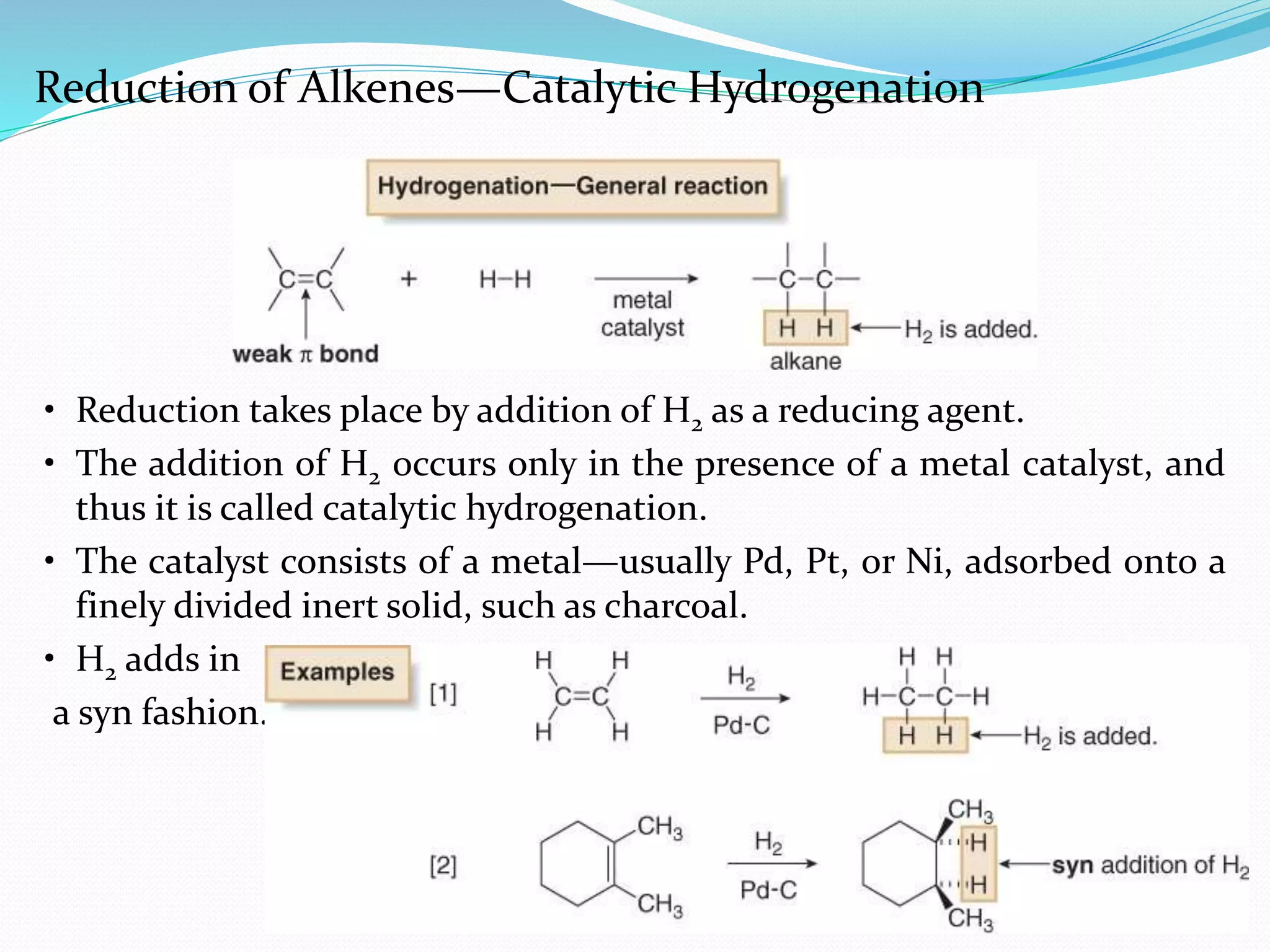
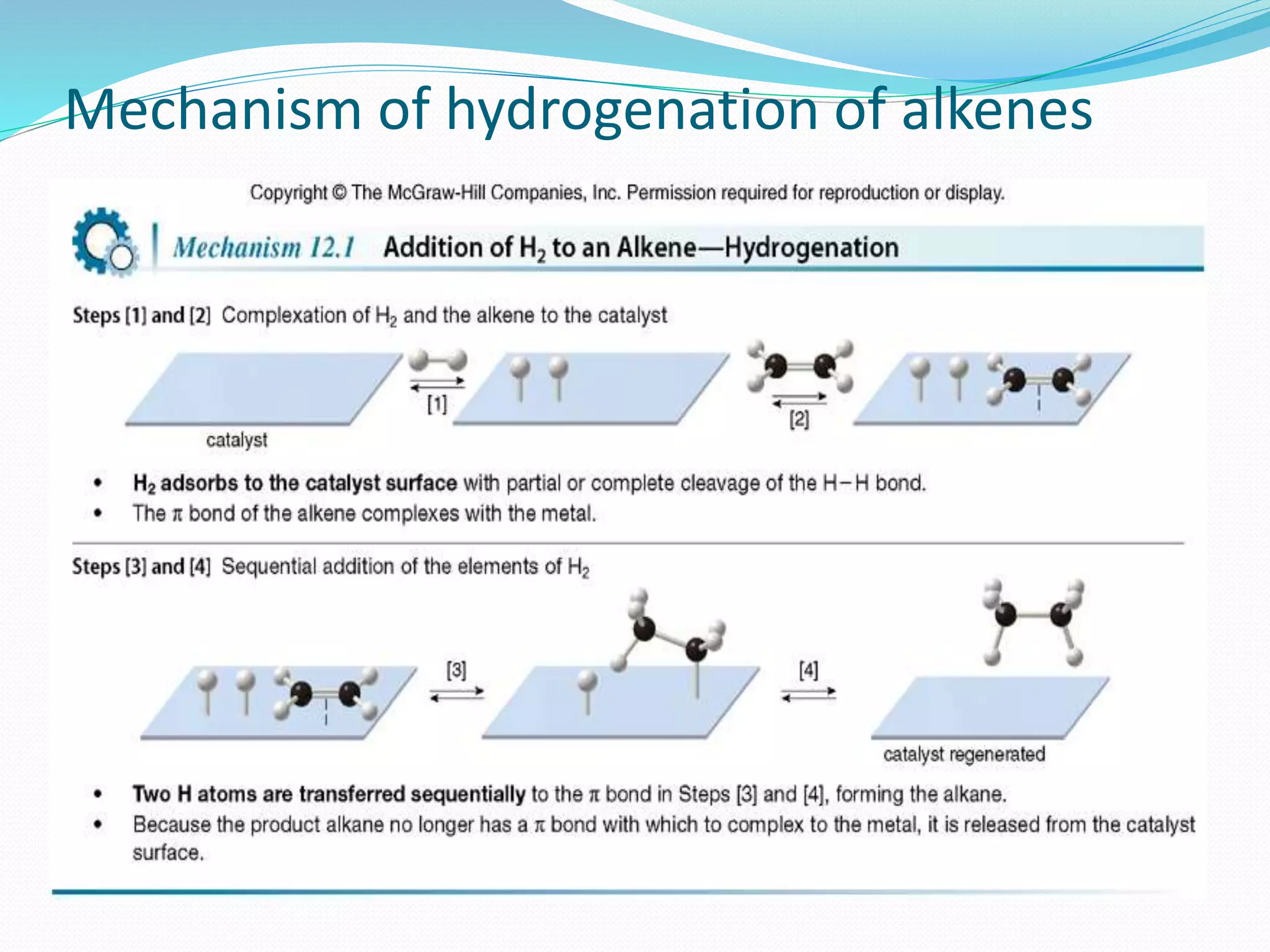
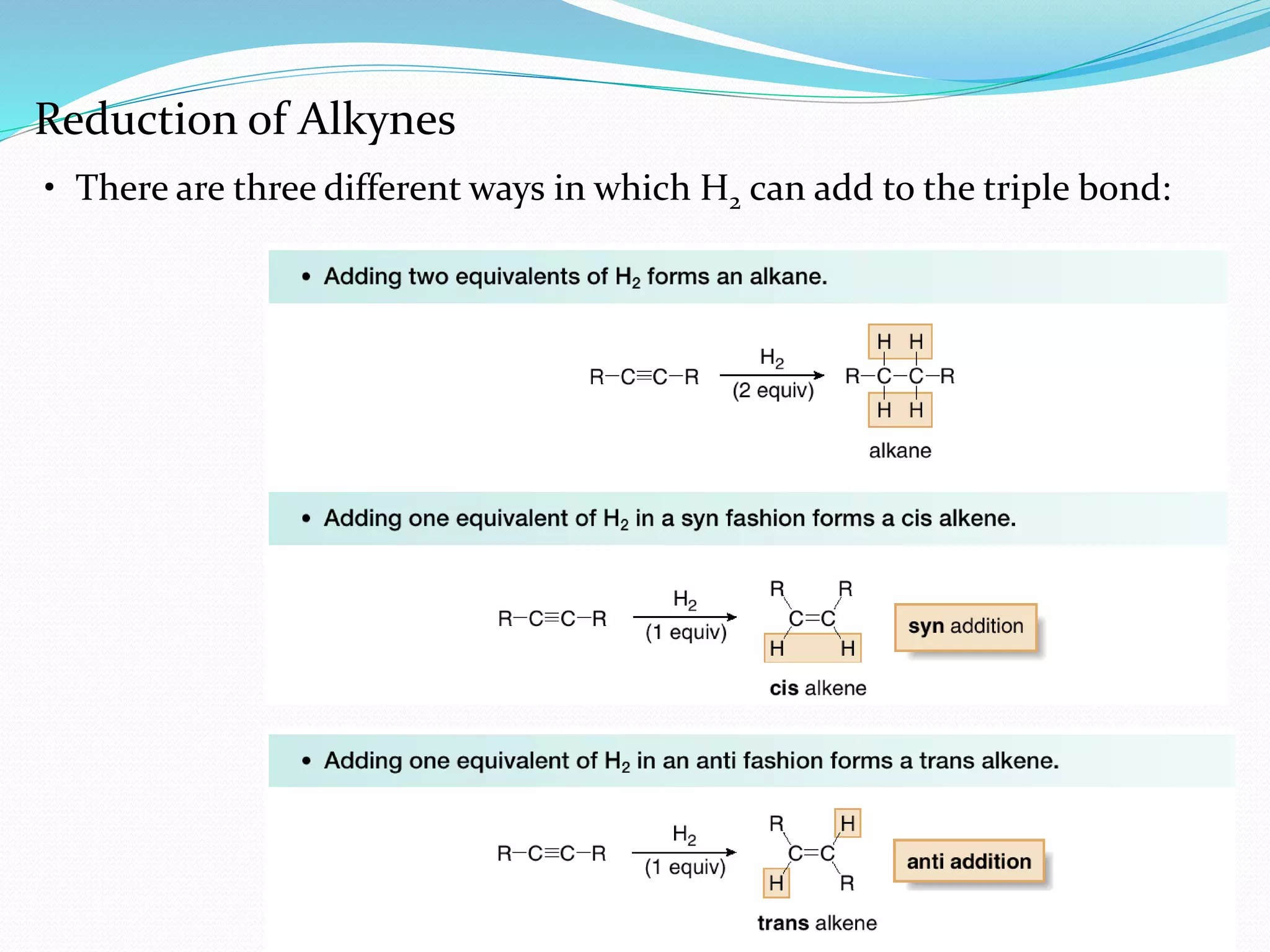
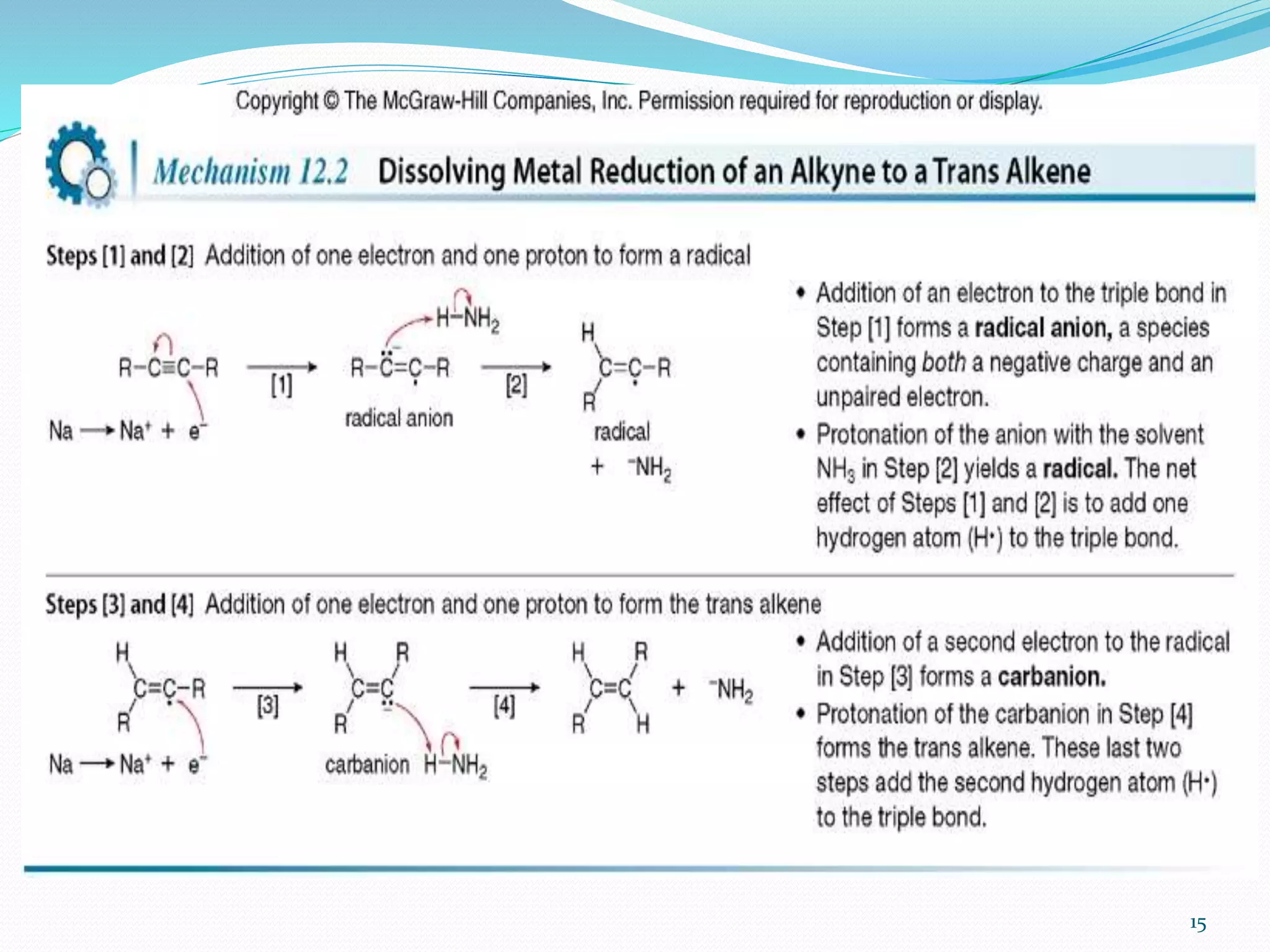
