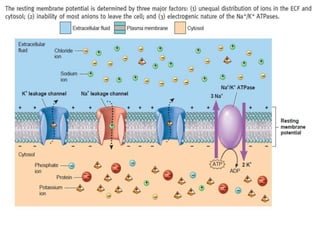
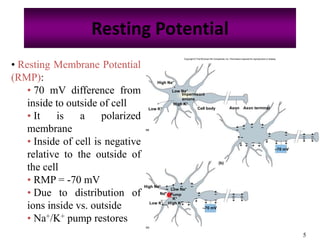
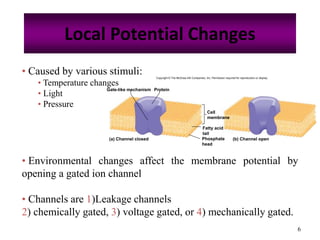
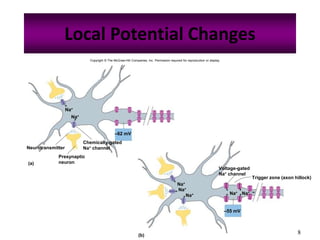
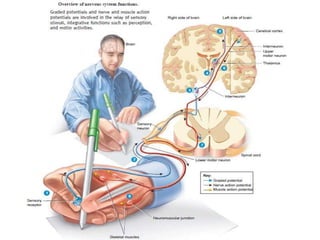
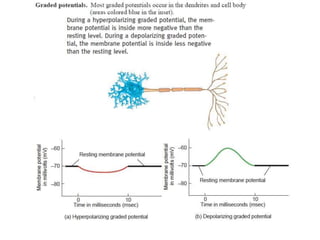
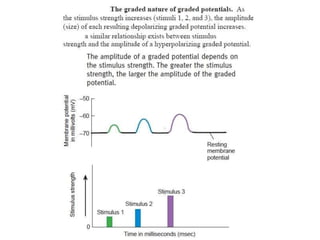
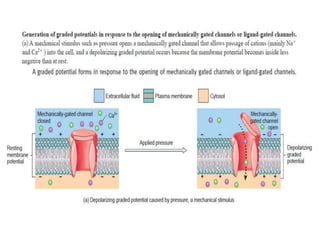
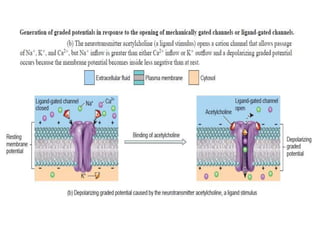
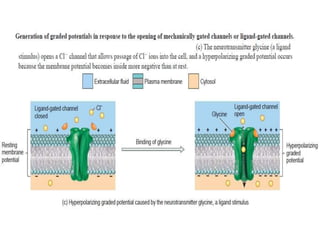
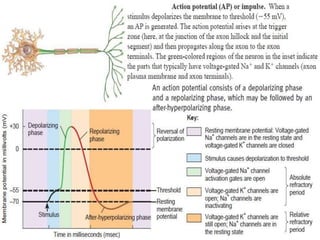
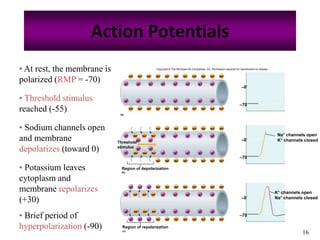
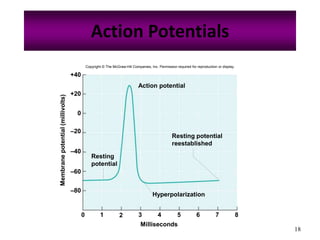
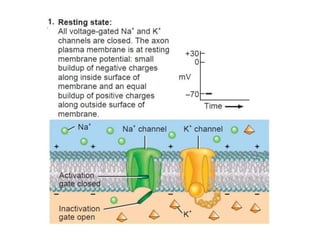
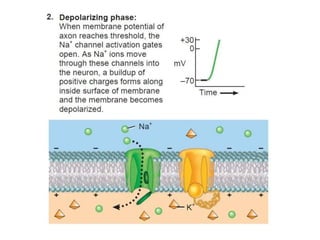
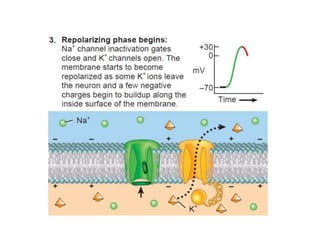
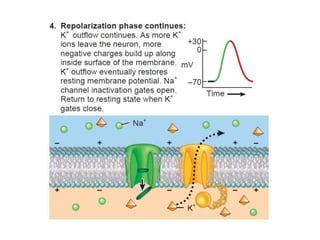
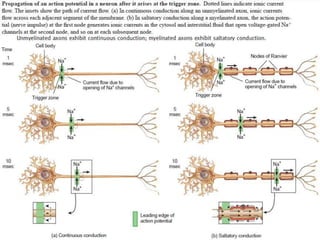
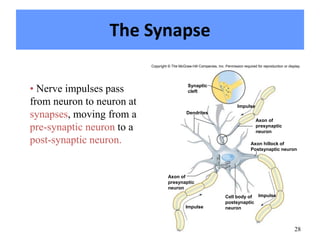
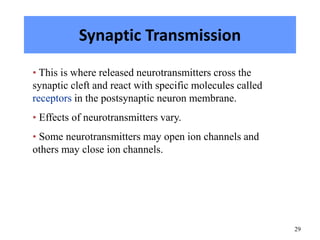
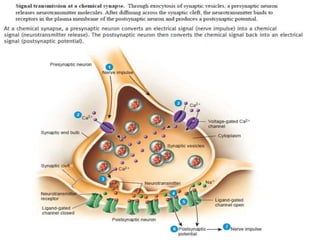
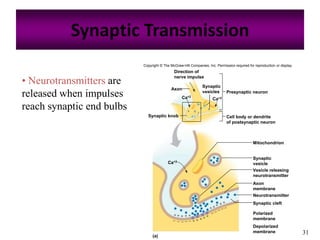
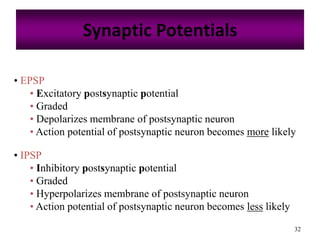
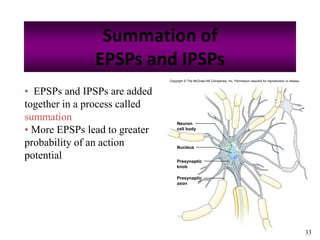
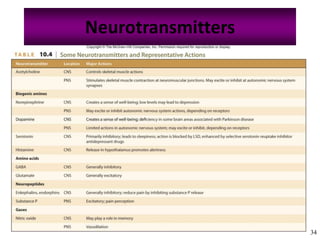
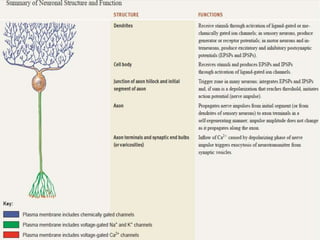
The nervous system controls and coordinates the body's activities through electrical and chemical signals transmitted through networks of neurons. Neurons transmit signals through action potentials, which are brief changes in the electrical potential across the cell membrane that allow signals to propagate rapidly along axons. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, generating excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potentials that influence whether or not an action potential occurs in the postsynaptic cell. This allows neurons to communicate with one another and coordinate the body's complex functions.