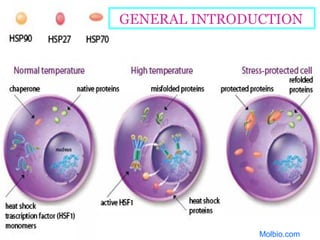
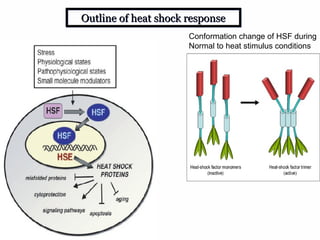
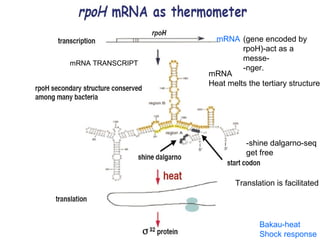
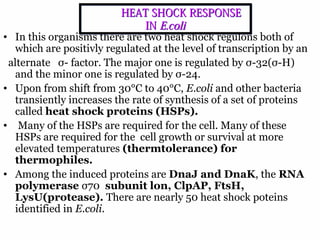
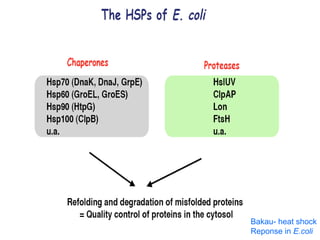
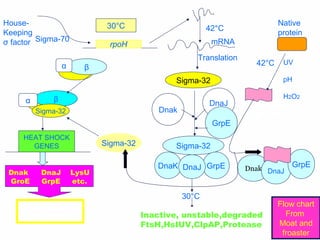
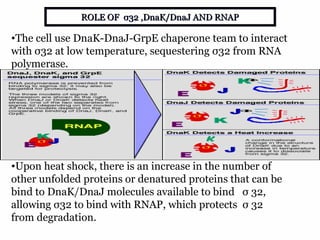
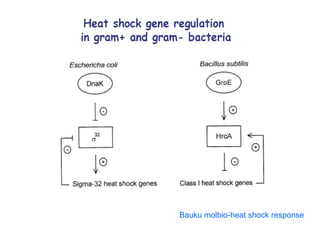
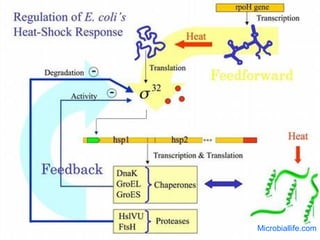
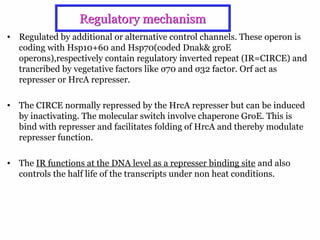
The document discusses the heat shock response in bacterial cells, focusing on E. coli's mechanisms to cope with various stressors such as temperature, nutrient deprivation, and toxic compounds. It outlines the regulatory principles of the heat shock response, emphasizing the role of the sigma factor σ32 and heat shock proteins (HSPs) in enhancing cellular survival under stress conditions. Additionally, it details the adaptive mechanisms that bacteria employ to manage stress effectively, including transcriptional and translational regulation of heat shock genes.