Embed presentation
Downloaded 116 times





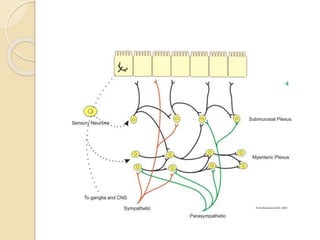




The enteric nervous system, which extends from the esophagus to the anus, contains approximately 100 million neurons and is organized into the myenteric and submucosal plexuses. The myenteric plexus enhances muscle contractions, while the submucosal plexus regulates local secretion and absorption. Parasympathetic stimulation from the vagus nerve increases enteric activity, while sympathetic stimulation inhibits muscle contractions via norepinephrine.








