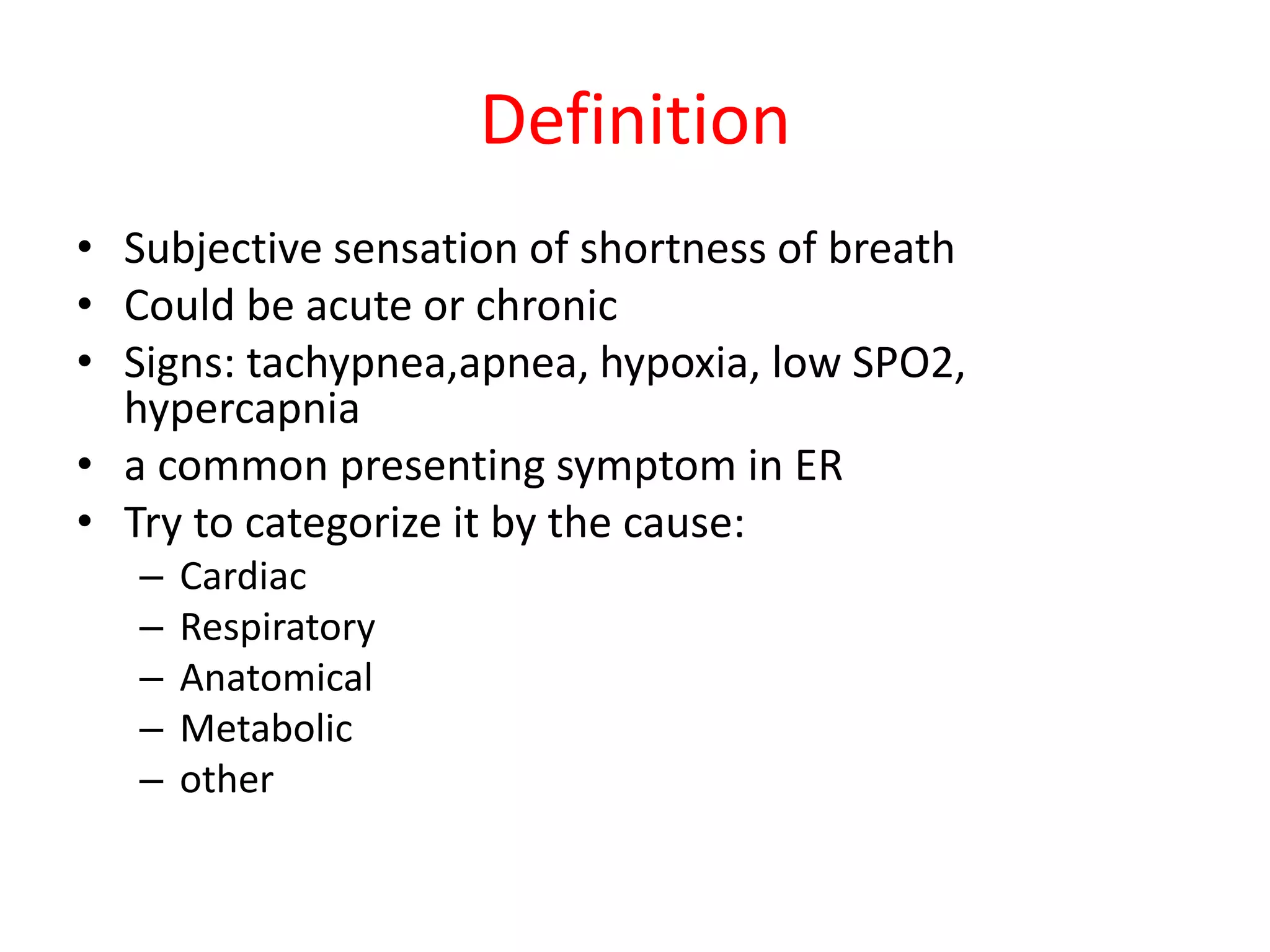
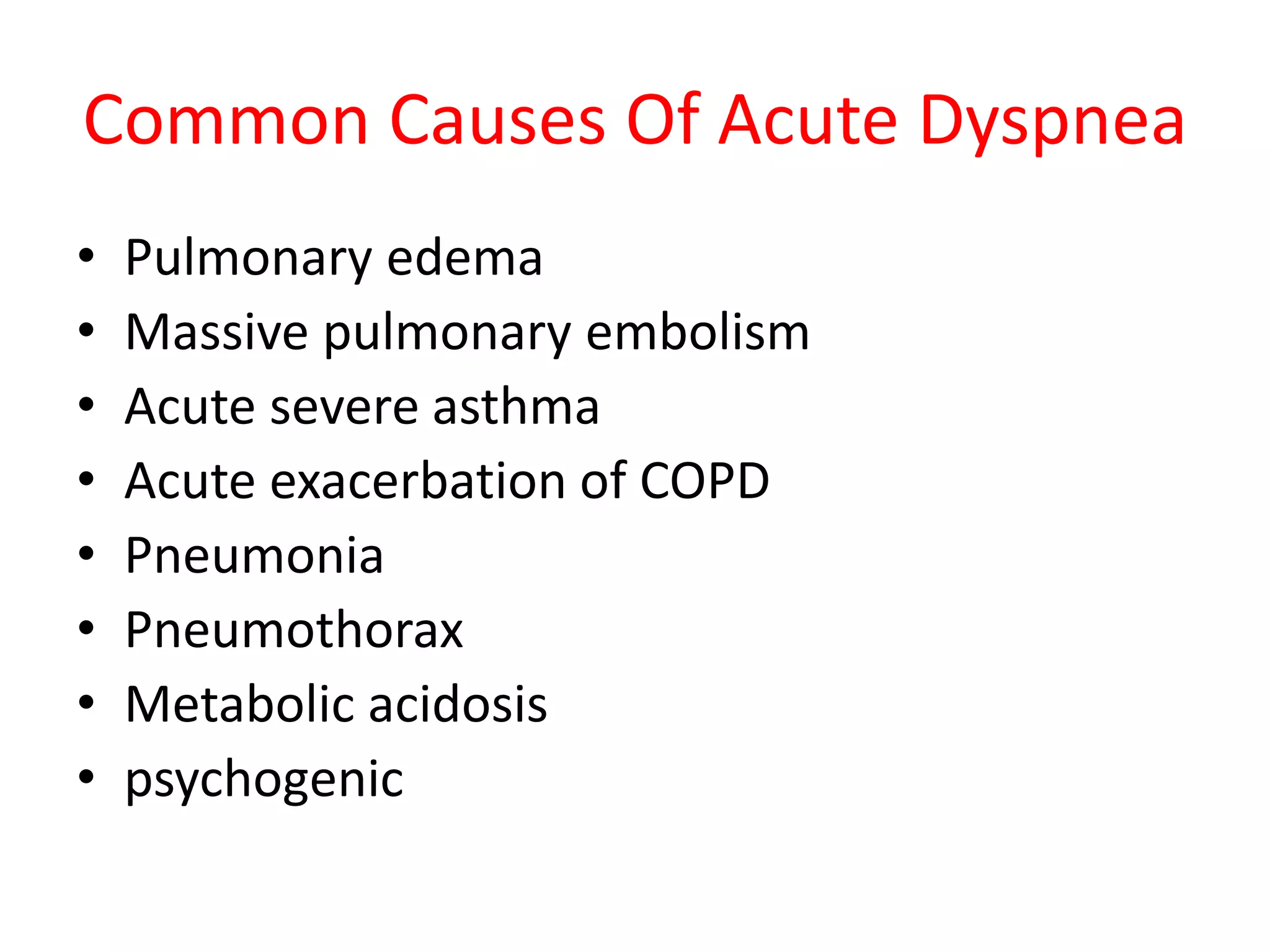
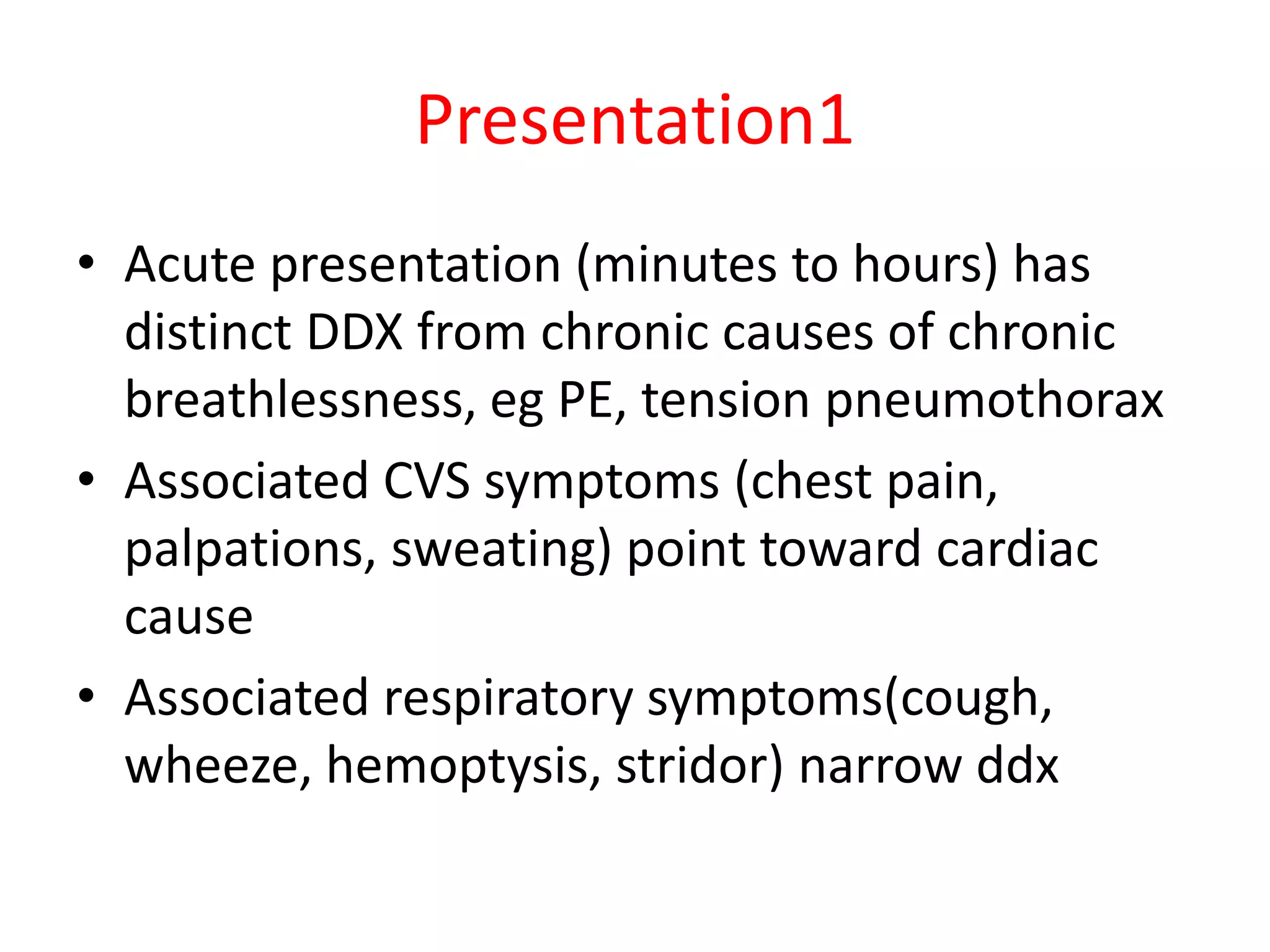
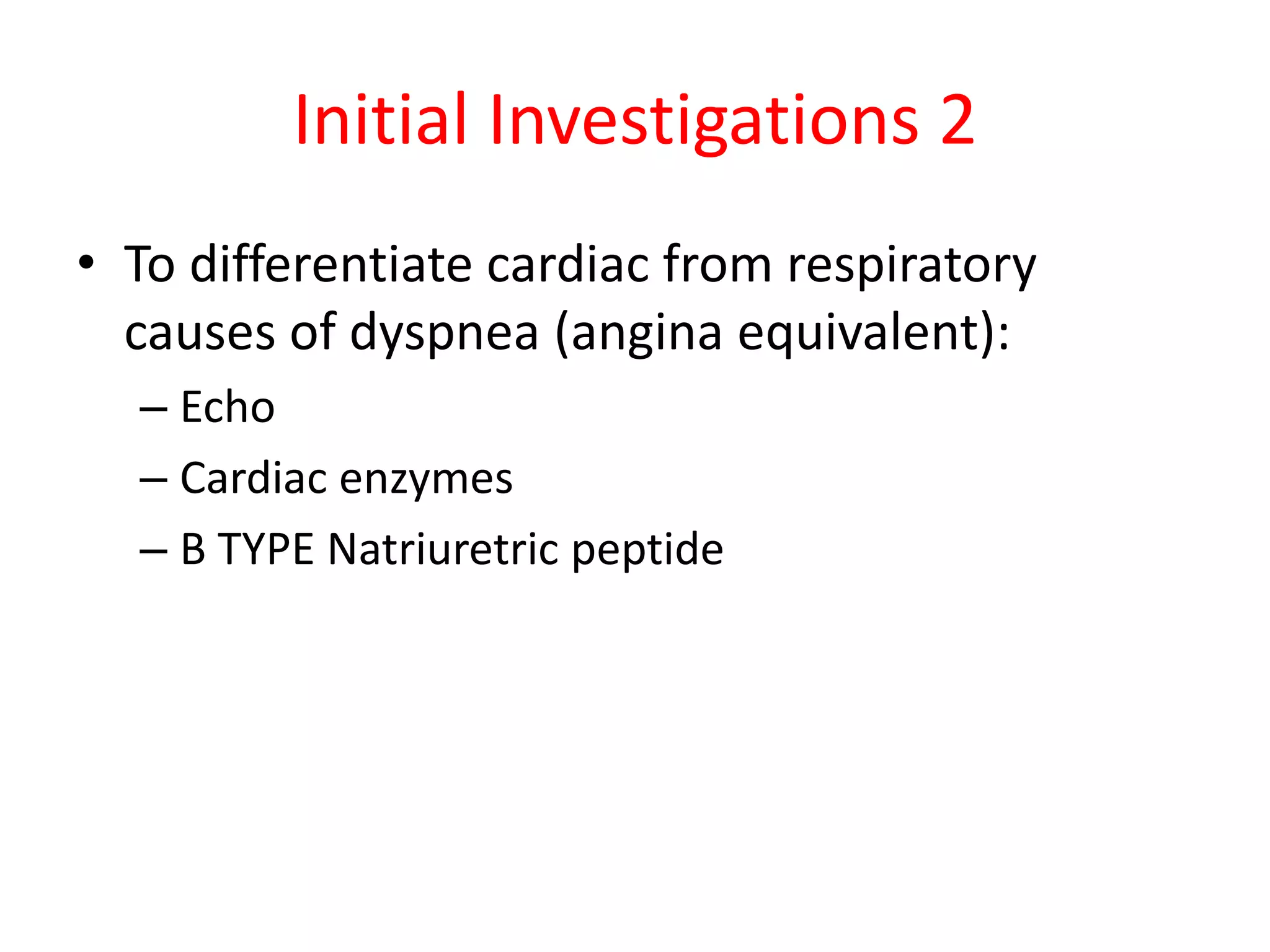
