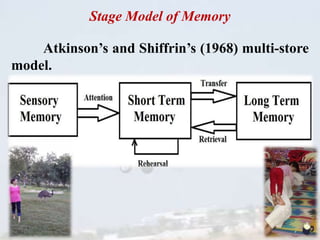
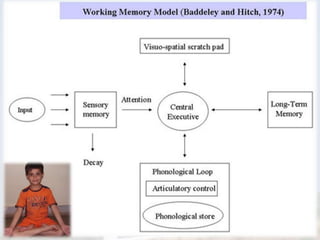
Short-term memory (STM) is an active information relay system that processes and temporarily holds information before it moves to long-term memory, with a typical capacity of 7±2 items. Key components of STM include the central executive, visuo-spatial sketch pad, and phonological loop, each responsible for different aspects of processing. Characteristics of STM include susceptibility to interruption, rapid decay of information, and phenomena like the recency effect and interference.