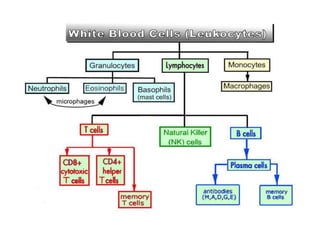
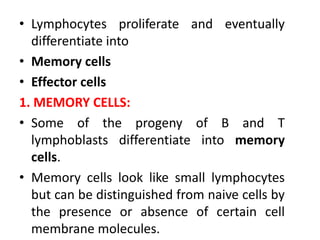
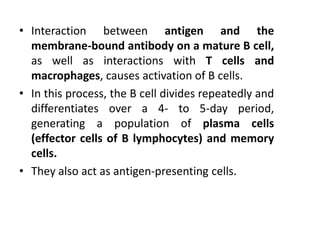
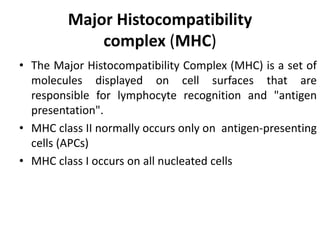
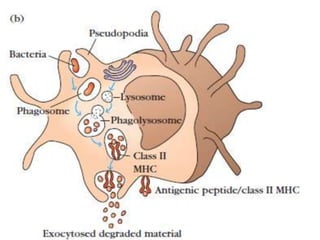
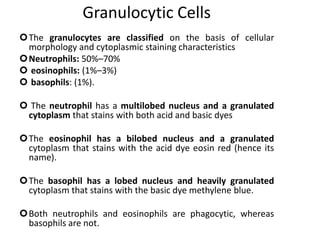
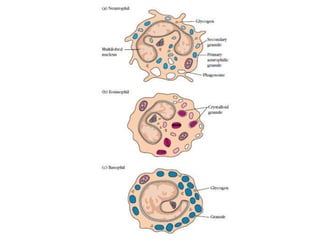
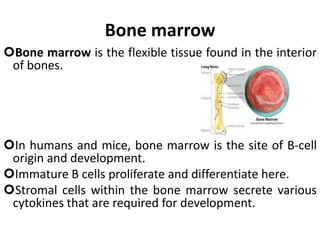
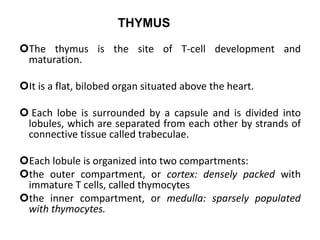
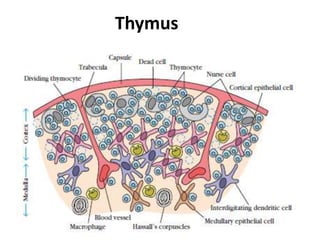
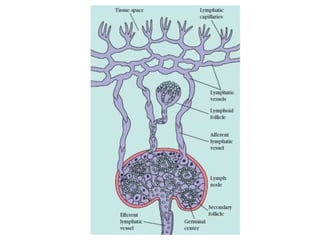
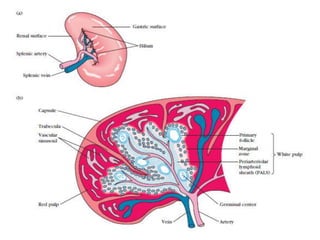
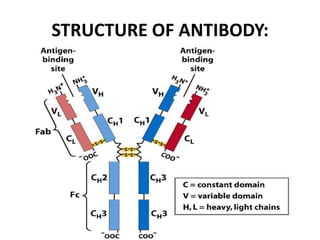
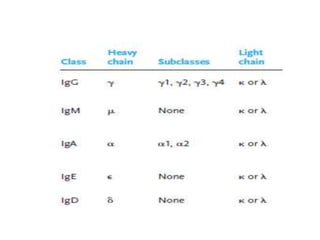
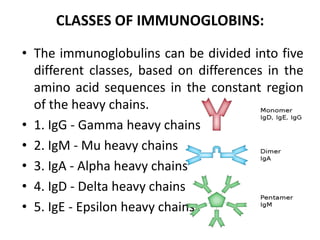
The immune system has two main branches - innate immunity which provides broad and immediate protection against pathogens, and adaptive immunity which provides pathogen-specific protection through immune cells and antibodies. The adaptive immune system includes B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that identify and destroy infected cells. Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by B cells that recognize pathogens by binding to them, marking them for destruction. They have a variable region that binds antigens and a constant region that activates immune responses. The classes of antibodies include IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD and IgE which have different structures and functions.