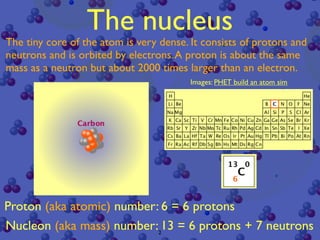
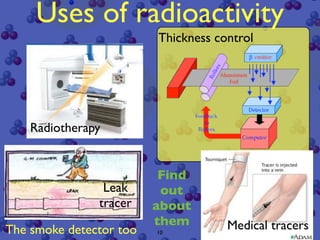
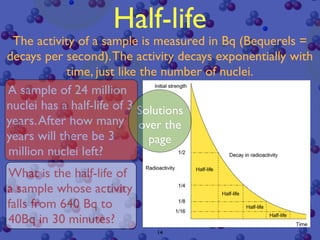
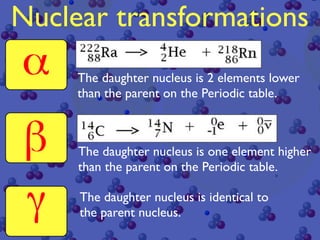
The document discusses the structure of atoms and radioactive decay. It describes the nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons orbited by electrons. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but different neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable and decay spontaneously by emitting an alpha or beta particle, changing the element. Radioactive materials can be detected by their ionizing radiation using devices like Geiger counters. Background radiation comes from natural and medical sources. Carbon-14 dating determines the age of once-living materials. Radioactivity has uses like thickness gauges but also health hazards that must be understood.