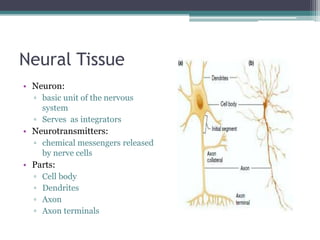
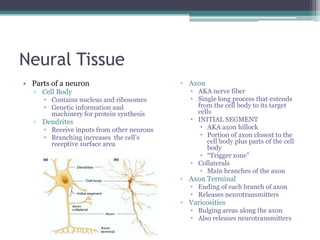
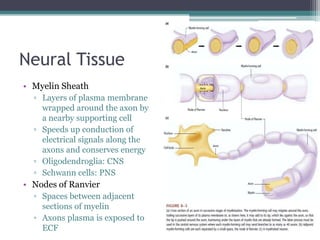
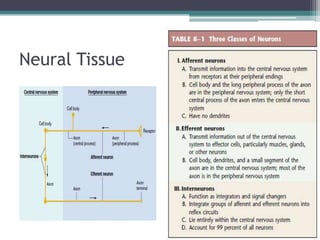
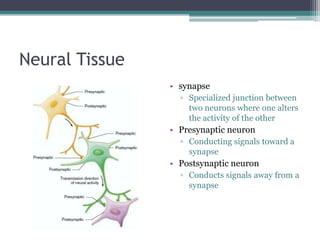
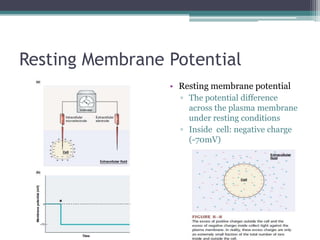
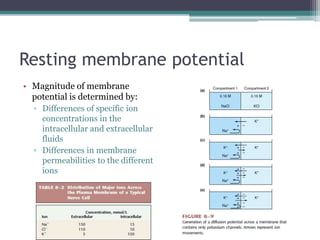
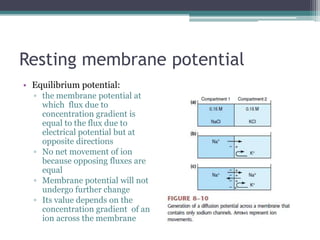
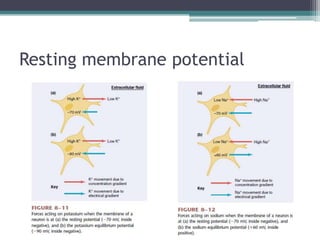
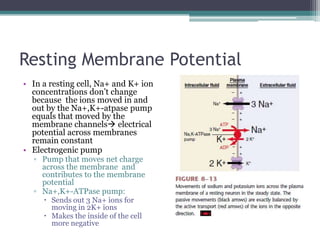
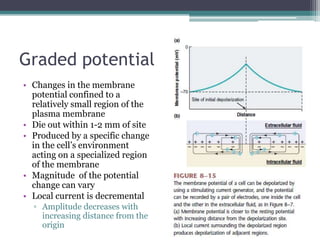
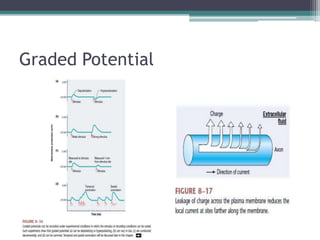
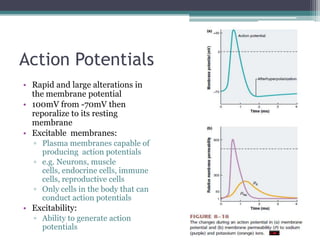
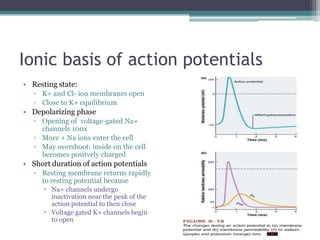
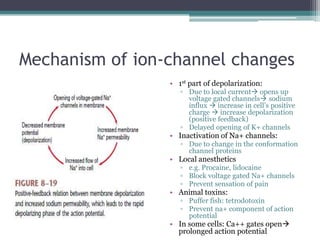
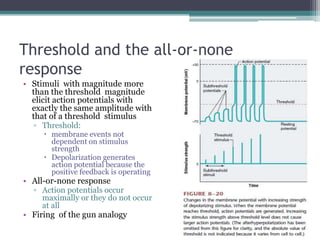
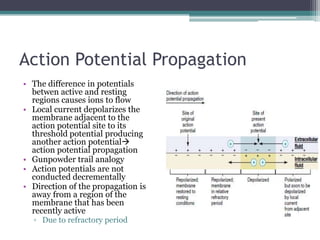
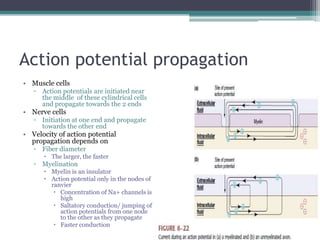
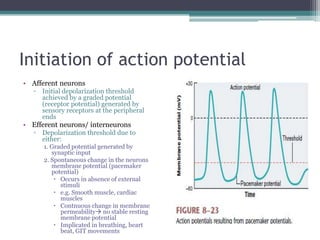
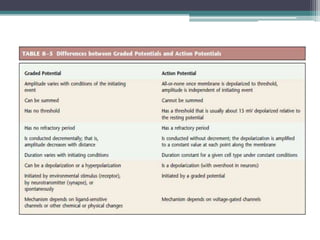
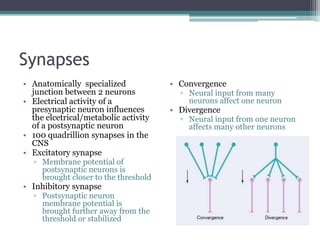
