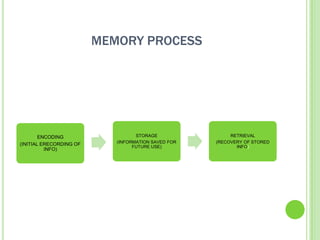
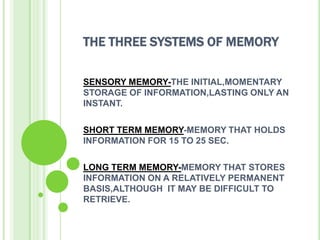
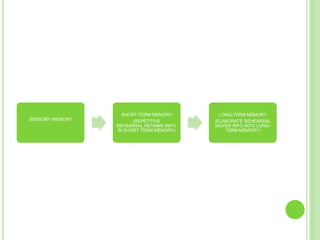
Memory is the process of encoding, storing, and retrieving information over time. It involves three main systems: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory stores initial perceptions briefly, while short-term memory holds information for around 15-25 seconds through rehearsal. Long-term memory stores information more permanently through different types like declarative and procedural memory. Encoding information from short-term to long-term memory can occur automatically or through effortful encoding methods like elaboration to form associations. Forgetting occurs when we can no longer retrieve stored information from long-term memory, potentially due to repression, interference, or distortion over time.