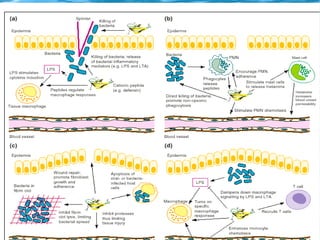
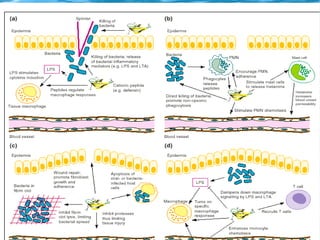
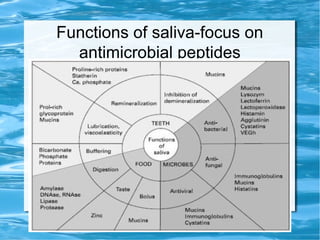
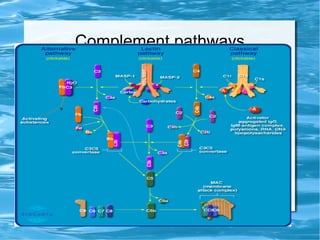
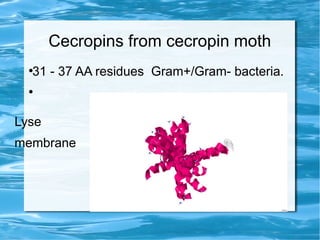
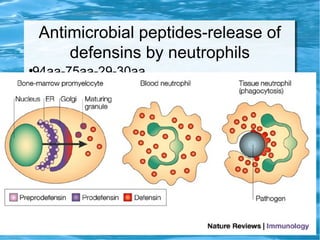
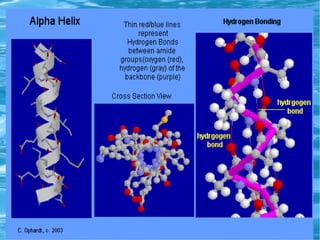
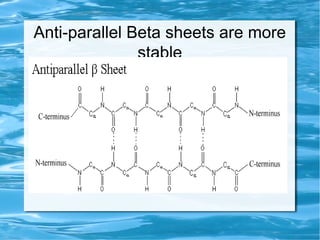
Antimicrobial peptides are polypeptide substances between 12-50 amino acids in length that have antimicrobial properties. They are classified based on their secondary structure as either beta-sheets, alpha-helices, extended coils or loop structures. They are found in many organisms and body locations where they participate in the innate immune system and have multifunctional roles beyond direct antimicrobial activity, including immunomodulation and cell migration. Their mechanisms of action generally involve interactions with and disruption of microbial membranes through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions.



















































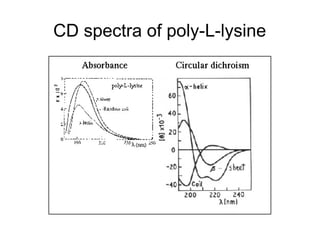
![CD spectra of the F17-6K peptide in an aqueous buffer (Aq) containing 20 mM Tris-HCl and 20
mM NaCl, pH 7.4, and in the same buffer with the addition of 20 mM SDS. The spectrum of all-d
F17-6K in SDS is presented for comparison. [θ], ellipticity (measured in degrees × square
centimeter per decimole).
Stark M et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3585-
3590](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antimicrobialpeptides-180727064035/85/Antimicrobial-peptides-64-320.jpg)