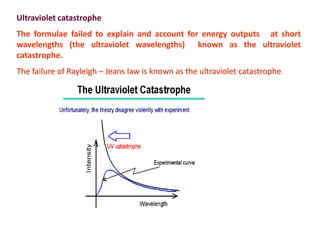
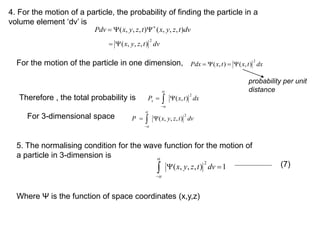
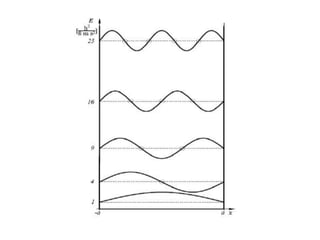
1) Max Planck proposed that the energy of electromagnetic radiation could only be emitted or absorbed in discrete quantized packets called quanta, with energy levels proportional to frequency. This resolved the ultraviolet catastrophe and led to the development of quantum theory.
2) Einstein extended Planck's idea of quantization to explain the photoelectric effect, proposing that light itself consists of discrete particle-like packets of energy called photons, with energy equal to Planck's constant times frequency.
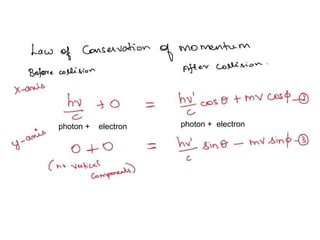
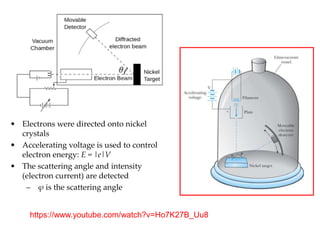
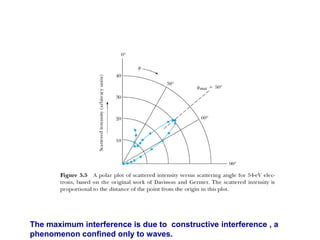
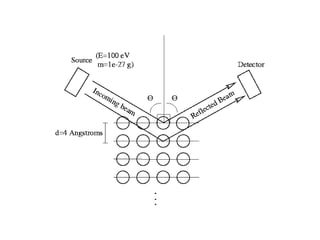
3) The Compton effect demonstrated that X-rays behave as particles when scattered by electrons, providing direct evidence that electromagnetic radiation has both wave and particle properties.