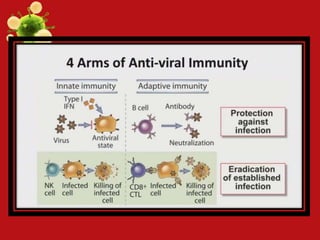
The document discusses the immune system's mechanisms for fighting different types of microbes:
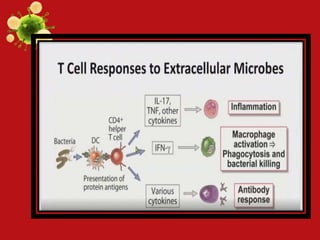
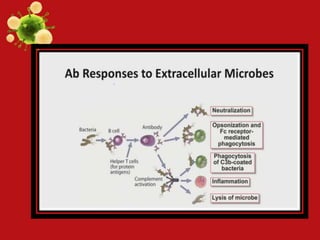
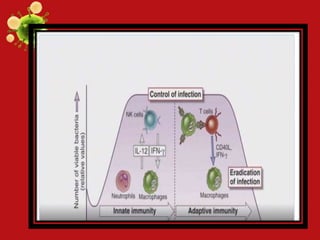
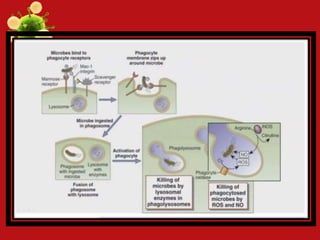
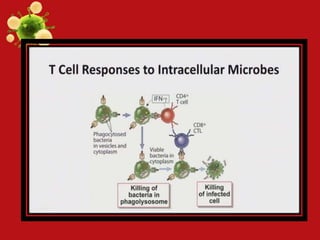
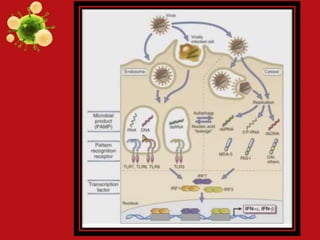
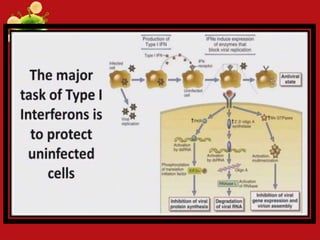
- Innate and adaptive immunity work together to fight extracellular bacteria through complement activation, phagocytosis, inflammation, antibodies, and CD4+ T cell activation. Intracellular bacteria are targeted through phagocyte, NK cell, and CD4+/CD8+ T cell activation. Viruses are combated via complement, NK cells, type 1 interferons, antibodies, and CD8+ T cells.
- The immune system responds specially to different microbes, though microbes can evade responses. Persistent infections occur when the immune system controls but does not eliminate microbes.
- Recent research includes culturing SARS-CoV-2,