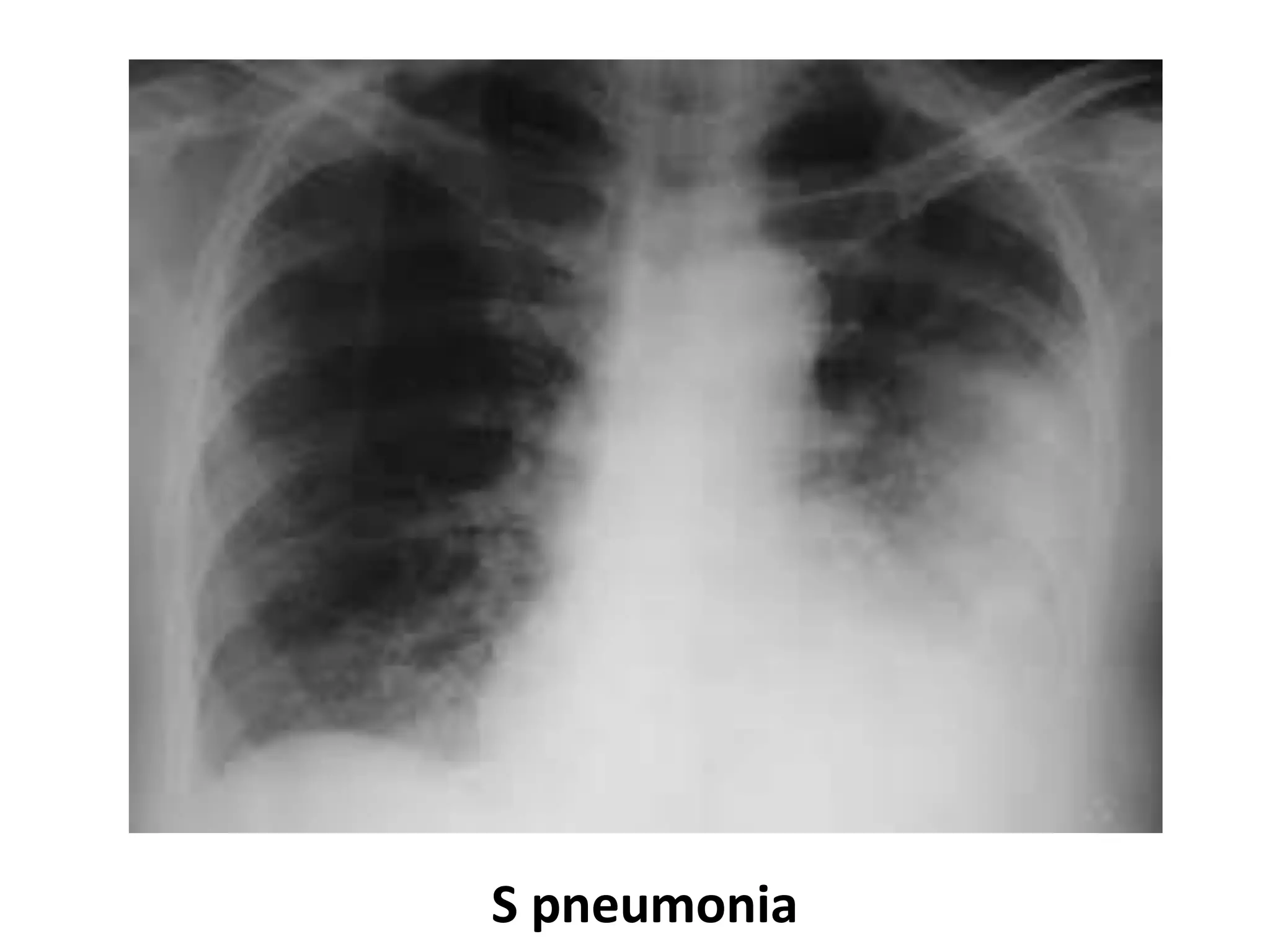
This document discusses the approach to a patient presenting with acute dyspnea. It defines dyspnea and lists common causes such as pulmonary edema, PE, asthma, and COPD. The assessment involves vital signs, breath sounds, oxygenation status, and cardiovascular examination. Initial investigations may include CXR, ECG, ABG, and PFTs. The case involves a 25-year-old man with sudden dyspnea during exercise. Exam finds deviated trachea and hyperresonant chest. The diagnosis is tension pneumothorax due to Marfan syndrome. The next step is chest drain placement.