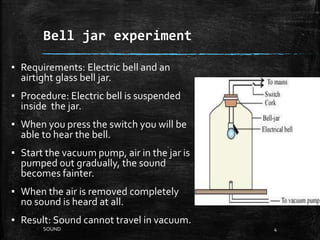
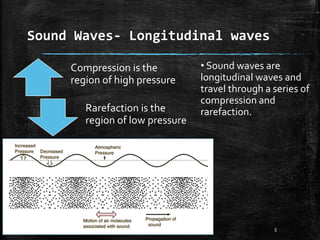
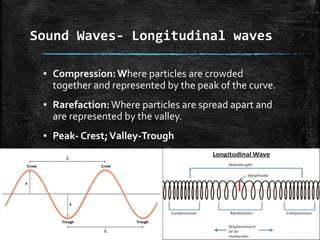
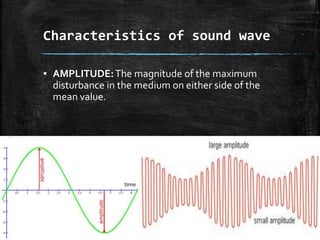
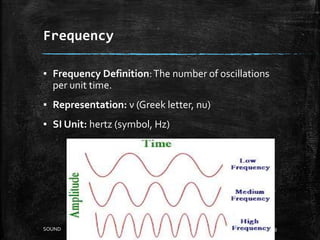
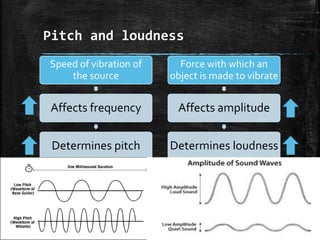
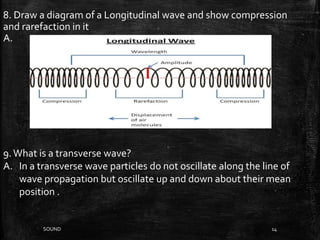
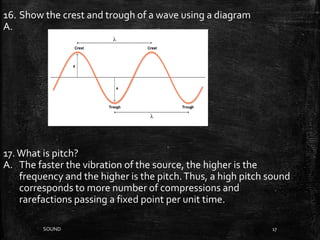
Sound is a form of energy that produces hearing in our ears. It is produced by vibration and travels as a longitudinal wave through compression and rarefaction regions in a medium. The Bell jar experiment showed that sound cannot travel through a vacuum. Sound waves are characterized by their amplitude, wavelength, frequency and speed. Pitch is determined by frequency of vibration and loudness by amplitude.