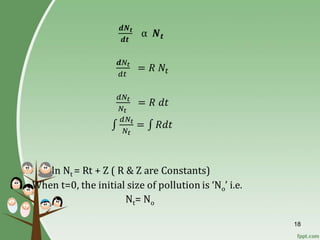
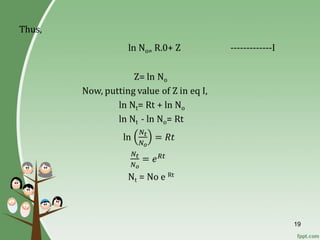
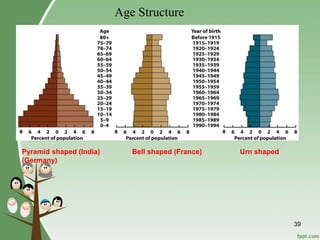
The document discusses various topics related to population studies including:
1. Definitions of population and population density.
2. Environmental factors like climate, soils, and water supply that influence population distribution and settlement patterns.
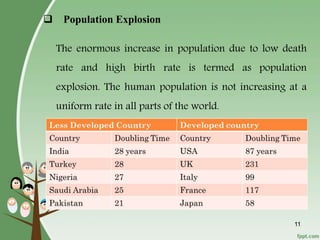
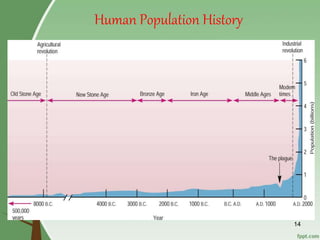
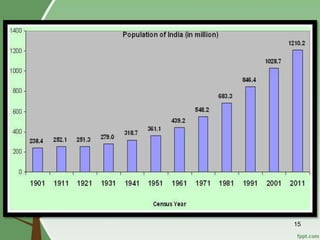
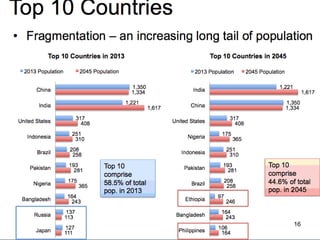
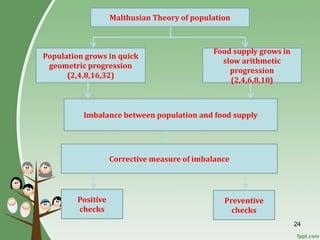
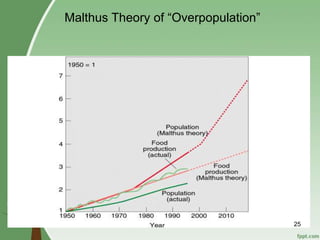
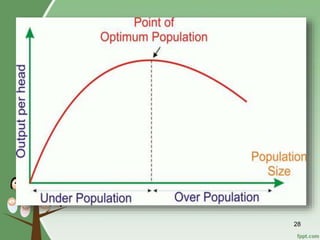
3. Overpopulation occurring when population exceeds the carrying capacity of the habitat. Reasons for overpopulation include increased birth rates and decreased mortality rates.
4. Effects of population explosion including overstress of natural resources and increased demand for food, water, and services.