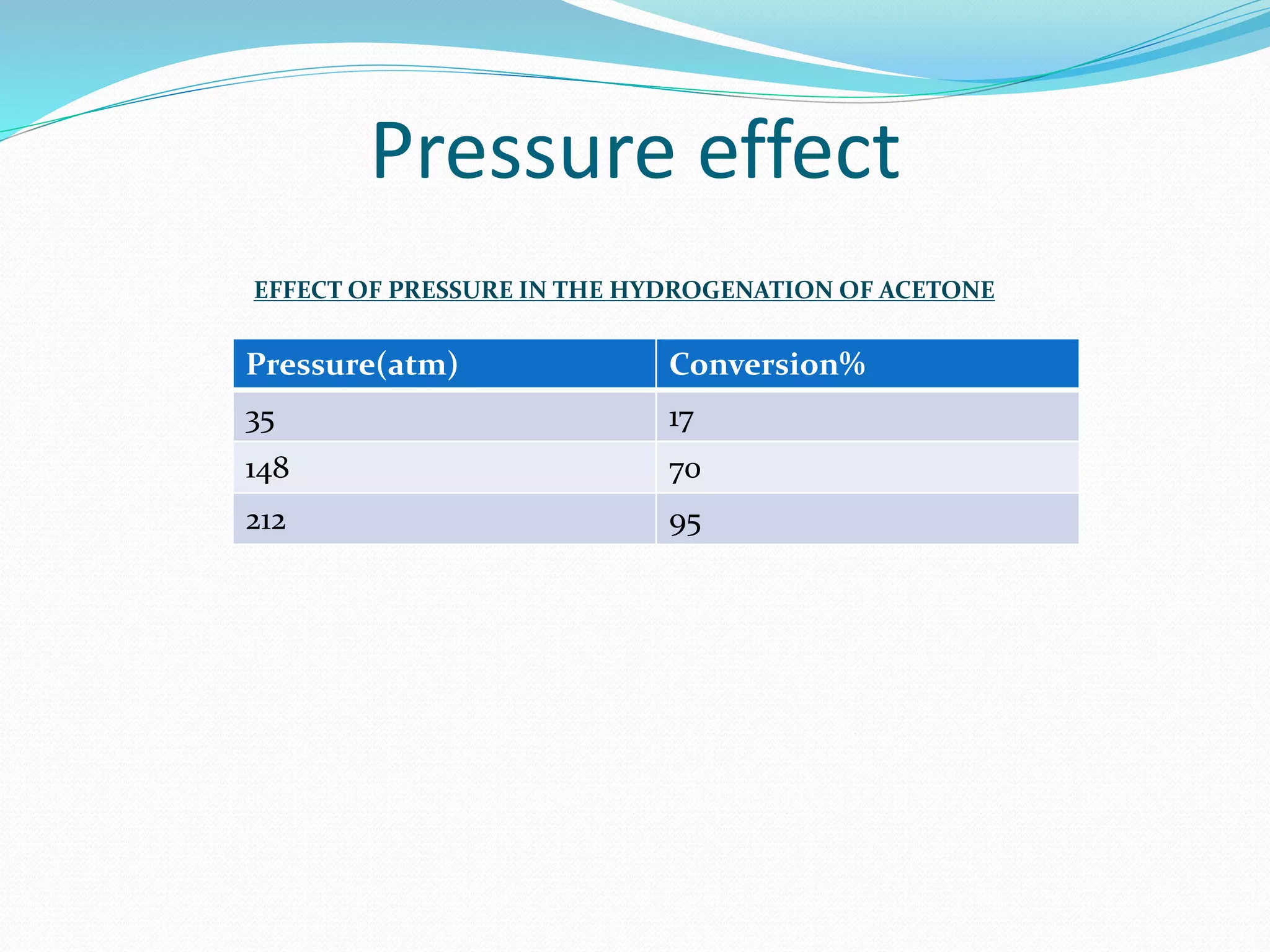
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between hydrogen gas and another compound or element in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. It involves the addition of hydrogen atoms to reduce double or triple bonds. There are three types of reductions that differ in how hydrogen is added. The reaction rate depends on factors like temperature, pressure, catalyst surface area, time, and the ratio of hydrogen to the compound being hydrogenated. In general, higher temperatures and pressures increase the reaction rate.