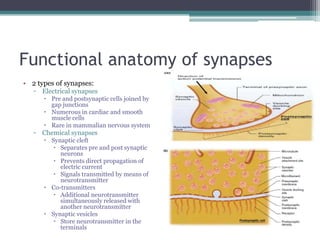
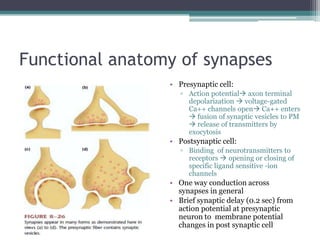
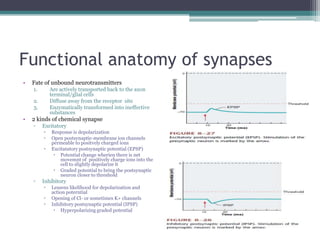
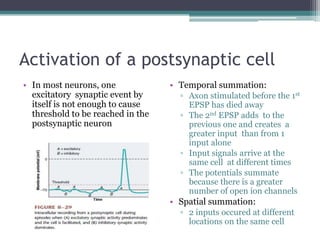
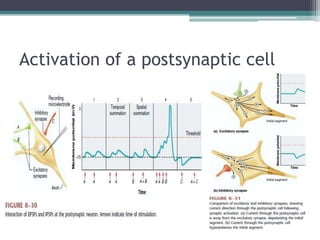
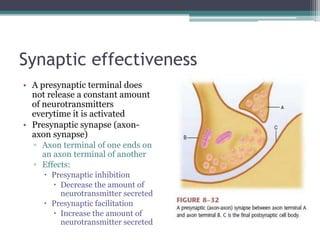
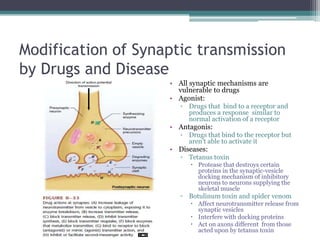
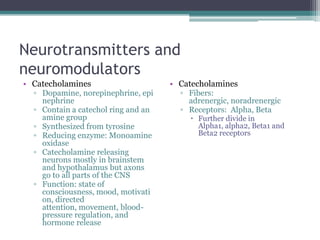
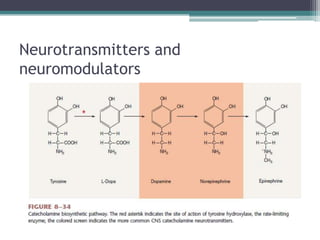
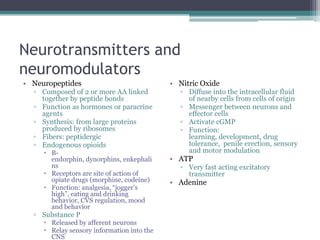
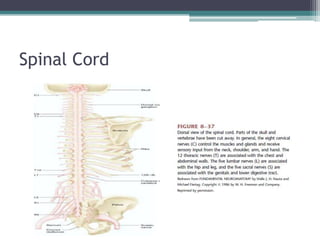
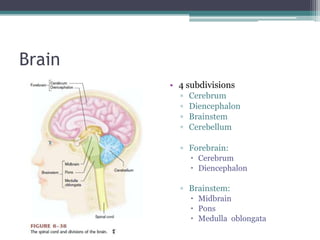
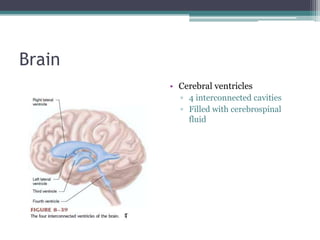
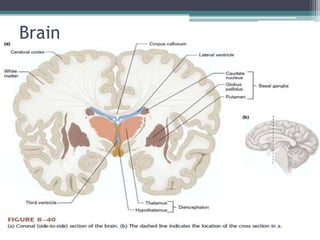
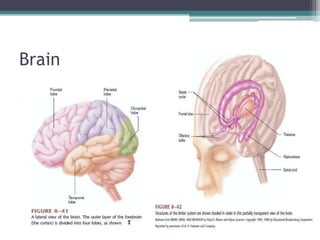
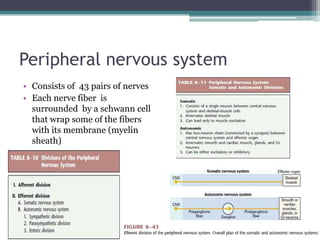
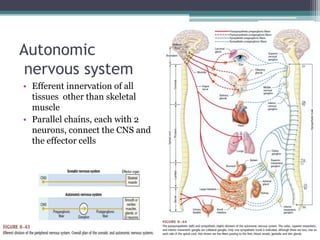
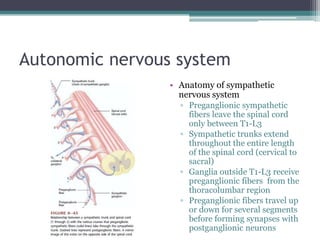
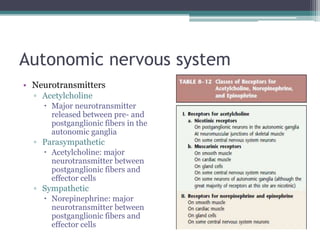
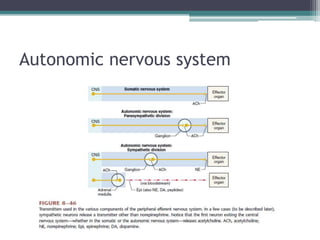
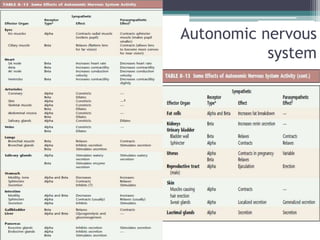
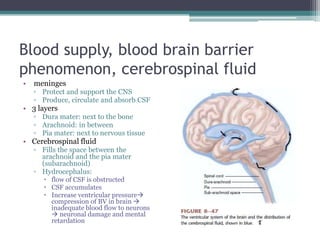
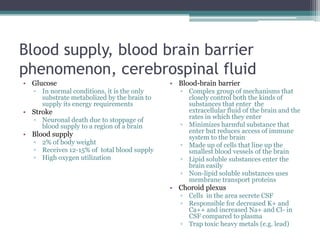
Neural control mechanisms involve neurons, which are the basic units that integrate and transmit electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. Neurons have cell bodies that contain genetic material and protein synthesis machinery. They receive inputs via dendrites and transmit signals along axons via the release of neurotransmitters at synapses. Neural signals can be graded potentials that decay over short distances or action potentials that propagate long distances down axons. The initiation and propagation of action potentials relies on voltage-gated ion channels and the precise control of sodium, potassium, and other ion concentrations. Synapses allow neurons to communicate via the release of neurotransmitters that can have excitatory or inhibitory effects on the receiving neuron.