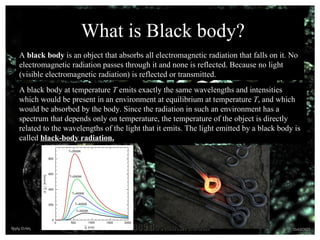
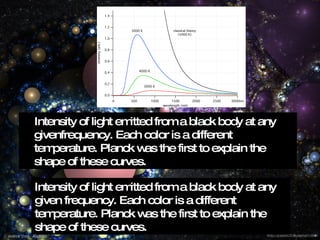
Max Planck, born on April 23, 1858, in Kiel, Germany, was a physicist known for his contributions to thermodynamics and quantum theory, particularly his derivation of Planck's constant and law of black-body radiation. He demonstrated that energy is emitted in discrete values or quanta, leading to significant advancements in the understanding of light and heat. Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918, Planck's work laid the foundation for future developments in quantum mechanics before his death in 1947.