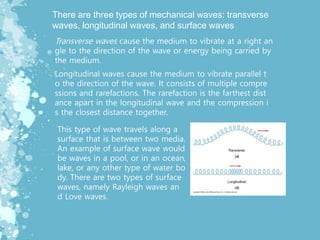
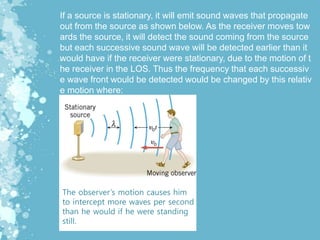
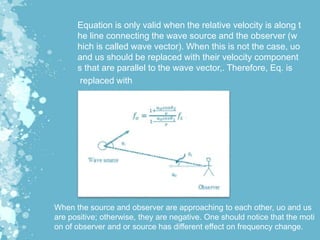
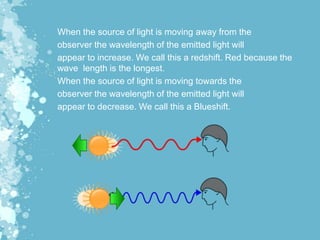
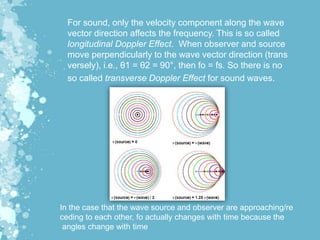
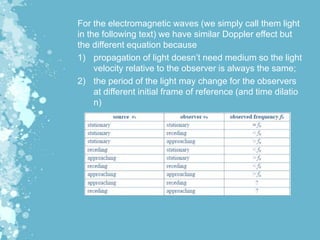
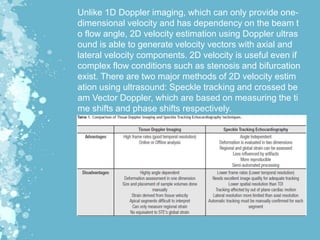
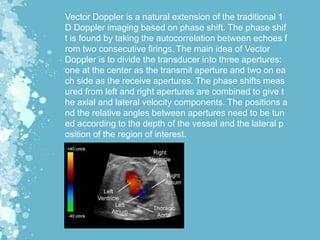
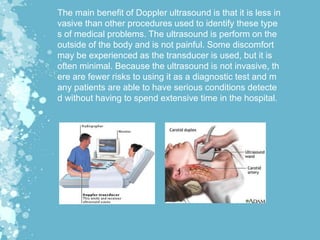
Mechanical waves transfer energy through a medium and include transverse, longitudinal, and surface waves. The Doppler effect describes how the frequency of a wave is changed relative to an observer based on their motion. Doppler echocardiography uses ultrasound to examine the heart and blood flow by detecting changes in frequency from reflected sound waves, allowing determination of flow speed and direction. It is a non-invasive procedure with benefits over more invasive testing for diagnosing cardiovascular conditions.