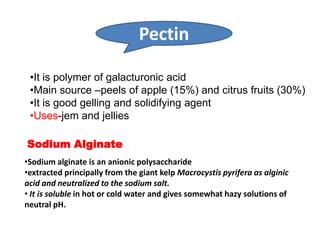
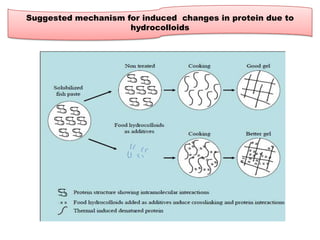
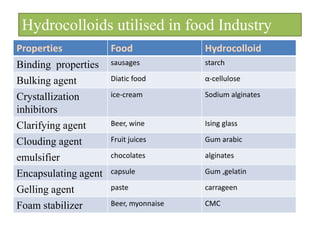
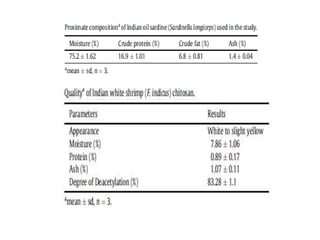
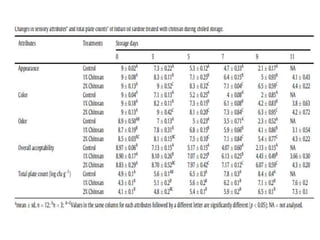
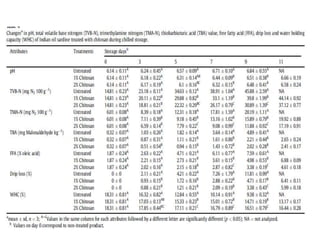
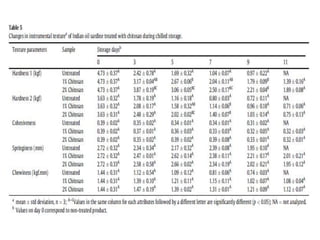
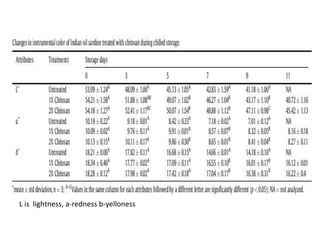
This document discusses hydrocolloids and their application in food coatings. It defines hydrocolloids as colloidal systems where particles are dispersed in water. Common sources of hydrocolloids include plants, seaweeds, microbes, and modified biopolymers. Hydrocolloids are used in the food industry as additives due to their neutral taste, edible nature, and ability to enhance texture and moisture retention in foods. Examples mentioned include starch, agar, pectin, alginates, carrageenan, guar gum, gum Arabic, xanthan gum, and cellulose derivatives. The document also discusses specific hydrocolloids like starch, pectin, sodium algin