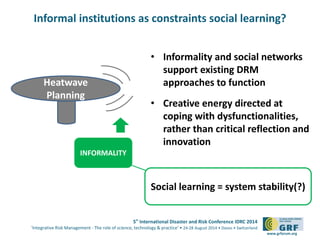
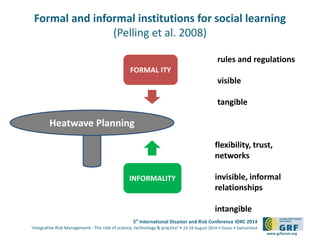
The document discusses the challenges of social learning in heatwave risk management by local authorities in London, highlighting both formal and informal institutional constraints. It emphasizes the role of informal networks in supporting disaster risk management (DRM) while questioning the assumption that learning necessarily leads to systemic change. The findings suggest that informal relationships can enhance coping mechanisms but may limit critical reflection and innovation in resilience planning.

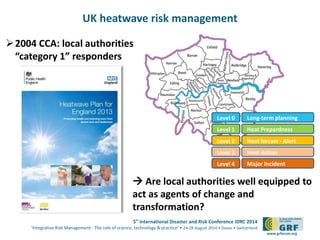

![Informal networks support formal DRM
5th International Disaster and Risk Conference IDRC 2014
‘Integrative Risk Management - The role of science, technology & practice‘ • 24-28 August 2014 • Davos • Switzerland
www.grforum.org
DYSFUNCTIONAL
COMMUNICATION
„ […] to talk to the GP
practices to sort out what
was happening there […]
we had to go through the
NHS England […]. But to get
a hold of these people […] is
actually really difficult,
especially during the level 3
alert.” (London CCG)
INFORMAL
RELATIONSHIPS
„We ended up circumventing
the official pathway […] We
went directly to the GP
practices to talk to them. […]
Our big luck was that those
people in the NHS England
[…] have worked [with us]
before, and we were able to
draw on these informal
relationships.” (London CCG)
Heatwave Planning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/idrcpresentationtabeling77-140826130134-phpapp01/85/IDRC_Presentation_T-Abeling-5-320.jpg)