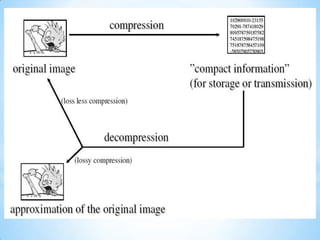
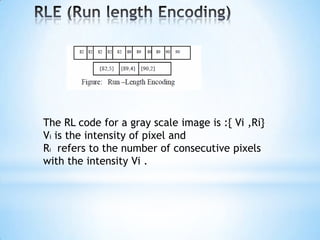
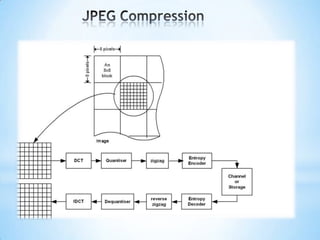
This document discusses image compression techniques. It explains that the goal of compression is to reduce the amount of data needed to represent a digital image by eliminating redundant information like coding, interpixel, and psychovisual redundancies. Compression can be lossy or lossless. Lossy methods allow for data loss but provide higher compression, while lossless preserves all image data. Common lossy techniques include JPEG, which uses discrete cosine transform and quantization, and lossless methods include run length and Huffman encoding.