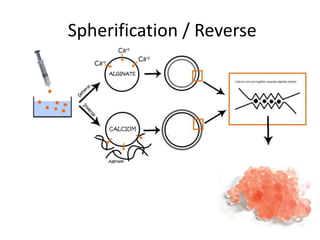
This document discusses modern cooking equipment and hydrocolloids used in kitchens. It describes various pieces of equipment such as the Thermomix, Pacojet, smoke gun, and vacuum packer. It also discusses hydrocolloids which are ingredients that control water, including their properties and considerations for use such as forming gels and interactions with ions. Popular hydrocolloids mentioned include gelatin, sodium alginate, xanthan gum, and carrageenan. Examples of their culinary uses are also provided.