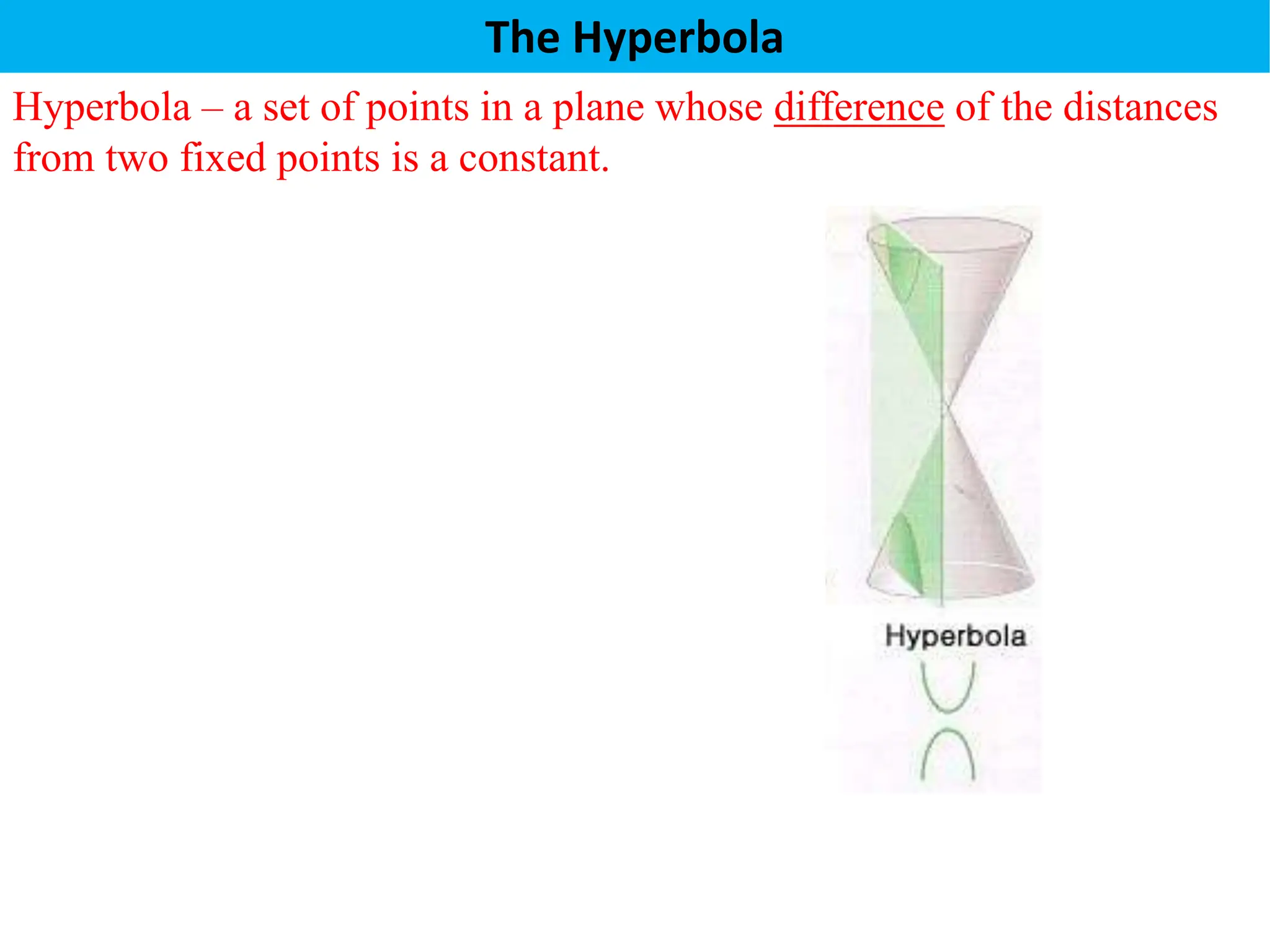
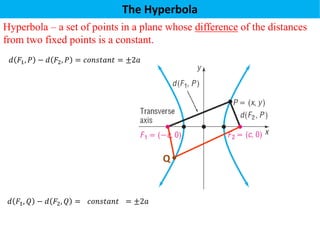
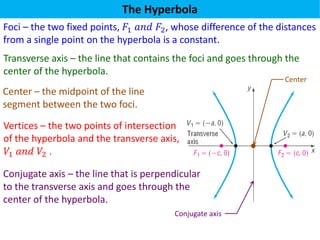
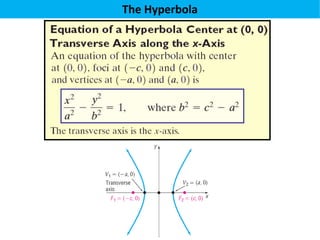
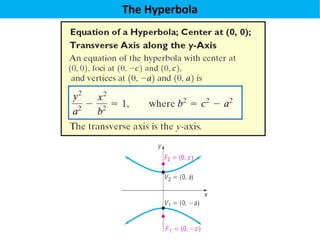
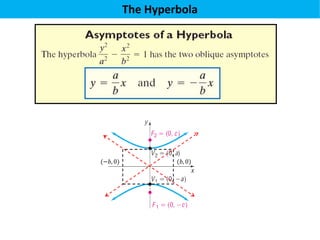
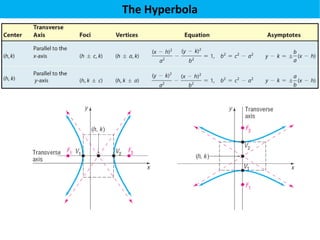
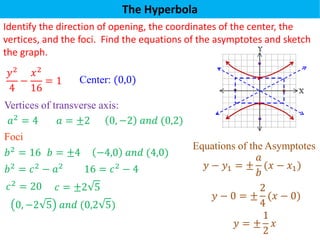
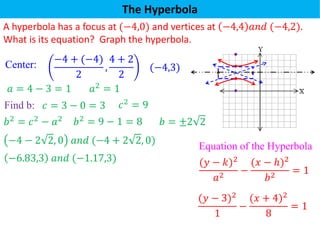
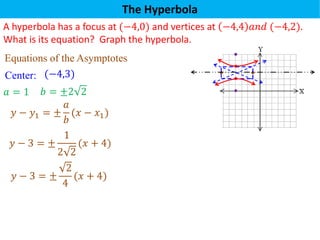
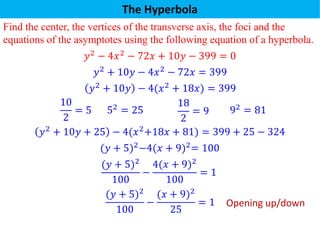
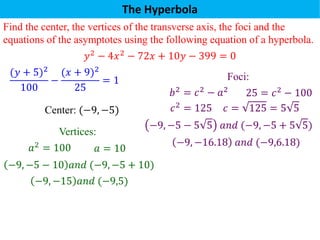
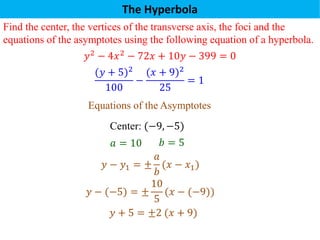
The document defines a hyperbola as a set of points where the difference between the distances from two fixed points (foci) is a constant. It provides details on key hyperbola elements including the transverse and conjugate axes, vertices, center, and foci. Examples are given demonstrating how to identify these elements from the equation of a hyperbola and sketch the graph. The last example solves for the center, vertices, foci and asymptote equations of a hyperbola given its equation.