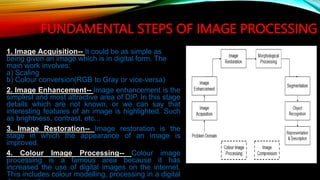
The document defines an image as a two-dimensional function and introduces digital image processing, which manipulates digital images using software. It outlines fundamental steps of image processing, including image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, and segmentation, among others. Furthermore, it emphasizes the complexity of object recognition and the importance of a knowledge base in managing high-resolution image databases.