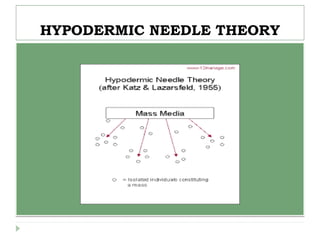
The document discusses the hypodermic needle theory, which posits that media messages influence audiences in a direct and immediate manner, likened to a bullet impacting the viewer's mind. It highlights various effects of mass media on children's behavior and societal attitudes, emphasizing criticisms of the theory's linear model and its assumption of a passive audience. Historical examples and theoretical frameworks related to media effects are presented, documenting how media has been used to reinforce existing ideologies.