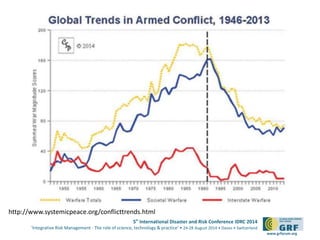
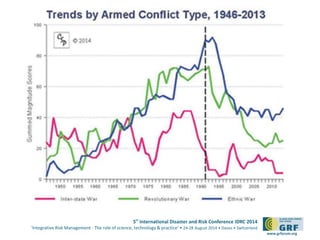
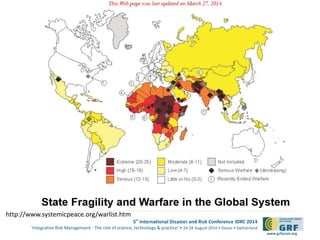
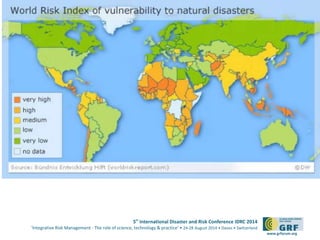
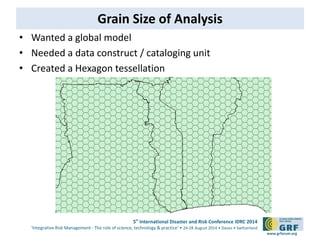
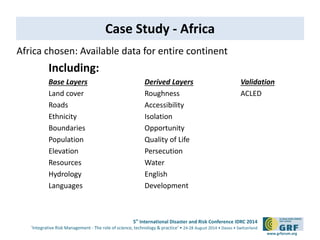
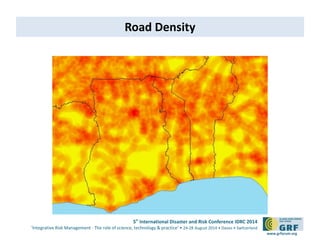
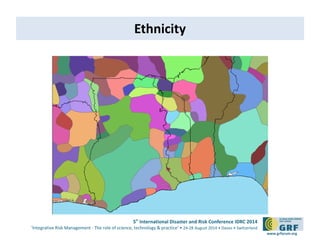
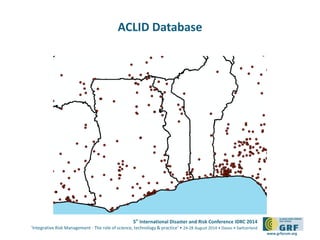
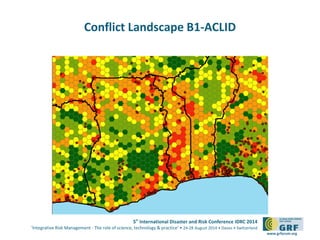
The document discusses the development of a continental conflict landscape in relation to disaster and risk management at the 5th International Disaster and Risk Conference in 2014. It emphasizes the natural occurrence of conflict in human relationships, driven by unmet needs and social differences, and highlights the importance of geospatial tools for understanding and mitigating conflict. Furthermore, it identifies gaps in disaster risk reduction and advocates for the integration of socio-cultural analysis and geospatial modeling in training, policy, and implementation strategies post-2015.