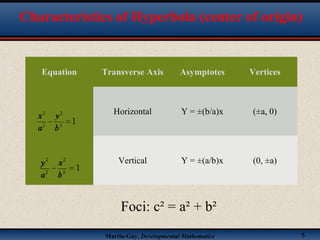
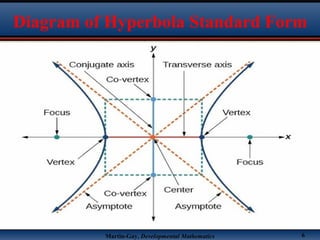
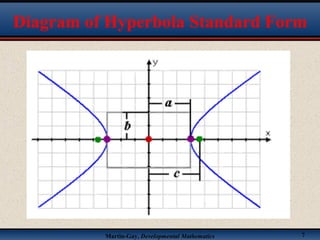
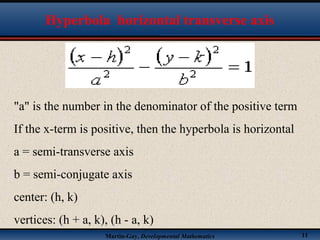
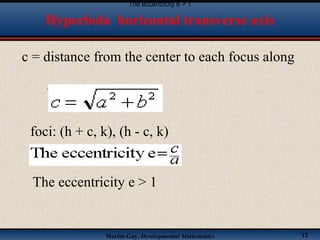
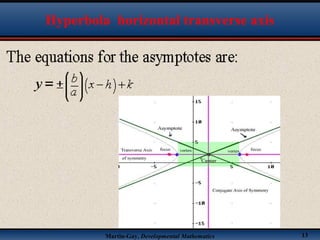
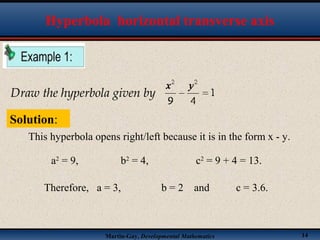
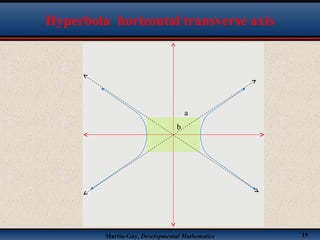
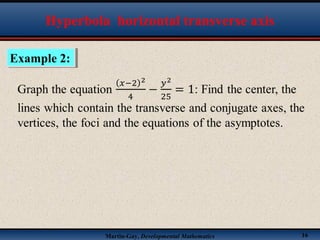
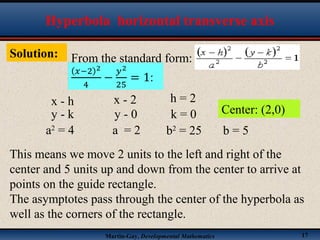
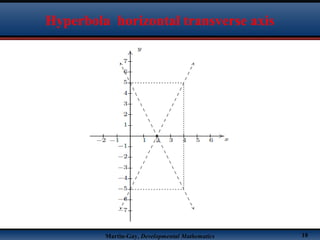
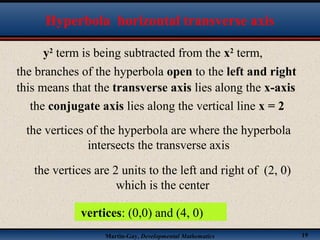
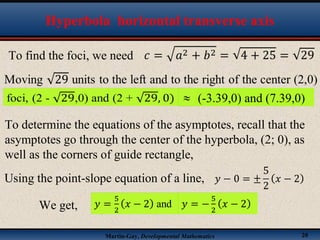
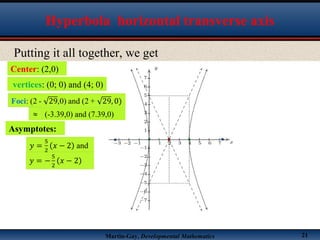
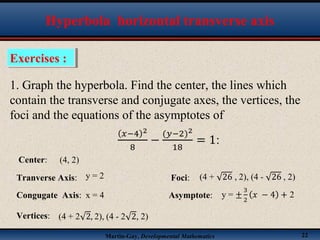
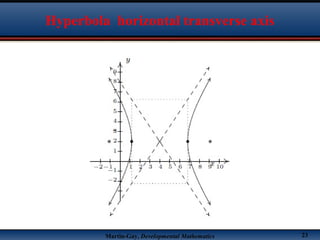
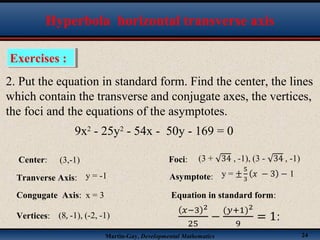
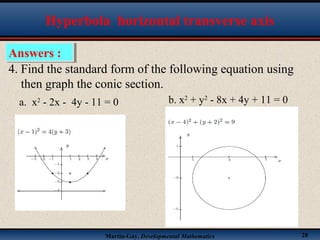
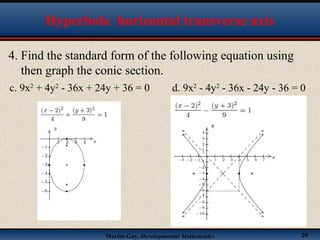
This document discusses hyperbolas. It defines a hyperbola as the set of points where the difference between the distance to two fixed points (the foci) is constant. A hyperbola has two branches and two asymptotes. The asymptotes contain the diagonals of a rectangle centered at the hyperbola's center. The document provides characteristics and equations for translating and graphing horizontal transverse axis hyperbolas. It includes examples of graphing hyperbolas from their standard form equations. Exercises at the end ask the reader to find standard forms and graph hyperbolas given certain properties.