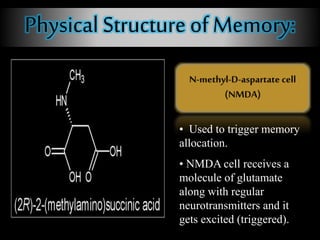
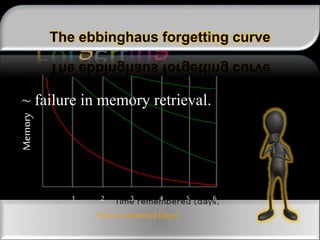
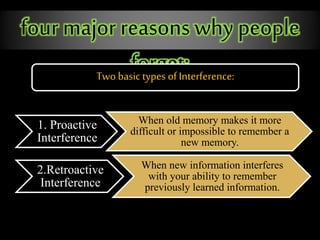
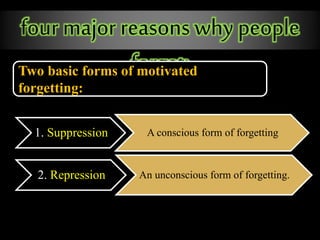
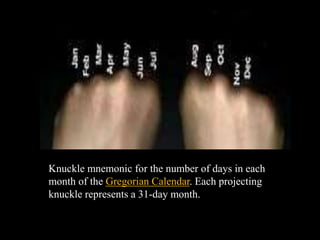
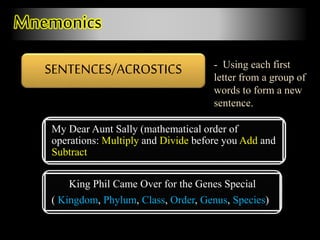
The document outlines the processes and stages of memory, including encoding, storage, and retrieval of information. It details types of memory, such as procedural and declarative, along with reasons for forgetting and various memorization techniques. An emphasis is placed on the importance of attention and rehearsal for memory retention, as well as the theory of forgetting over time.