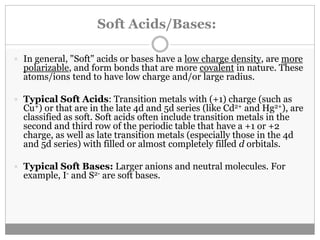
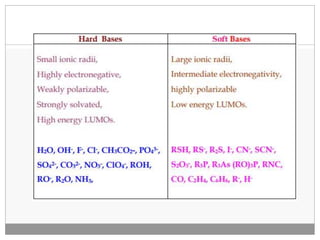
Pearson's HSAB concept classifies Lewis acids and bases into hard and soft categories based on charge density, polarizability, and the nature of bonds formed. Hard acids prefer to bind with hard bases to form ionic complexes, while soft acids favor interactions with soft bases for covalent complexes. This concept has numerous applications in organic reaction mechanisms, metal-ligand interactions, and solubility in water, though it has limitations such as contradictions with Fajans' rules.