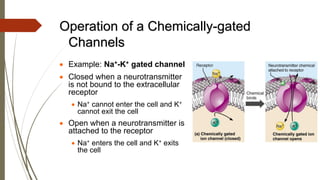
The document discusses cell membrane potential and action potentials. It explains that cell membranes maintain a voltage gradient called the membrane potential due to different ion concentrations inside and outside the cell. Ion channels, including passive, chemically-gated, and voltage-gated channels, control the flow of ions across the membrane and influence the membrane potential. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly changes from its normal resting potential of -70mV to +30mV before repolarizing back. This wave of depolarization propagates along the membrane via opening and closing of sodium and potassium ion channels.