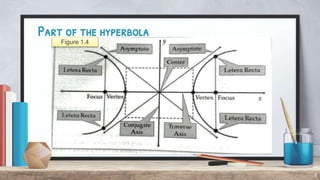
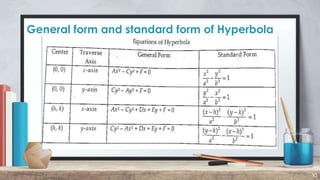
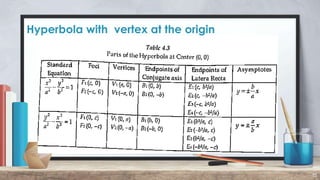
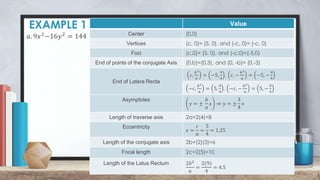
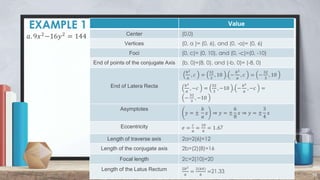
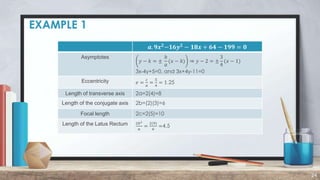
The document defines and provides examples of converting general hyperbola equations to standard form. A hyperbola is defined as the set of all points where the difference between the distances from two fixed points (foci) is a constant. Examples show converting equations to standard form by completing the square and identifying the center, vertices, foci, and axes. Standard form is x^2/a^2 - y^2/b^2 = 1, where a and b are the distances to the vertices and conjugate axis endpoints from the center.