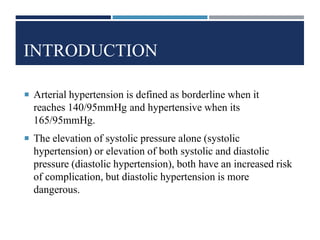
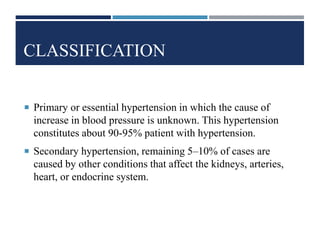
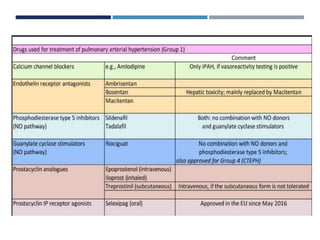
This document discusses arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). It defines borderline and hypertensive blood pressure thresholds and notes that elevated diastolic pressure is more dangerous than just systolic. The majority of hypertension cases are primary (essential) where the cause is unknown, while secondary cases are caused by underlying conditions. Risk factors include family history, being overweight, and certain drugs or medical conditions. Long-term complications can include heart enlargement, blood clots, arrhythmias, bleeding in the lungs, and pregnancy risks. The diagnosis involves blood tests, EKGs, breathing tests, echocardiograms and potentially right heart catheterization. Treatments include medications that open blood vessels, stimulate nitric oxide, inhibit ACE,