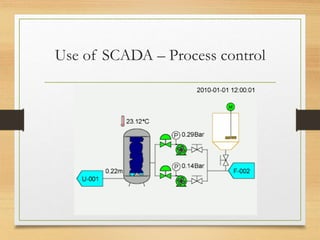
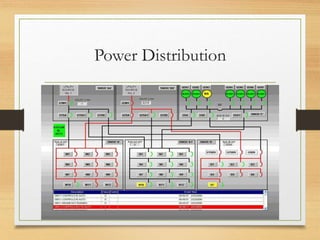
SCADA systems are used to remotely monitor and control equipment and industrial processes. They consist of a central master computer system that collects real-time data from remote terminal units (RTUs) connected to sensors and machinery. The master system interfaces with human operators through human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that present data and status information. SCADA systems allow industrial processes to be automated and monitored remotely, improving productivity and reducing costs compared to manual operation and monitoring. They are commonly used in applications like power generation, water and sewage systems, manufacturing, and buildings.