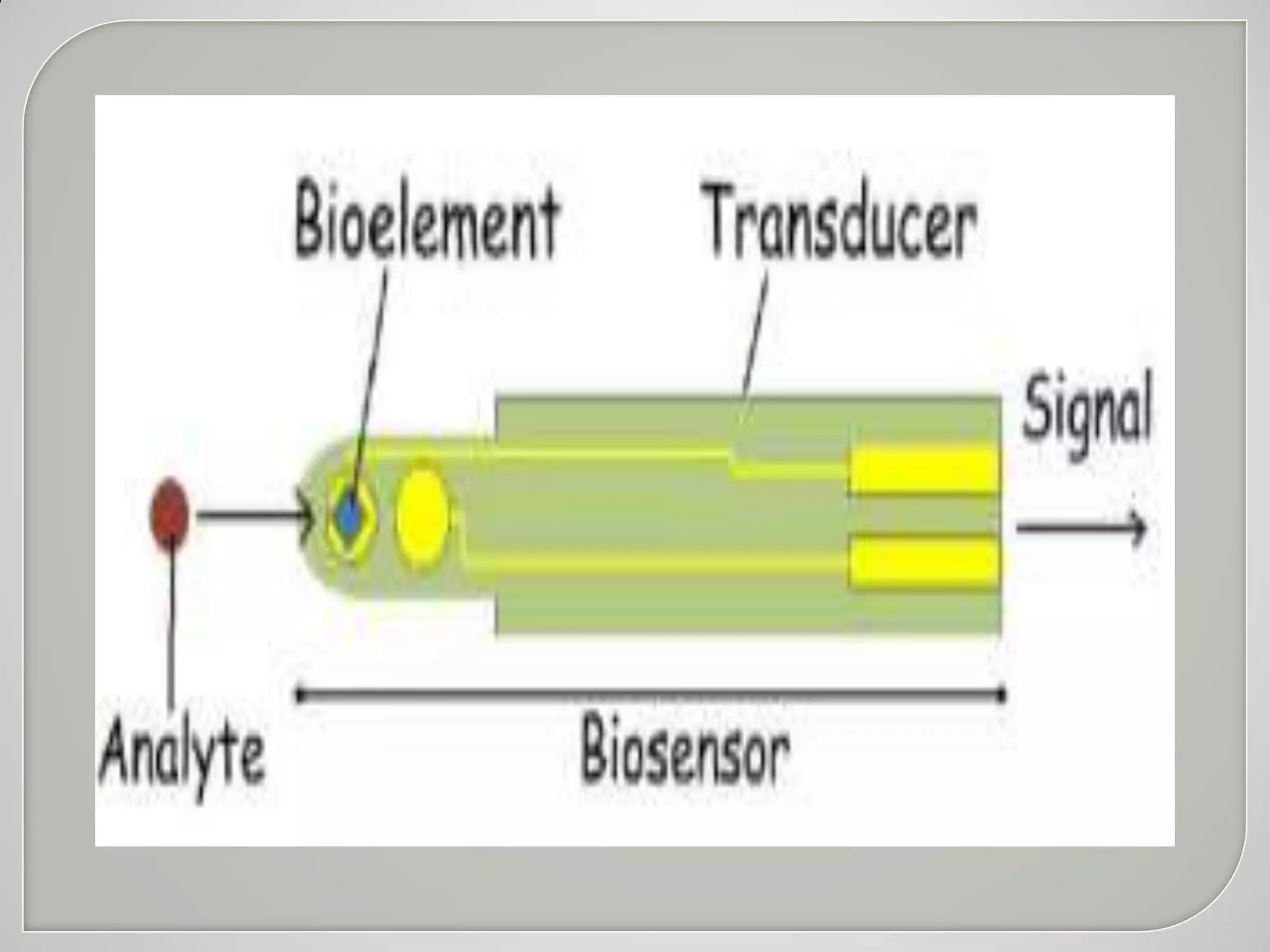
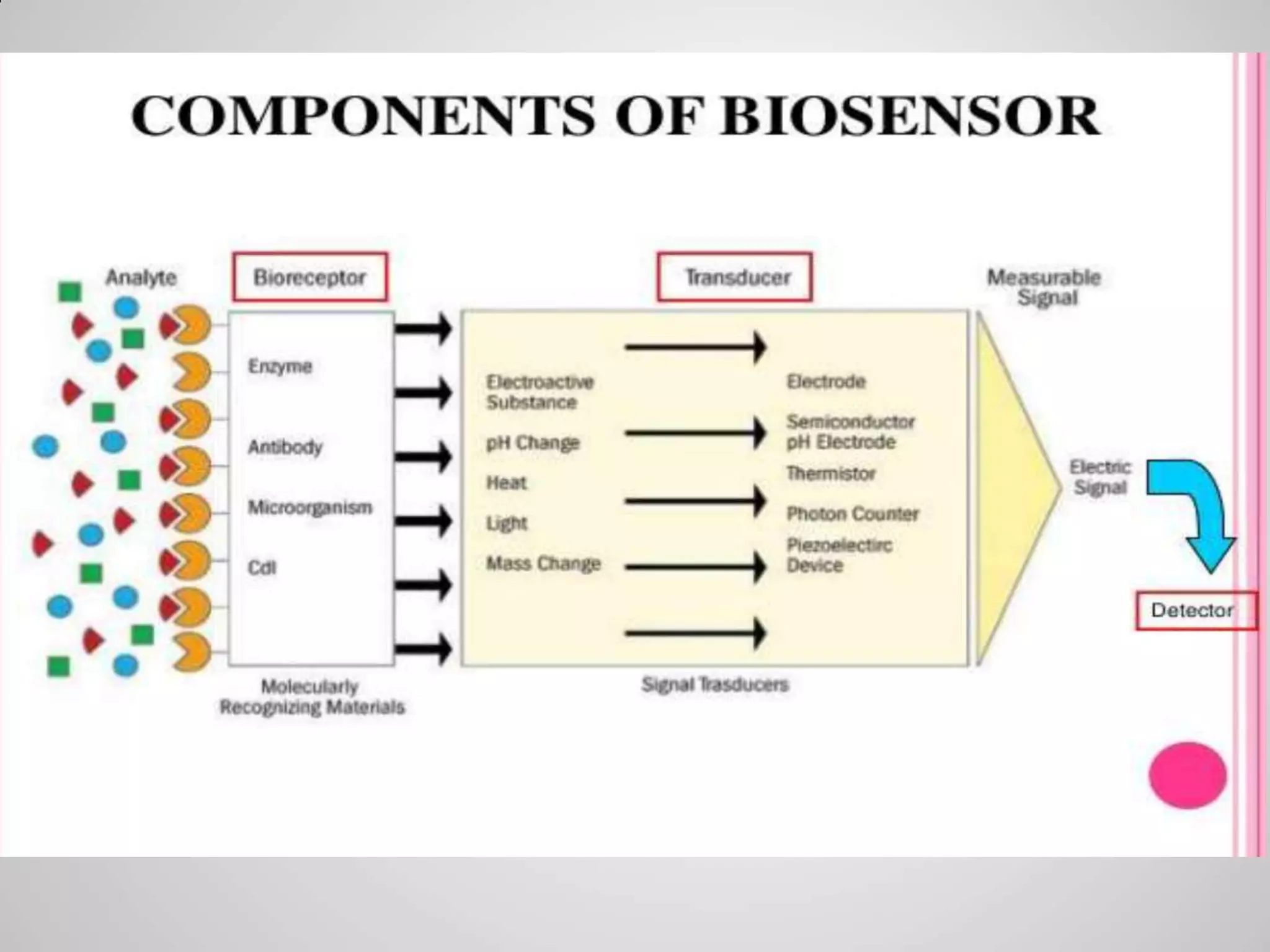
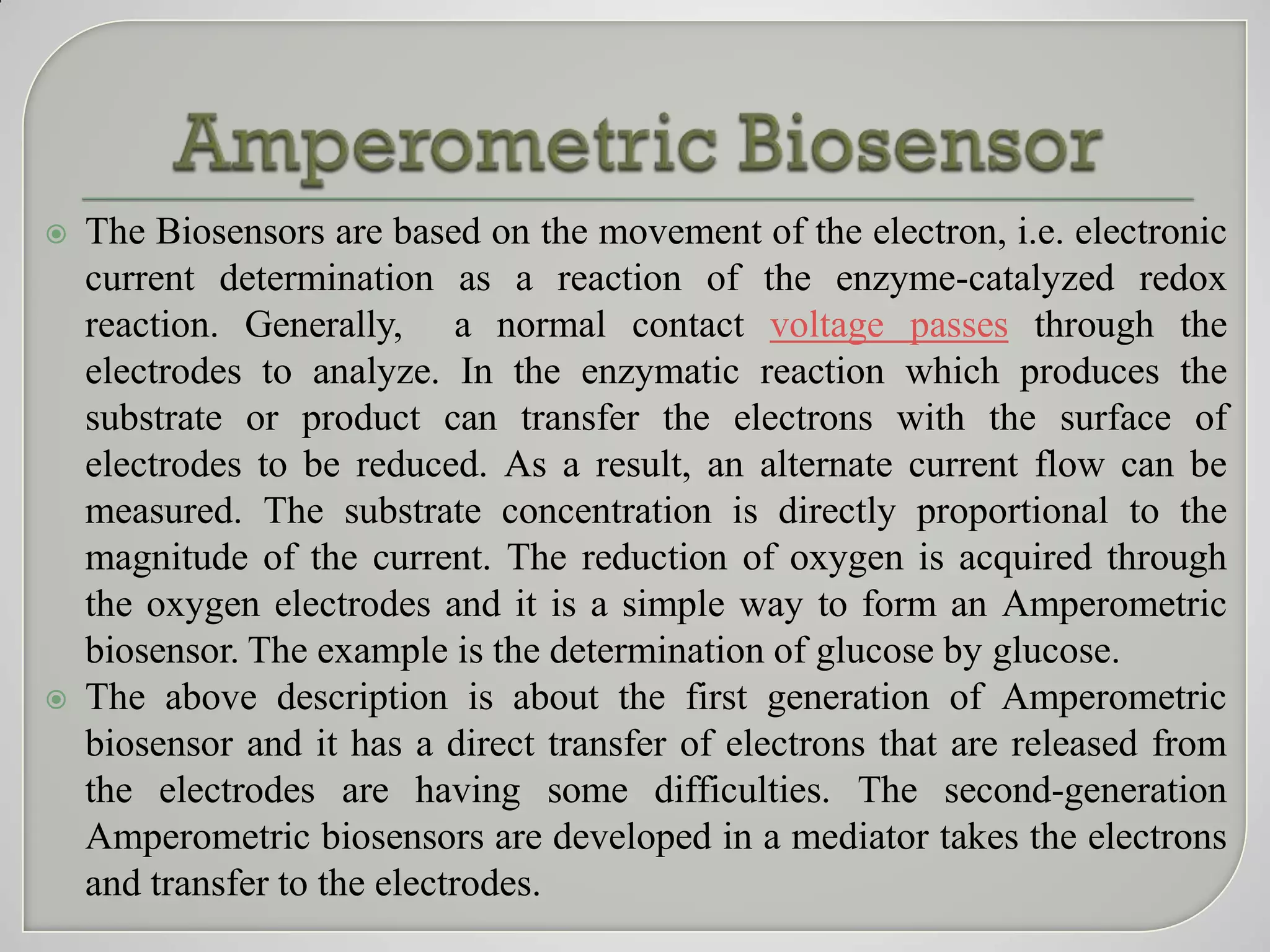
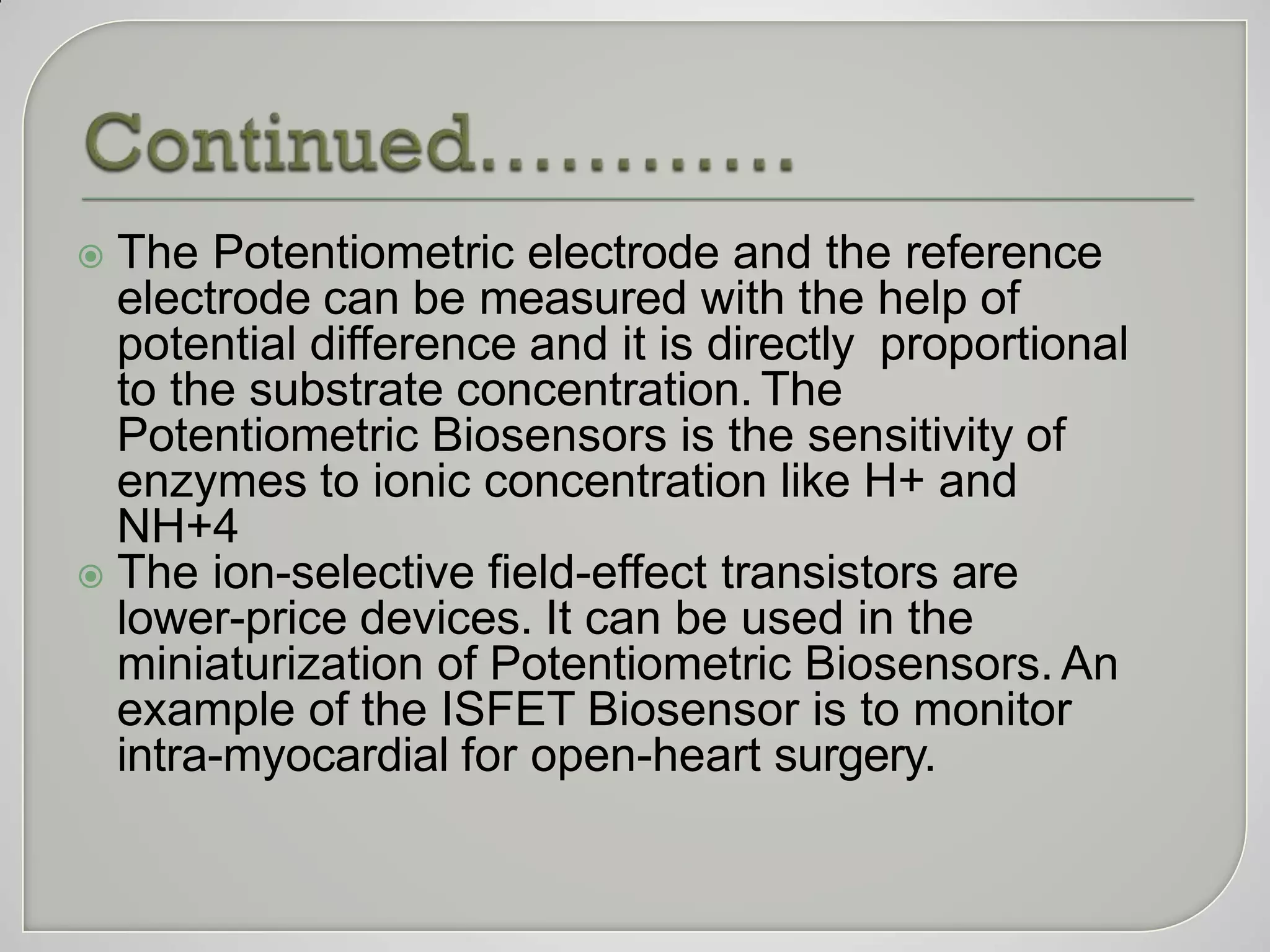
Biosensors convert biological responses into electrical signals and were pioneered by Professor Leland C. Clark. They should provide accurate, precise, reproducible results using cheap, small, portable devices operable by semi-skilled users. Biosensors contain bioreceptors, transducers, signal processors and displays. Depending on the transducer, examples include electrochemical, amperometric, potentiometric, conductometric, thermometric, optical and piezoelectric biosensors. Biosensors have wide applications in medicine such as glucose monitoring, infectious disease diagnosis, and detection of cardiac markers.