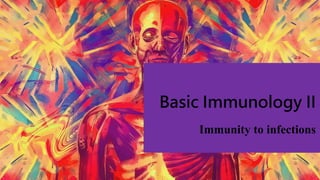
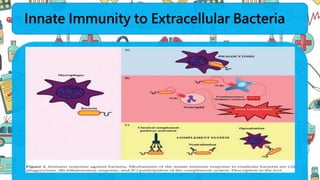
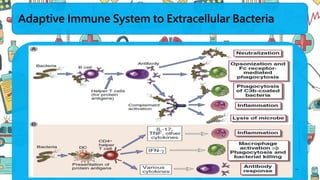
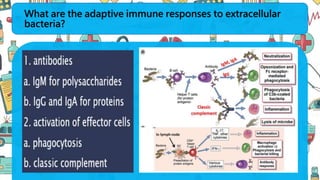
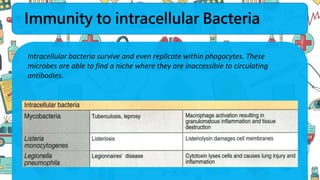
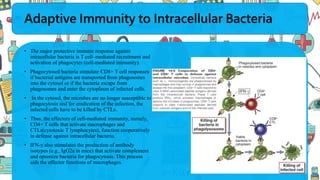
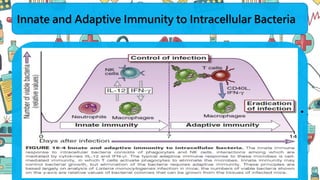
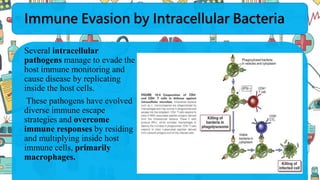
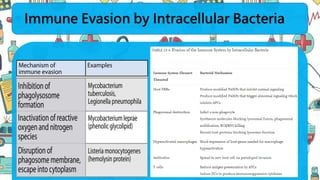
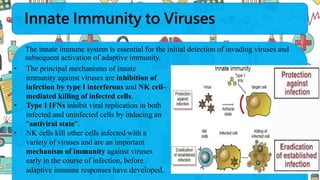
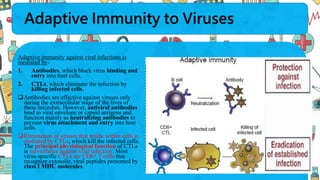
The immune system responds to different microbes through innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity uses mechanisms like phagocytosis, inflammation, and complement activation to respond quickly. Adaptive immunity produces antibodies and T cells for long-lasting protection. Extracellular bacteria are targeted by antibodies, phagocytes, and the complement system. Intracellular bacteria are responded to by NK cells, phagocytes, and CD8 T cells that activate macrophages. Viruses induce type I interferons and are targeted by antibodies and cytotoxic T lymphocytes that kill infected cells. Microbes have evolved ways to evade these immune responses like altering antigens, inhibiting antigen presentation, or infecting immune cells.