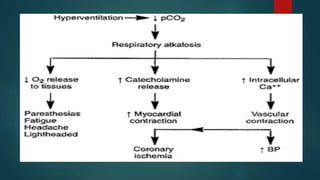
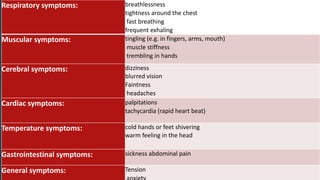
Hyperventilation syndrome (HVS) occurs when someone breathes more quickly and shallowly than their body needs, causing a rapid reduction in carbon dioxide levels and other physiological changes. There are two main types - acute HVS causes symptoms like suffocation, anxiety, chest pain and tingling, while chronic HVS is associated with frequent deep exhaling and nonspecific somatic symptoms. Diagnosis involves testing to rule out other potential causes, and treatment focuses on relaxation techniques, stress reduction, and sometimes medication to manage anxiety.
![Hyperventilation
Syndrome
DR. SHAHBAZ AHMAD PT
DPT [UIPT][UOL]
MS-MSK-PT [UIPT][UOL]
LECTURER [LIHS][LCPS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperventilationsyndrome-191130182347/85/Hyperventilation-syndrome-1-320.jpg)