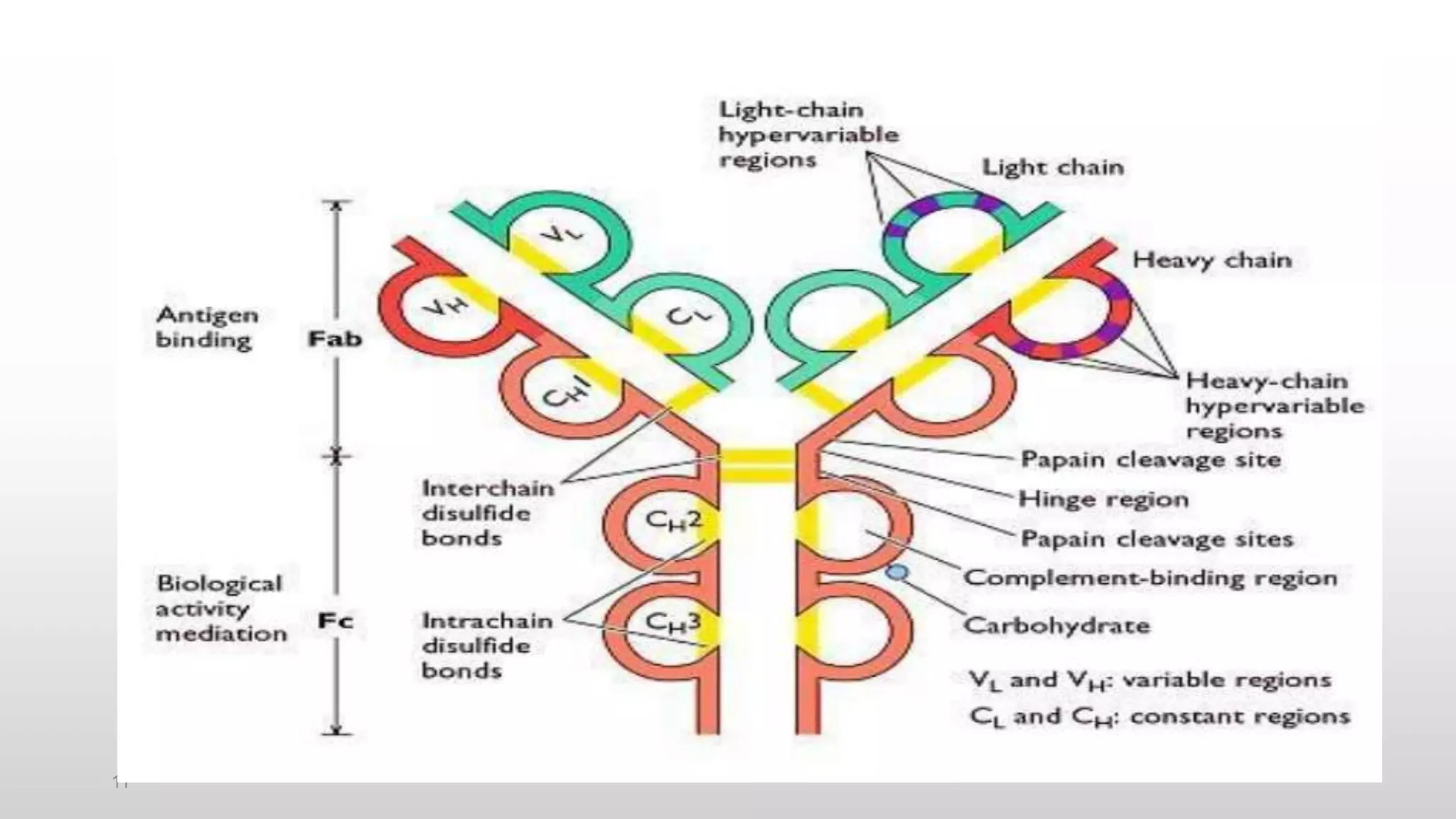
Immunoglobulin or antibody molecules have a basic Y-shaped structure composed of four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. Each chain contains a constant region and a variable region. The variable regions from the heavy and light chains fold together to form the antigen-binding site. There are five classes of heavy chains (gamma, alpha, mu, delta, epsilon) that determine the five immunoglobulin classes (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE). Each immunoglobulin class has different properties, distribution, and roles in the immune system.