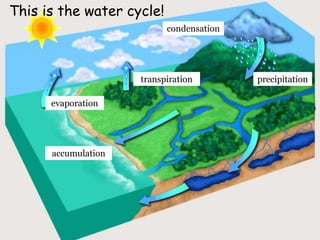
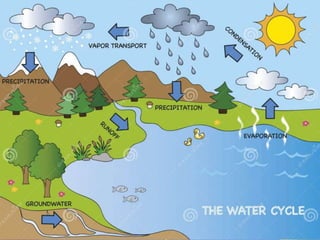
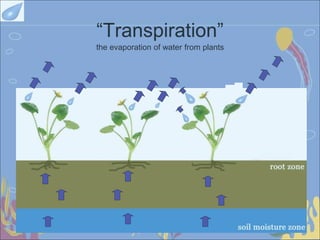
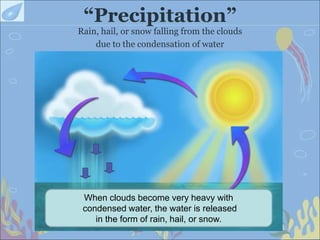
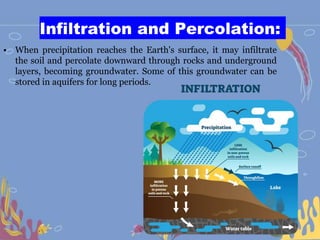
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface through evaporation, transpiration, condensation and precipitation. It involves the conversion of water between liquid, solid and gas as it circulates through the atmosphere, oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater and land. The water cycle is crucial for maintaining the climate and providing freshwater for ecosystems to sustain life on Earth. It consists of several key processes including transpiration, evaporation, condensation, precipitation, accumulation, infiltration and percolation, and surface runoff.