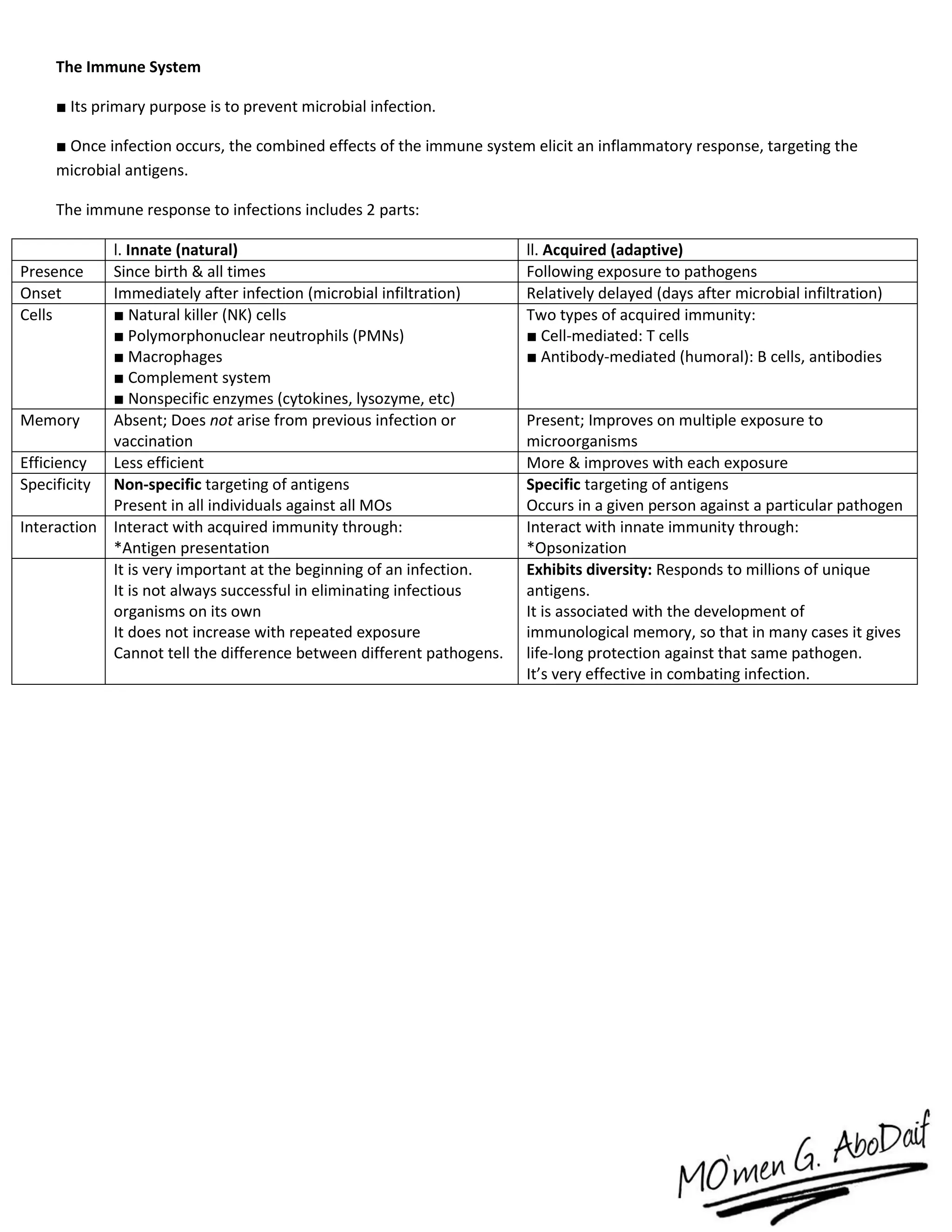
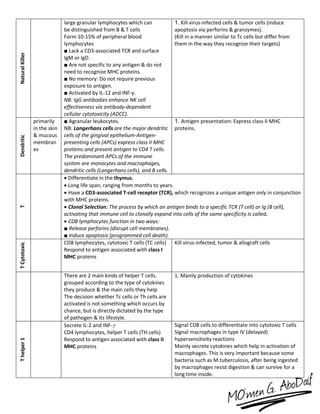
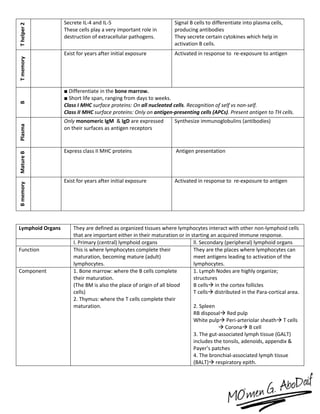
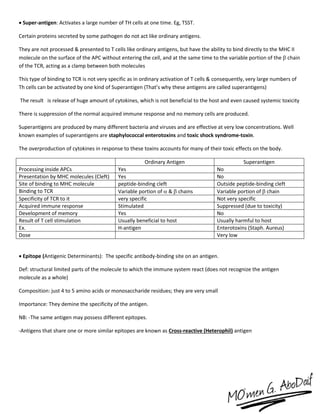
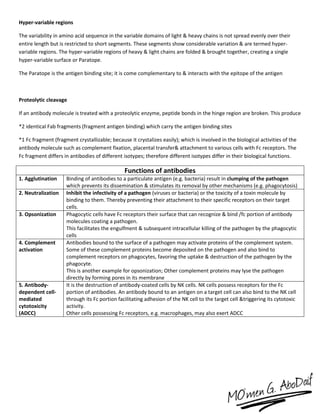
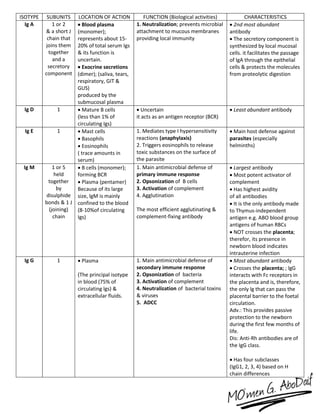
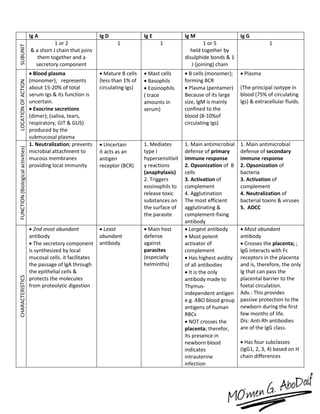
The immune system has both innate and acquired responses. The innate response is non-specific and provides immediate protection against infection. The acquired response is antigen-specific and develops over time through exposure to pathogens. It provides long-lasting immunity through immunological memory. The two main cell types of the acquired response are B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies while T cells help activate other immune cells. Together they provide a highly targeted defense against pathogens.