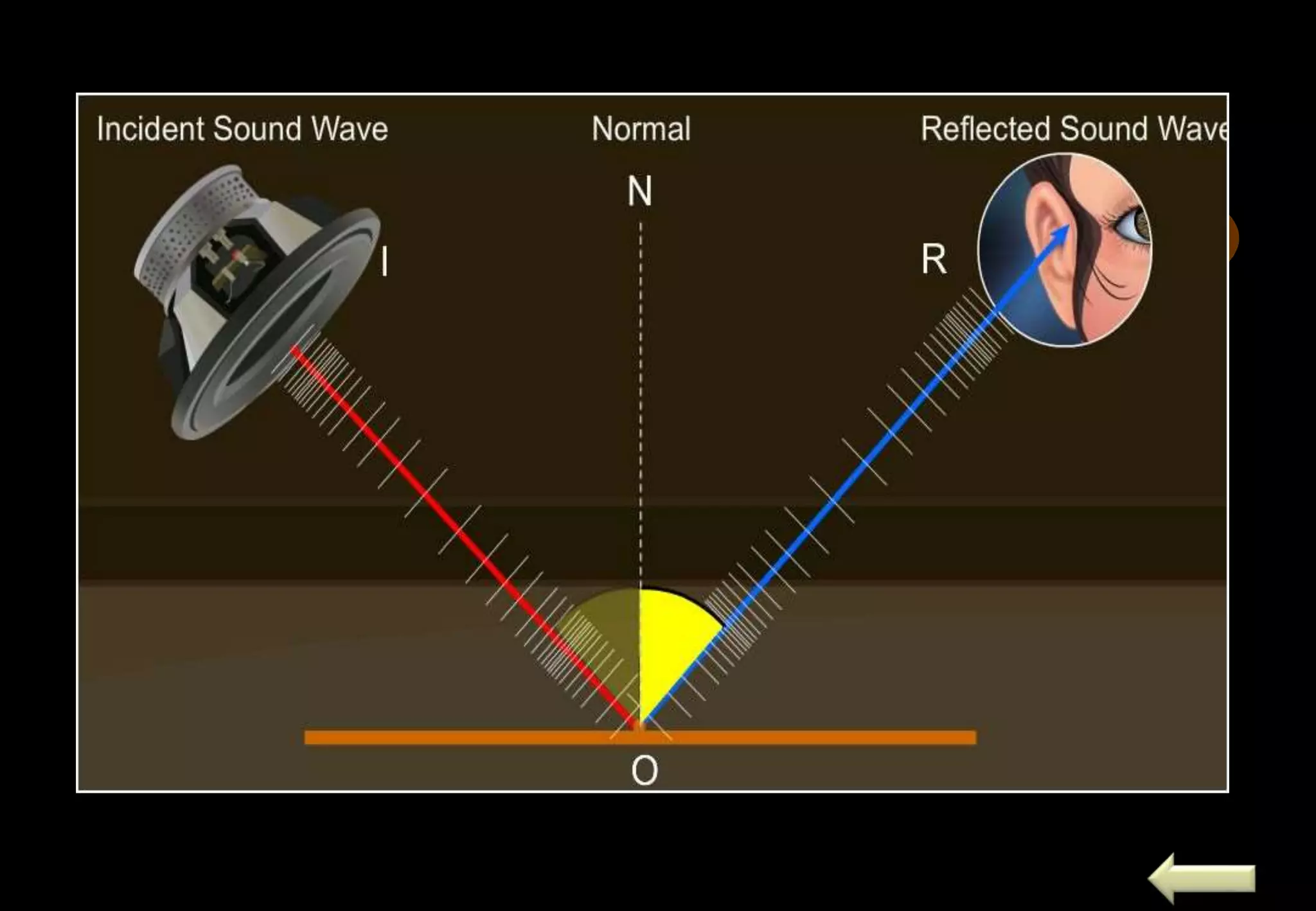
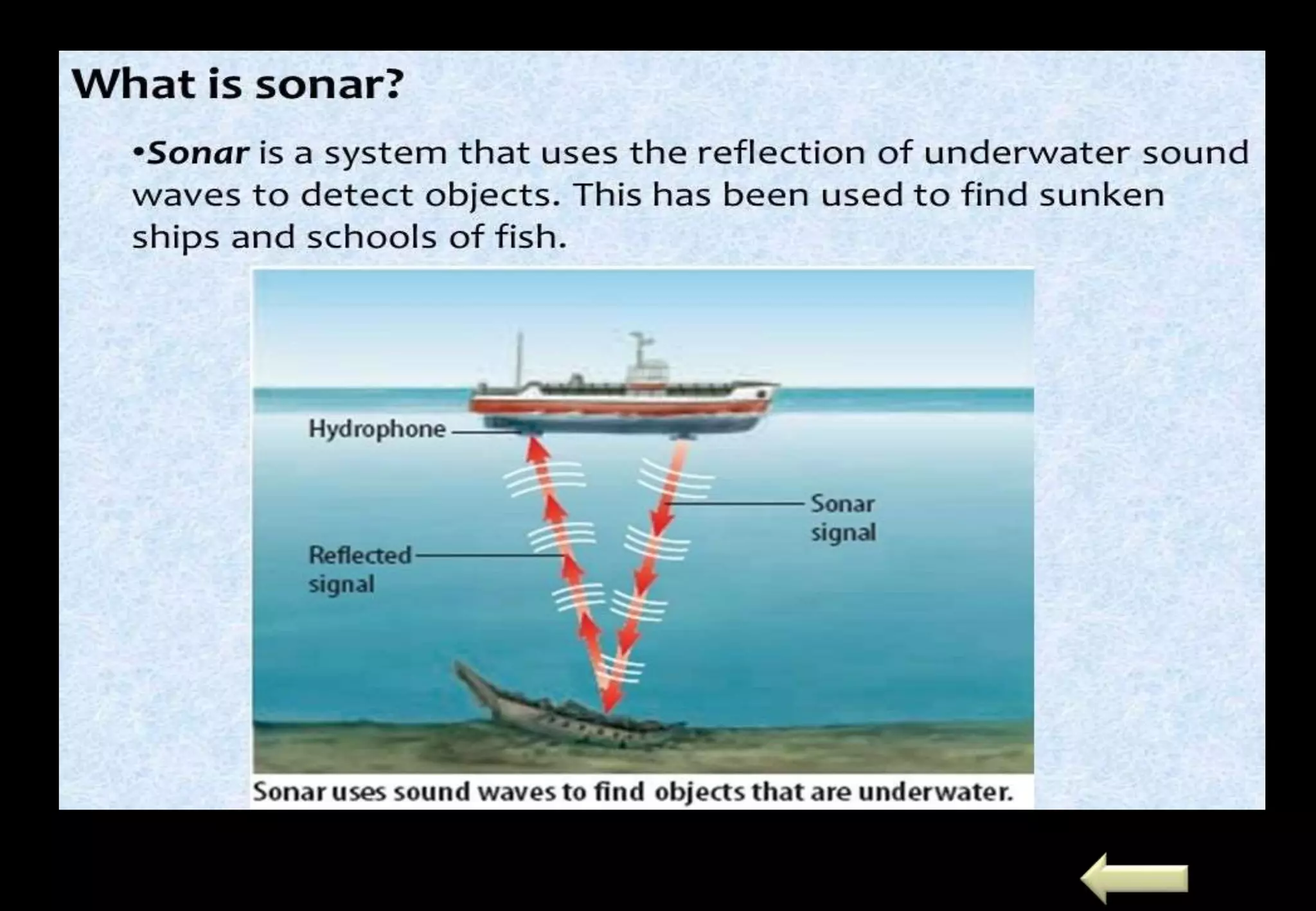
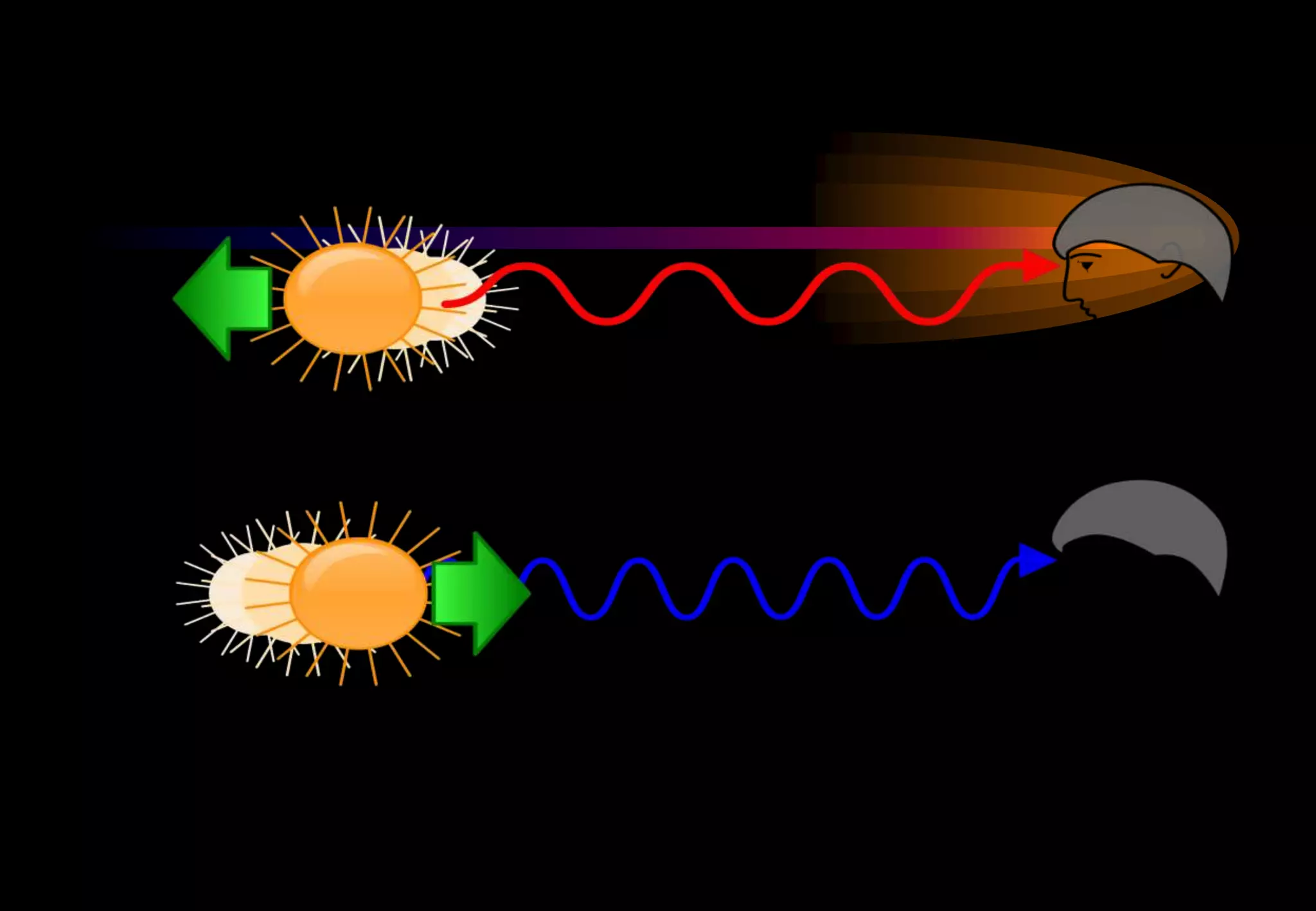
Sound is a form of energy that enables the sensation of hearing. It is produced by vibration and travels in the form of longitudinal waves, requiring a medium for propagation. Sound waves can be reflected, refracted, and their speed depends on the properties of the medium. Sound is classified into infrasonic, audible and ultrasonic ranges. Ultrasound has many medical and industrial applications such as sonar, ultrasound scanning, and Doppler effect. Doppler effect is an apparent change in frequency due to relative motion of source and observer. It is used in traffic control, satellite tracking and astrophysics.