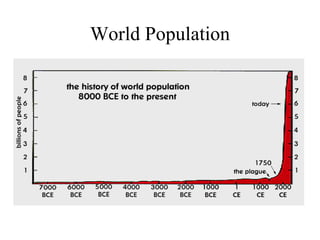
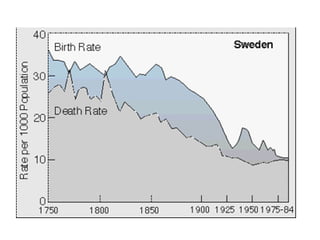
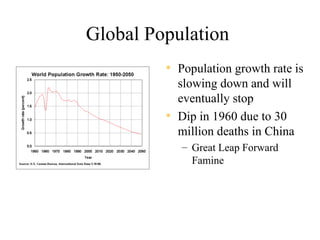
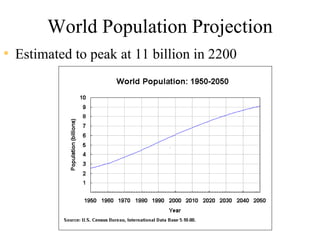
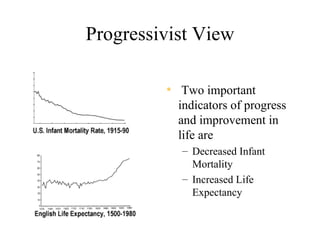
The document discusses population trends and issues related to population growth. It provides historical context starting with Thomas Malthus in the late 18th century who argued that population tends to grow faster than food supply. It then covers key thinkers and their perspectives on population like Paul Ehrlich who warned of mass starvation in the late 1960s. Global population data is presented showing growth rates slowing but still projected to reach 11 billion by 2200. Challenges faced in food production to keep pace with population are discussed. Different views on population issues from progressivists to social equity perspectives are outlined. Specific country examples related to population policy and their impacts are also summarized.