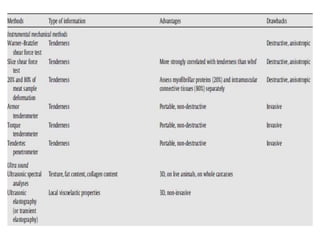
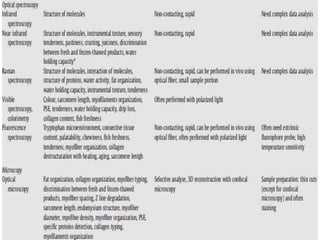
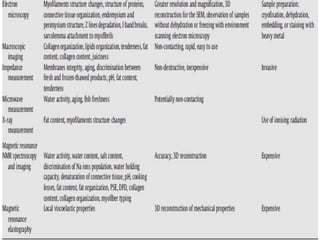
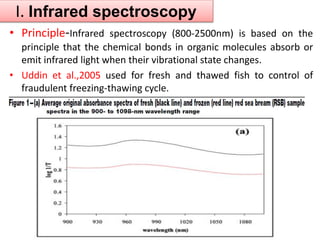
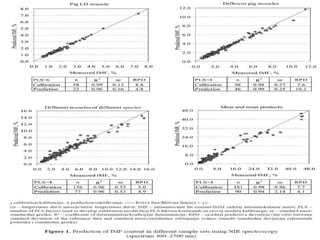
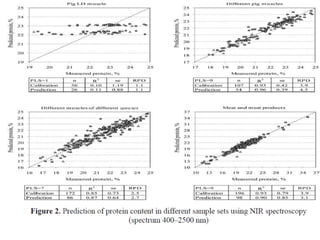
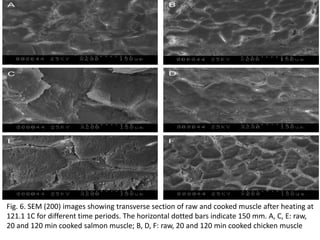
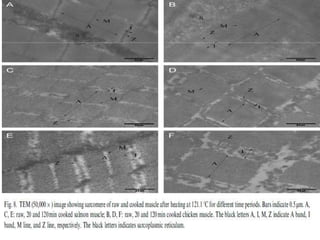
This document discusses biophysical methods for assessing meat quality, including mechanical, optical, and imaging techniques. Mechanical methods measure texture properties directly using instruments like texture analyzers or indirectly using techniques like rheometry and ultrasound. Optical methods include spectroscopic techniques like infrared, Raman, and fluorescence spectroscopy as well as imaging methods like microscopy, histology, and spectroscopy. Imaging techniques provide information on muscle structure at various microscopic scales. Additional methods discussed are X-ray measurements and nuclear magnetic resonance, which provide compositional information. The document concludes that while these biophysical methods show potential for meat quality analysis, more research is still needed to develop fast, accurate, and low-cost commercial solutions.